Exchange 2010 to 2016 Migration
Migrating to Exchange Server 2016 is an important step for organizations aiming to improve email performance, strengthen security, and stay compatible with modern business applications. Since Microsoft ended support for Exchange Server 2010 on October 13, 2020, systems still running on 2010 no longer receive critical updates or security patches, leaving them vulnerable to potential threats, performance issues, and data loss.
Upgrading to Exchange Server 2016 eliminates these risks while offering enhanced reliability, advanced features, and a modernized user experience. Businesses that migrate mailbox from Exchange 2010 to 2016 can take advantage of improved scalability, better integration with Office applications, and stronger security compliance.
If you’re planning an Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration, EdbMails Exchange migration software makes the process simple and error-free. Its user-friendly interface guides you through every stage, helping even first-time users perform a secure and successful migration.
EdbMails supports incremental migration, ensuring that only new or modified data is transferred after the initial move, saving time and bandwidth. With concurrent mailbox migration , multiple mailboxes can be migrated simultaneously, significantly reducing total migration time. The software also includes automatic throttling management, which optimizes server performance during the transfer, achieving zero downtime for users. Whether you need to migrate from Exchange 2010 to 2016 or move multiple mailboxes in bulk, EdbMails provides a reliable, secure, and efficient solution that ensures complete data integrity throughout your migration journey.
EdbMails simplifies the process to migrate mailbox from Exchange 2010 to 2016 by automatically creating mailboxes on the target server, removing the need for manual setup and reducing administrative overhead. Its automatic mailbox mapping feature intelligently matches source and destination mailboxes, further minimizing manual configuration and ensuring an accurate, error-free migration. Additionally, EdbMails offers advanced filtering options that let you migrate only the data you need, such as specific folders, date ranges, or item types, a giving you complete control over what’s transferred. This ensures a more efficient and organized migration experience
The following sections detail everything you need to know to migrate Exchange 2010 to 2016 step by step, including the reasons for migration, the best methods, system prerequisites, the migration process, post-migration tasks, and the key advantages of using EdbMails for Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration.
Reasons to migrate from Exchange 2010 to 2016
Exchange 2016 brings a host of advanced features that significantly enhance its functionality compared to Exchange 2010. Notably, it introduces a centralized Exchange Admin Center (EAC) that streamlines server management and administration. In a notable departure from previous iterations, Exchange 2016 consolidates server roles into two primary categories: Mailbox and Edge Transport. This version also incorporates critical updates such as data loss prevention, refined mail flow rules, In-Place archiving, retention policies, eDiscovery capabilities, and strengthened anti-malware protection.
To maximize the benefits of these enhancements, it is crucial to understand the new features introduced in Exchange server 2016, as well as any elements that have been replaced or discontinued 2016. With these advancements in mind, now presents an opportune moment to strategize and initiate the Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration, ensuring your organization remains secure and efficient in its email management.
Exchange 2010 and 2016 Coexistence Scenario
Exchange Server 2010 and 2016 can coexist within the same Active Directory (AD) environment, allowing organizations to smoothly migrate mailbox from Exchange 2010 to 2016 without service disruption. This coexistence setup enables mail flow and user access across both servers during the migration phase, ensuring business continuity. Before you migrate Exchange 2010 to 2016, make sure that Exchange 2010 has Update Rollup 11 for Service Pack 3 (SP3) or a later version installed. This update ensures compatibility and stability between the two environments.
Exchange 2016 also supports coexistence with Exchange 2013 and enables hybrid deployments with Microsoft 365, giving businesses greater flexibility during the migration process. By maintaining an Exchange 2010 and 2016 coexistence environment, organizations can complete the migration efficiently while ensuring minimal downtime and maximum reliability.
Best method to upgrade Exchange 2010 to 2016
When upgrading from Exchange 2010 to 2016, there are several migration methods available, including manual migrations, native Exchange tools, or third-party software solutions. Manual migrations can be intricate and time-consuming, requiring extensive technical expertise and meticulous planning to prevent data loss and reduce downtime. While native Exchange tools can also be utilized, they often rely on complex PowerShell scripts, which may lead to errors, particularly in larger environments.
Among third-party tools, EdbMails is a standout choice for migrating from Exchange 2010 to 2016. It supports direct migration, ensuring the seamless transfer of all data, including mailboxes, public folders, archive mailboxes, shared mailboxes, emails, contacts, calendars, and more.
What sets EdbMails apart is its cost-effectiveness, providing a comprehensive solution for businesses of all sizes without compromising on functionality. By automating the migration process, EdbMails removes the need for manual intervention or complex scripting, enabling a quicker, more efficient upgrade.
Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration checklist
When migrating from Exchange 2010 to 2016, careful planning and preparation are crucial for ensuring compatibility and a smooth transition. To help you with this process, here’s a simple checklist of important steps to ensure a successful migration:
- Create a comprehensive inventory of all items to be migrated while identifying the necessary resources, including hardware, software, network specifications, and available bandwidth.
- Ensure that all email clients are updated to their latest versions and cumulative updates are installed.
- Prepare end users for the migration by informing stakeholders about the upcoming changes.
- Clarify the data to be migrated, such as mailboxes, public folders, archive mailboxes and shared mailboxes.
- Document the configurations at both the Active Directory forest and domain levels.
- Familiarize yourself with the enhancements in Exchange 2016 and Office 365, particularly if planning for a hybrid deployment.
- Configure the required mailboxes and public folders on the target server, and conduct a test migration to verify functionality.
- Execute the actual migration to Exchange 2016 and confirm the accuracy of the transferred data.
- Update MX records and set up Outlook for all users across the organization.
- Decommission the Exchange 2010 servers only after ensuring that mail flow is functioning correctly in the new environment.
Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration prerequisites
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange 2016 setup requirements.
Before you migrate your mailbox data to Exchange 2019, ensure that your current environment and hardware is compatible for the migration. The following links will help you to know about the network, hardware,.NET framework and operating system requirements for installing Exchange server 2016.
- Network and directory requirement for Exchange 2016
- Hardware Requirements for Exchange 2016
- Supported operating systems for Exchange 2016
- Supported .NET Framework in Exchange 2016
- Supported Outlook clients in Exchange 2016
Note: Exchange 2016 requires Active Directory forest functional level of Windows Server 2008 R2 or higher and a .NET Framework 4.8 on a Cumulative Update (CU) of 15. The Mailbox and Edge Transport servers require Windows Server 2012 Standard or Datacenter and higher. See the Exchange 2016 server supportability matrix for more information.
- Step 2: Prepare your system with the following prerequisites for Exchange 2016
Ensure that you meet the following prerequisites for Active Directory, Windows 2016 Mailbox server and Windows 2016 Edge Transport servers for installing Exchange 2016.
- Step 3: Decide how you want to migrate 2010 to 2016 Exchange
Consider if you want to migrate email using the Exchange cutover method, staged or with the Hybrid deployment. EdbMails can help you with the 2010 to 2016 Exchange migration without downtime or data loss. The advantage with it is that you can keep using your mailboxes during the migration without disconnecting your Exchange server.
