What are Microsoft Security defaults in Azure AD?
Security defaults are Microsoft settings designed to protect your organization from identity-related attacks such as phishing, hacking, and unauthorized access. By default, these settings secure your accounts using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and provide a basic level of protection for all users.
What should I know about these settings?
Security defaults block applications that use legacy authentication protocols that do not support modern Office 365 authentication. For example, if security defaults are enabled, you must use an email client that supports modern authentication to log in to your account.
Enabling security defaults also changes how you, as an admin, and your users log in to Office 365 services:
- Prevents less secure apps and legacy authentication from outdated email clients. It also restricts login access through IMAP, POP3, SMTP, or Remote PowerShell.
- Enforces Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all users, requiring them to set up MFA during sign-in.
- Mandates MFA for privileged accounts in Azure Active Directory to access services such as Azure CLI and the Azure portal.
If you want to use Conditional Access policies (which allow you to customize security settings), you must first disable security defaults before applying those policies.
Enable or disable Microsoft Security Defaults in Office 365
You can enable or disable these security settings anytime through the Microsoft Azure portal. Authentication to your Office 365 account may fail even if you have already enabled MFA and App Password.
In some cases, you may also see the following prompt when signing in to Office 365:
“Microsoft has enabled security defaults to keep your account secure.”
In such situations, disabling security defaults may be necessary. Keep in mind that only a global administrator can make these changes.
Steps to turn off Security Defaults in Office 365
- Step 1: Log in to Office 365 using global administrator credentials.