Current environment and requirement Ideal migration approach How does the migration take place? You want to perform a complete Exchange 2016 migration in a single event and in a limited time frame. Exchange 2010 to 2016 cutover migration Set up the target Exchange server and migrate everything in a single sitting. Suitable for large mailbox migration You have little time and want to migrate mailboxes from Exchange 2010 to 2016 in phases or over the weekends Staged Exchange migration Migrate your mailboxes and mail data in stages and migrate the most recent data first, followed by the others. You want to migrate from Exchange 2010 to a Hybrid 2016 and Office 365 environment Exchange Hybrid migration to Office 365 Migrate from the source server to a Hybrid Exchange and Office 365 environment. See the prerequisites for a Hybrid deployment - Step 4: Setup the target Exchange server 2016 for migration
Given below is a list of key points for installing and preparing the Exchange 2016 server for migration.
- Prepare AD and domains
- Before installing Exchange Server 2016, prepare your Active Directory forest and its domains for the new version of Exchange.
- If you have a separate team to manage the Active Directory schema, you must extend the active directory schema, else proceed to the next step to prepare the Active Directory.
- If you have multiple domains you need to additionally prepare the Active Directory domains.
- Install Exchange server 2016
Ensure that you meet the server system requirements and prerequisites outlined in the preceding sections. Next, install Exchange 2016 mailbox server and edge transport server using the setup wizard.
- Prepare a clean Exchange 2016 target environment
- Create and configure a Send connector to send mail outside the Exchange organization.
- By default, Exchange automatically creates receive connectors for inbound mail flow when the mailbox server is installed. However, if you want to configure custom receive connectors for certain mail flow scenarios, follow the steps in the link.
- Add accepted domains to allow recipients to send and receive email from another domain.
- Configure the default email address policy to add the accepted domain to every recipient in the organization.
- Configure external URLs (domains) on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internet (outside the organization’s network).
- Configure internal URLs on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internal network.
- Configure SSL certificates from a third-party certificate authority for services such as Outlook Anywhere and Exchange ActiveSync.
- Verify the Exchange server installation by running the command Get-ExchangeServer on the Exchange Management Shell (EMS)
- Create mailboxes target Exchange 2016 server
Make sure to create mailboxes on the target server for the migration and assign appropriate licenses to each one. You can use EdbMails to automatically create mailboxes on your target server. If you prefer to create the mailboxes manually, follow the link below:
Steps to create mailboxes in Exchange server
If you are planning to migrate public folders ensure to create public folder on the target server and assign the admin permissions
- Install cumulative updates (CU) on Exchange server 2010
For migrating Exchange server 2010 to Exchange 2016, it is required that you have installed the latest cumulative updates (CU) on the source server (2010).
- Create trust relationship between forests (Optional)
A forest trust is an authentication between two domains within the same Active Directory forest which creates a trust between two root domains for exchanging information. By creating a trust in advance, it is possible to address the trust issues during or after the migration. See steps if you want to perform cross forest migration from Exchange 2010 to 2016.
Note: This step applies to Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012. Creating a trust relationship is not required for SBS based environments.
- Assign management roles to the admin account
Ensure that you have set the following permissions to the admin account on the source (2010) and target server (2016)
- On the source server:
- ApplicationImpersonation
- View-Only Configuration - Run the cmdlet New-ManagementRoleAssignment using the Exchange Management Shell to assign the View-Only Configuration role to the admin.
- Organization Management role group. It is an elevated permission that is required to migrate Public folders.
- On the target server:
- ApplicationImpersonation
- View-Only Recipients
- View-Only Configuration
- On the source server:
- Verify the mailbox of the admin account
Check to see if the admin account that has been assigned management roles has a valid and non-hidden mailbox on the Exchange 2010 server. This property also applies to all the other user mailboxes.
- Configure the throttling and message-size limits
You can manually change the EWS throttling and message size limits on the target Exchange 2016 server by following the steps outlined in the links below.
- Prepare AD and domains
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange 2016 setup requirements.
Migrate from Exchange 2010 to 2016 step by step guide
After you have finished the pre-migration preparations, proceed with the migration using EdbMails.
Refer to the recommended best practices for Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration.
Step 1: Download and install EdbMails Exchange migration software
- Download EdbMails and install the application on your computer running on Windows OS that can connect to both the source and target Exchange servers.
- Launch the application and click either ‘Login’ by entering the email address and password or click ‘Start Your Free Trial’.
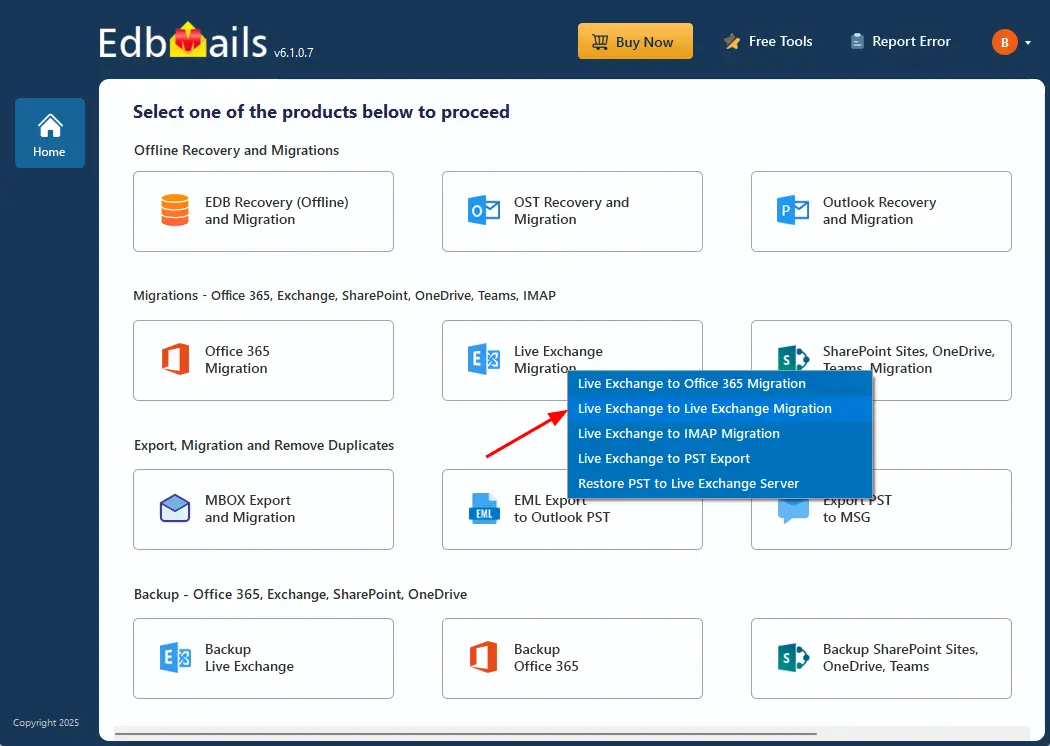
- Select 'Live Exchange Migration’ option.
- Choose ‘Live Exchange to Live Exchange Migration’ option.
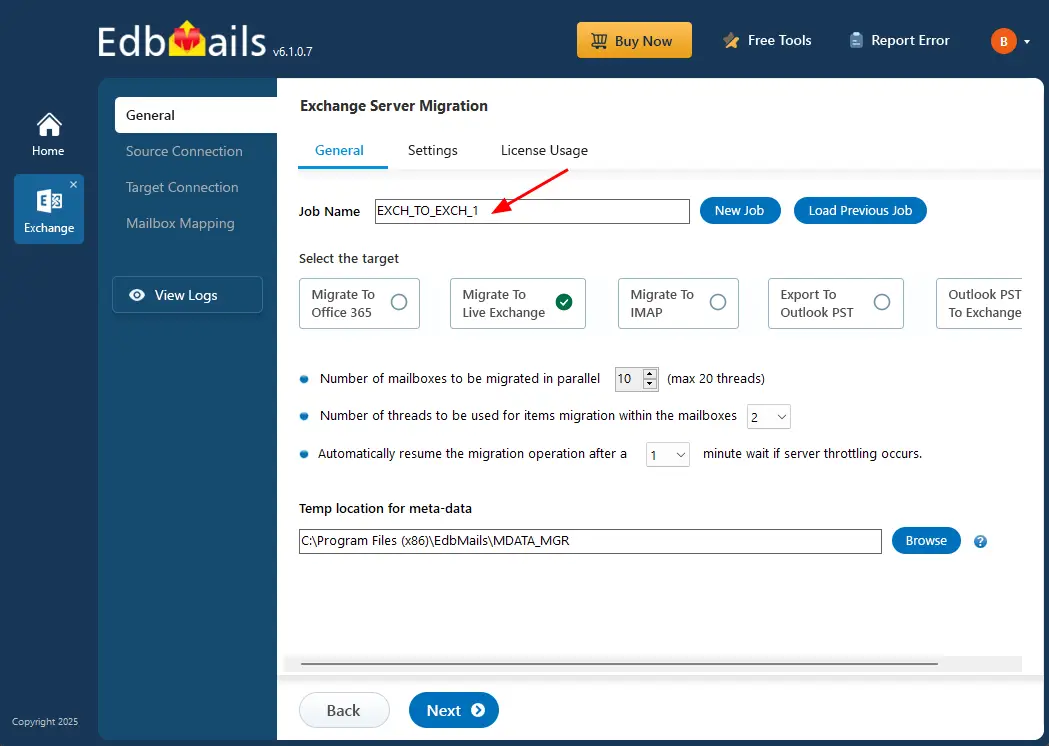
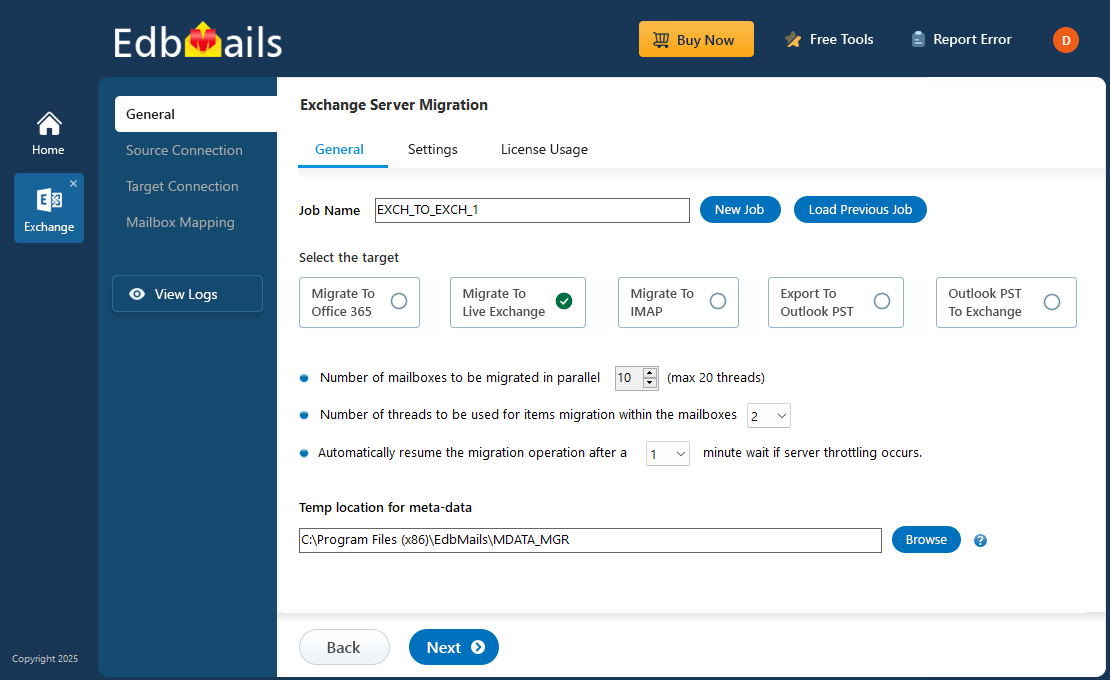
- You can go with the default job name or click ‘New Job’ to enter a custom name.
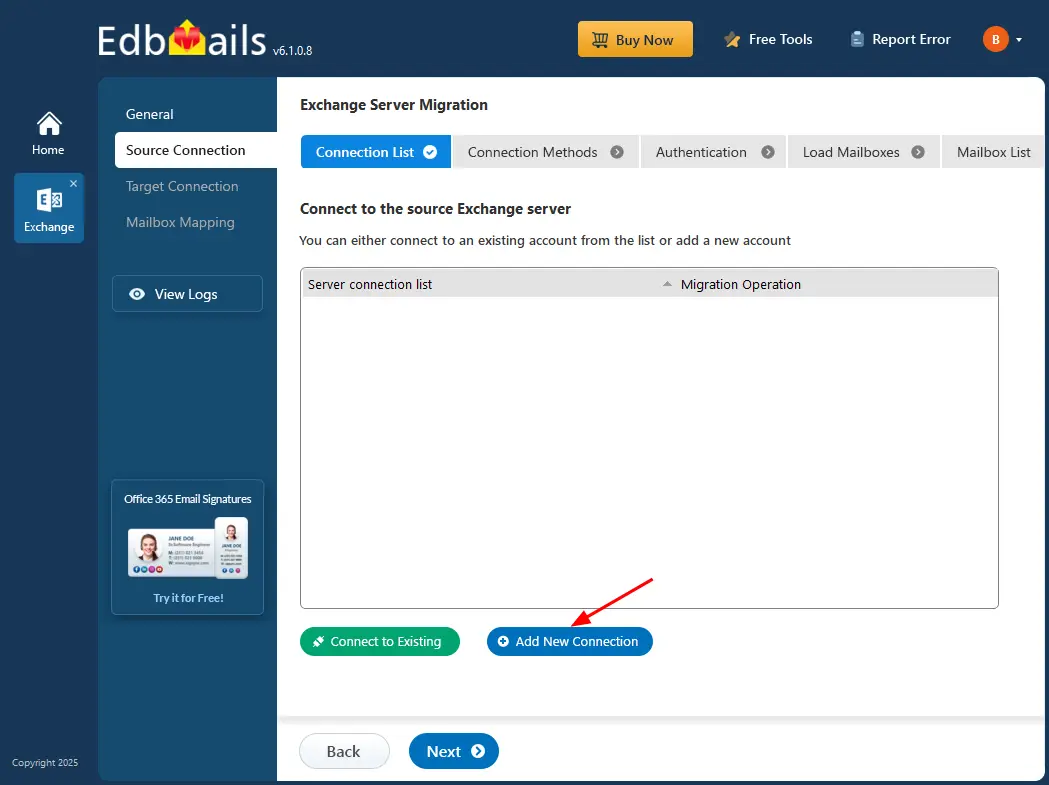
Step 2: Connect to source Exchange server 2010
- Click ‘Add New Connection’ to configure a new connection to the source Exchange server. If a connection has already been set up, select it from the list and click ‘Connect to Existing’.
Different options to connect to Exchange servering EdbMails.
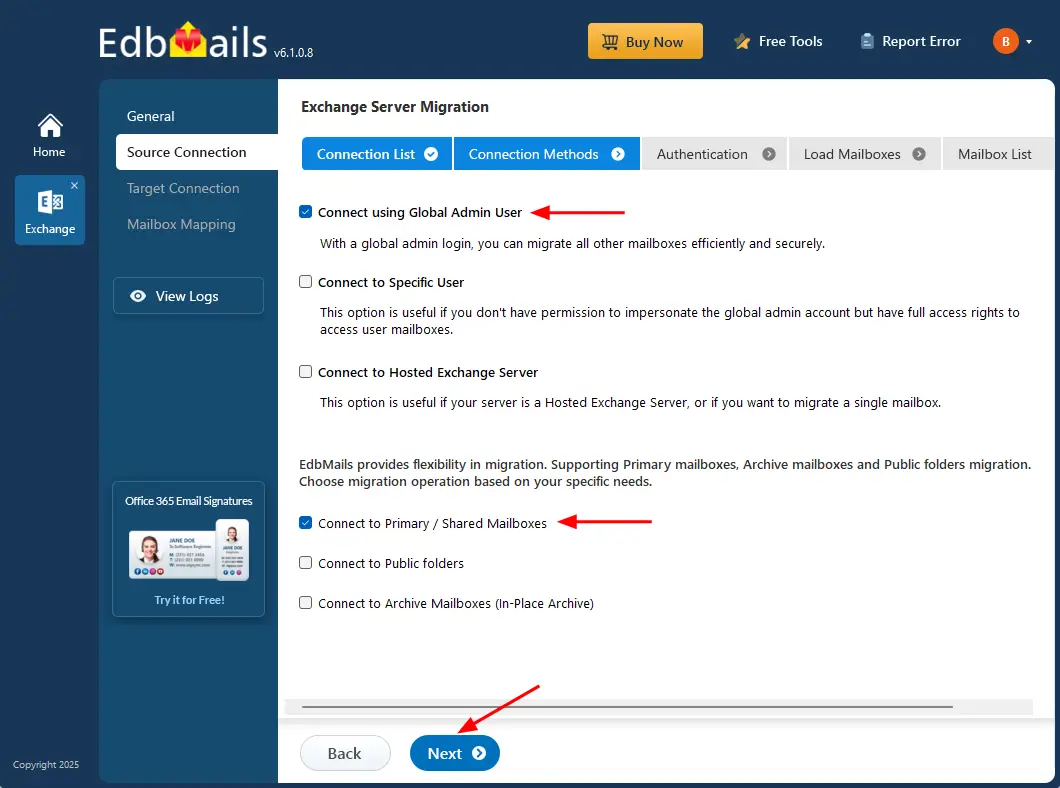
- Select the required connection options and click the ‘Next’ button.
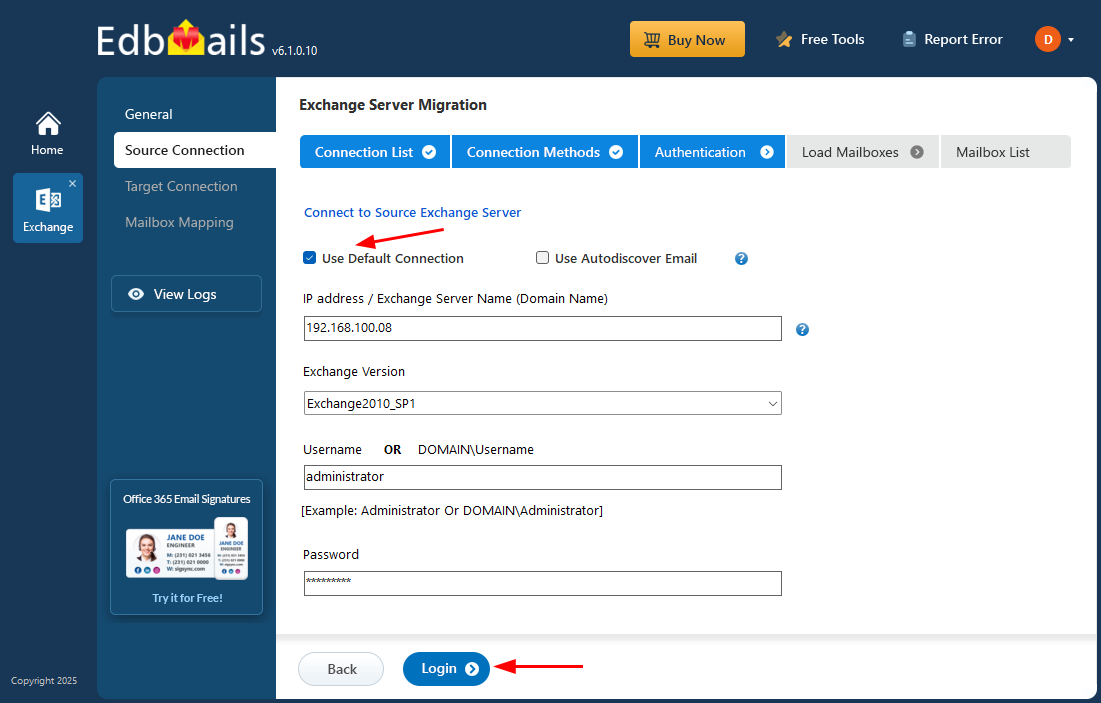
- Provide the source Exchange server credentials and click ‘Login’ to authenticate
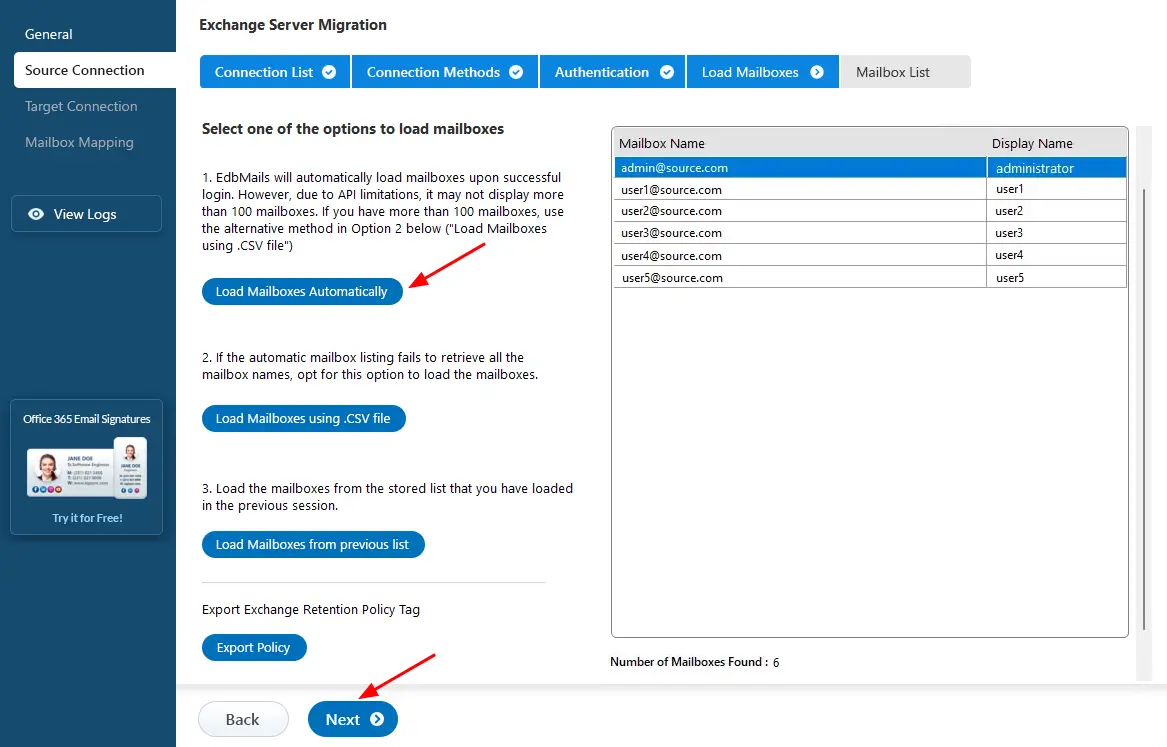
- After successfully logging into your source server, you have the option to load the mailboxes. EdbMails can automatically load the mailboxes. Alternatively, you can manually load the mailboxes using a CSV file.
- Click ‘Add New Connection’ to configure a new connection to the source Exchange server. If a connection has already been set up, select it from the list and click ‘Connect to Existing’.
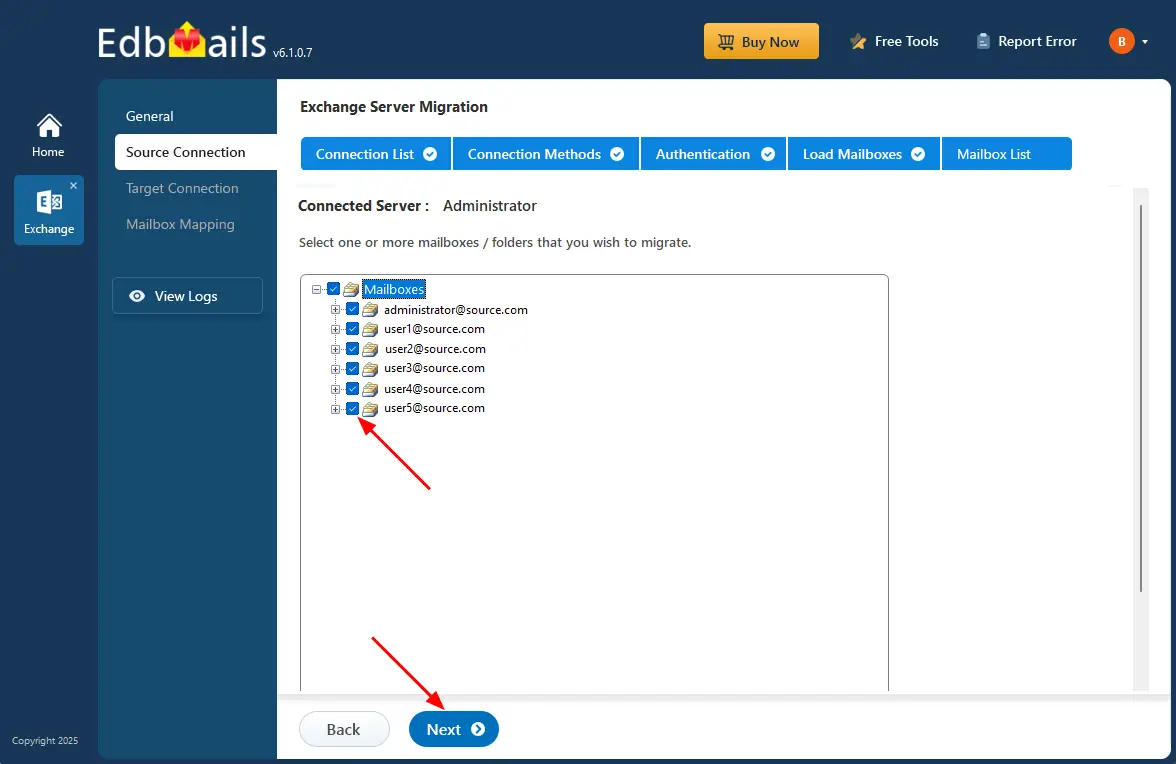
Step 3: Choose the mailboxes for migration
- Choose the mailboxes from your Exchange 2010 server that you wish to migrate to Exchange 2016. Make sure to select all the necessary mailboxes before moving forward.
- Click the ‘Next’ button.
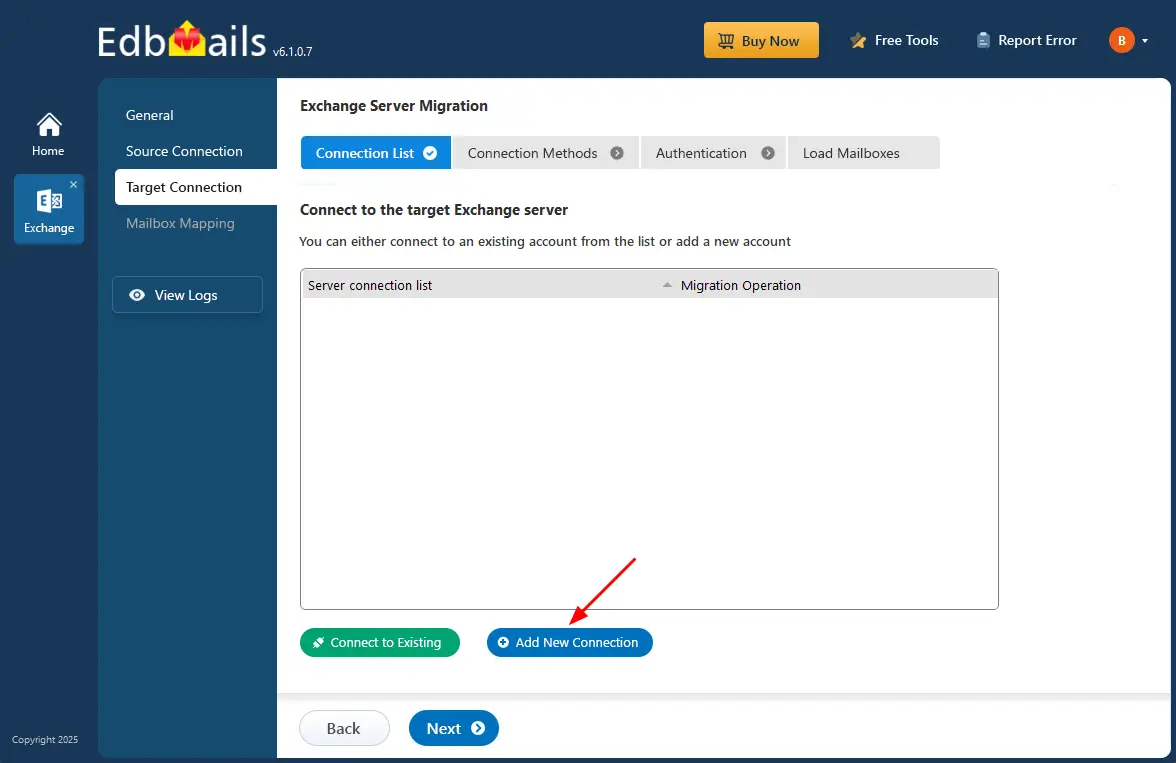
Step 4: Connect to target Exchange 2016 server
- To set up a new connection to the target Exchange server, click ‘Add New Connection’. If you wish to use a previously configured connection, select it from the list and click ‘Connect to Existing’ to continue the migration process.
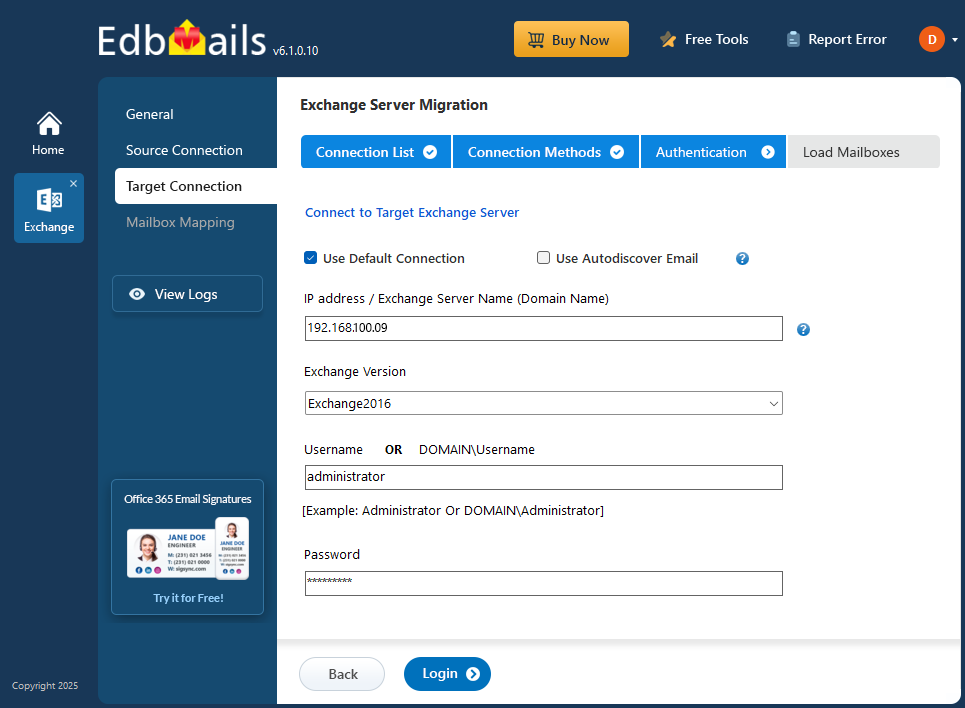
- Choose the required options to connect to your target Exchange server and click the ‘Next’ button.
- Enter the target Exchange 2016 server details and click the ‘Login’ button
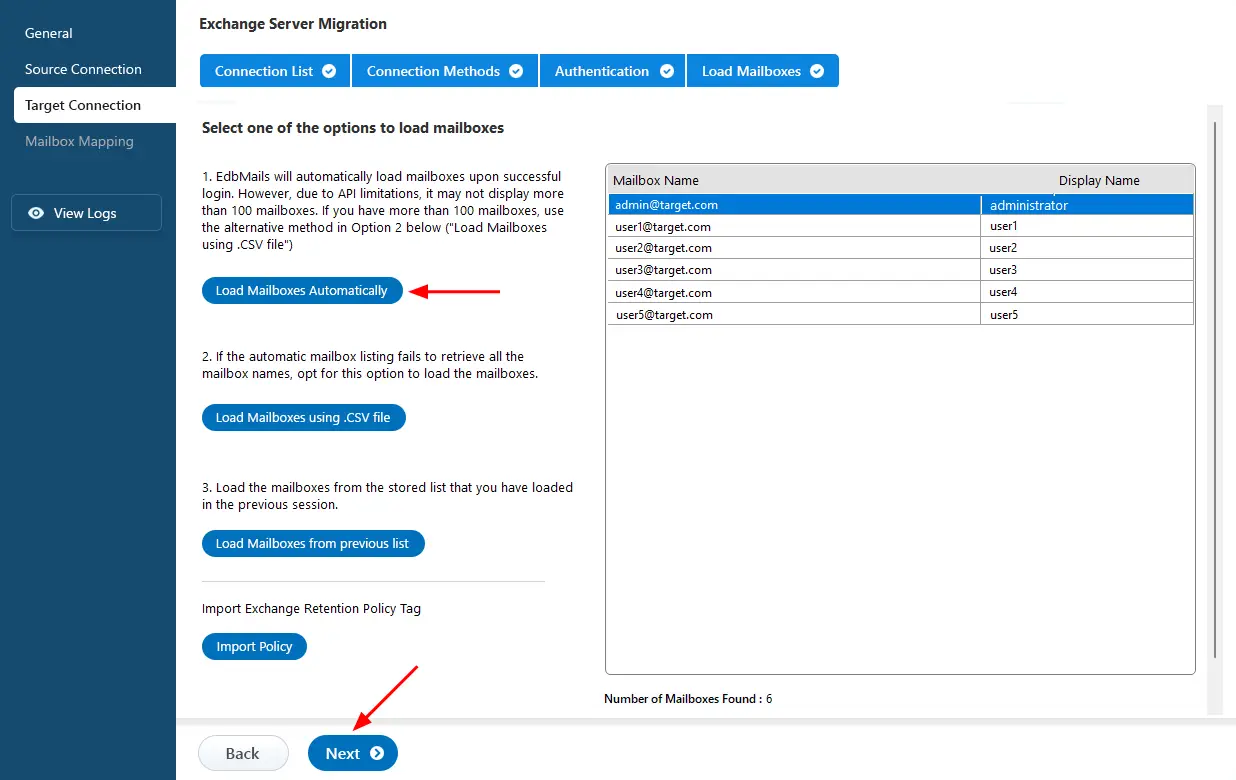
- After successfully login to your target Exchange 2016 server, select the option to load the mailboxes, you can manually load the mailboxes using a CSV file.
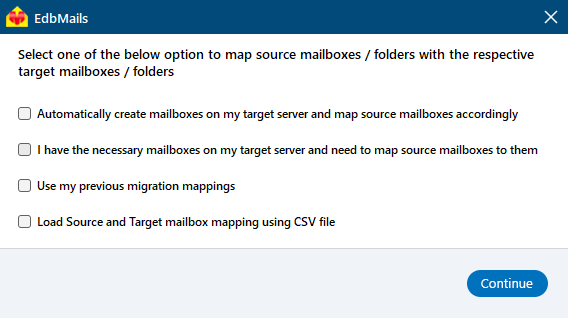
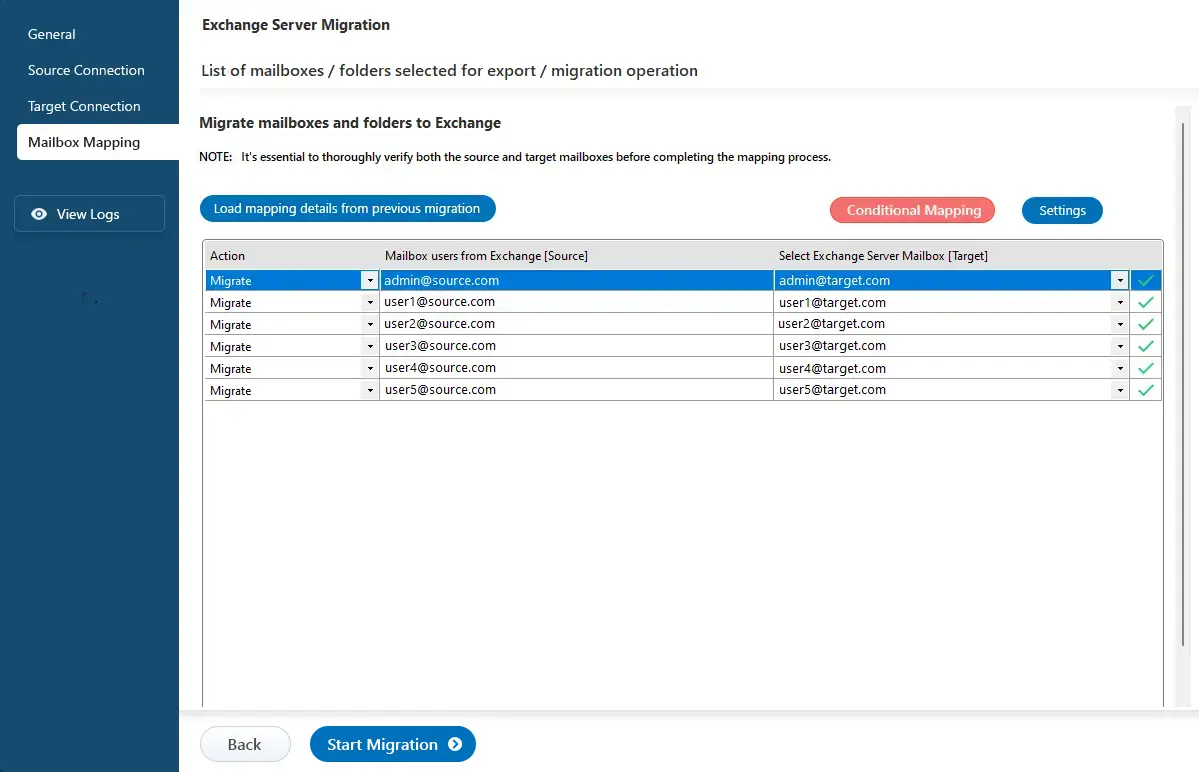
Step 5: Map the source and target Exchange server mailboxes
- Select the appropriate mapping option.
- EdbMails automatically maps mailboxes between the source and the target Exchange servers. This feature is especially useful when migrating a large number of mailboxes, as it reduces manual effort and saves time during the overall migration process.
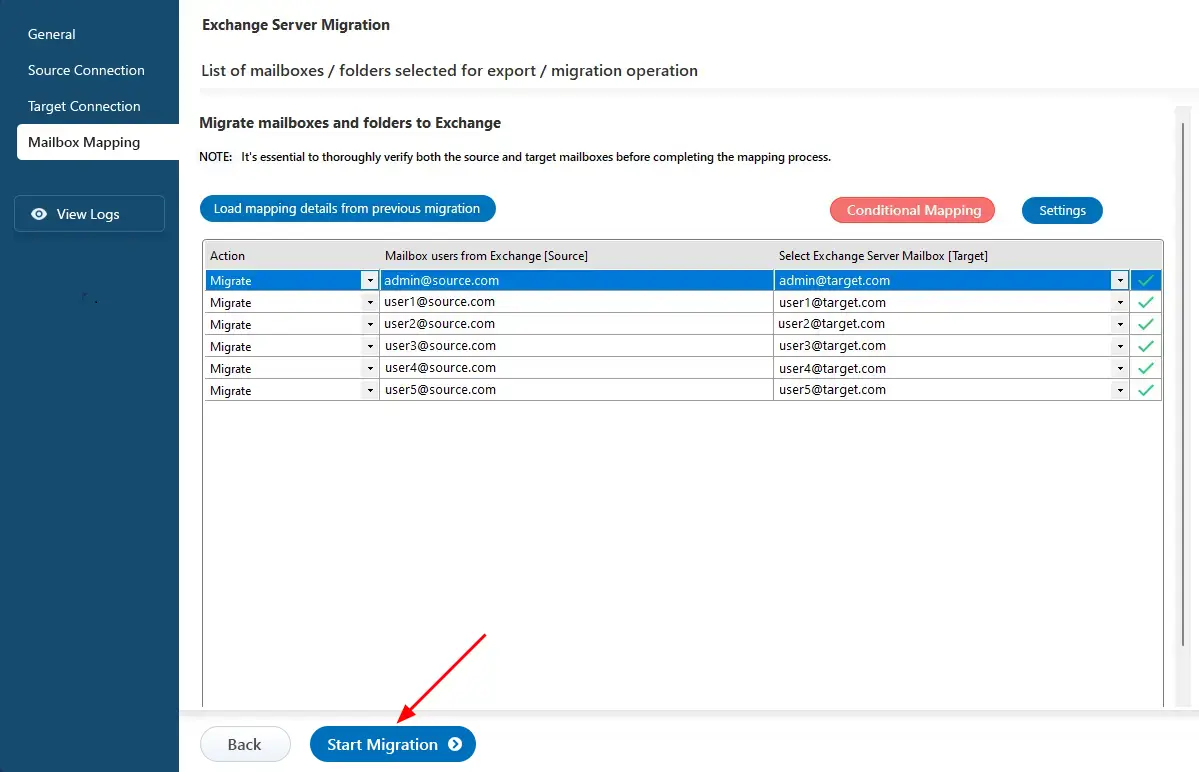
Step 6: Start Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2016 migration
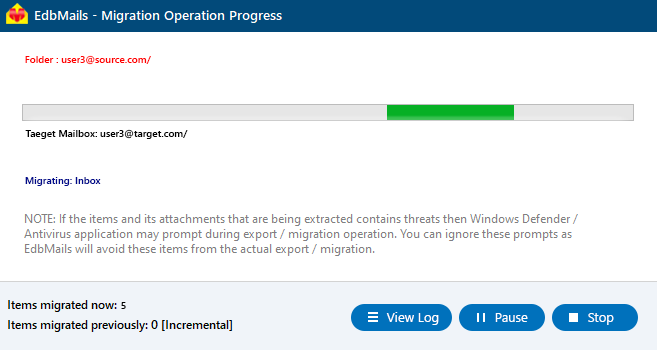
- Once the mailbox mapping is complete, click ‘Start Migration’ to begin transferring mailboxes to the target Exchange server.
- Now that the migration has been initiated, you can see the migration status in the progress bar. Once the migration is complete, EdbMails will prompt you to review the migration status with logs.
- Click the 'View Logs' button to view the migration report. Also, log in to your target Exchange server and verify the items
Exchange 2010 to 2016: post-migration tasks
- Step 1: Update the MX records and test the email routing
To receive messages on the Exchange server 2016, update MX records to enable email to work with the new server you have migrated to. In addition, configure the Autodiscover record to allow Outlook to connect to the migrated mailboxes. Test email routing to make sure that email is being delivered to the correct mailboxes on the Exchange 2016 server.
- Step 2: Create a new Outlook profile for users in the new domain
Ensure you have the latest version of Outlook client installed on your computer to avoid compatibility issues. Configure the Outlook profile for each user in your domain if Outlook has problems connecting to the new Exchange server.
- Step 3: Decommission and uninstall Exchange server 2010
Allow a few days to confirm proper email reception and ensure that all systems are functioning as anticipated. Once confirmed, proceed with decommissioning the source Exchange server. Follow the instructions provided on Microsoft's website to learn how to uninstall Exchange Server 2010 after completing the migration to Exchange 2016.
- Step 1: Update the MX records and test the email routing
Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration troubleshooting
Check the Exchange migration troubleshooting guide for effective solutions to typical migration challenges you might face.
Advantages of EdbMails for Exchange 2010 to 2016 Migration
EdbMails provides a powerful and reliable solution to migrate mailbox from Exchange 2010 to 2016 with high accuracy and zero downtime. It simplifies the migration process, minimizes manual tasks, and ensures complete data integrity throughout the transition.
- EdbMails supports cutover, staged, and hybrid migration methods, giving organizations the flexibility to choose the best approach based on their needs.
- There are no limitations on mailbox size when you migrate Exchange 2010 to 2016 using EdbMails, allowing large mailboxes to be transferred seamlessly.
- The software enables migration of Exchange 2010 mailboxes, archive mailboxes, and public folders directly to Exchange 2016 servers without data loss.
- With incremental migration, EdbMails ensures that only new or modified items are migrated during subsequent operations, avoiding any duplication on the target server.
- It allows the migration of Exchange public folders to shared mailboxes for better organization and accessibility.
- You can perform a direct migration from any Exchange Server version (2007–2019) without facing coexistence or compatibility issues.
- EdbMails offers advanced filtering options that let you migrate selected items based on date range, sender or recipient address, subject, attachments, or message status (read/unread).
- Automatic mailbox mapping intelligently matches mailboxes between the source and target servers, reducing manual effort and configuration time.
- Its user-friendly graphical interface eliminates the need for PowerShell scripts, making the process simple even for first-time users.
- EdbMails provides free and extensive 24/7 technical support via live chat, email, or phone, ensuring expert help is always available when needed.
EdbMails ensures a smooth, secure, and efficient migration experience, helping organizations migrate from Exchange 2010 to 2016 step by step with confidence and minimal disruption.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the steps to migrate Exchange 2010 to 2016?
The following steps summarize how you can migrate Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2016.
- Plan and prepare for the migration
This step includes identifying the scope of the migration, creating a schedule, and gathering all the necessary resources.
- Install Exchange 2016
This step includes installing the Exchange 2016 software on a new server and preparing the server for migration.
- Configure Exchange 2016
It involves configuring the Exchange 2016 server and setting up features such as email routing, public folders, and client access.
- Migrate the mailboxes with EdbMails
In this step, migrate the mailbox data from Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2016. You can choose from various methods, such as a cutover migration, staged migration, hybrid migration or migration with an EDB file depending on your requirements.
- Decommission Exchange 2010
After the migration is complete, you can decommission the Exchange 2010 server and remove it from the network.
- Plan and prepare for the migration
What are the prerequisites for migrating from Exchange 2010 to 2016?
You must meet the following prerequisites before you can start the migration
- Server running Exchange 2010 with Service Pack 3 or later installed.
- A new server running a supported version of Windows Server, such as Windows Server 2012 or later.
- A valid Exchange 2016 license and mailboxes created on the target.
- Set impersonation rights for the global admin user on both the source and target servers if you are using the global admin user to connect to the Exchange server in the EdbMails application.
- Enough disk space, memory and bandwidth to accommodate the Exchange 2016 installation and migration.
Can I migrate directly from Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2016?
Yes, with EdbMails, you can perform an Exchange migration from 2010 to 2016 without the necessity of upgrading to an intermediate version of Exchange server. Ensure to install the latest service pack and rollup update for Exchange 2010 Service Pack (SP3) before commencing the migration.
Can I migrate my public folders from Exchange 2010 to 2016?
Yes, EdbMails supports Exchange 2010 to 2016 Public folder migration. You won't need to handle a long series of PowerShell scripts or worry about executing them in a specific order. There's also no need to create CSV mapping files.
How long does it take to migrate from Exchange 2010 to 2016?
The length of time it takes to migrate from Exchange 2010 to 2016 depends on several factors including the source of the data, data type and density, network bandwidth, hardware settings, migration methods, and throttling. EdbMails facilitates concurrent migration of multiple mailboxes, significantly enhancing performance. Installing EdbMails on various computers and migrating different mailboxes further optimizes overall efficiency.
Can I use the same SMTP domain name for Exchange 2016 that I used or Exchange 2010?
Yes, you can use the same SMTP domain name for Exchange 2016 that you used for Exchange 2010. However, you must ensure that the necessary DNS records are configured correctly and that the domain is verified in Office 365 (if you are using a hybrid deployment).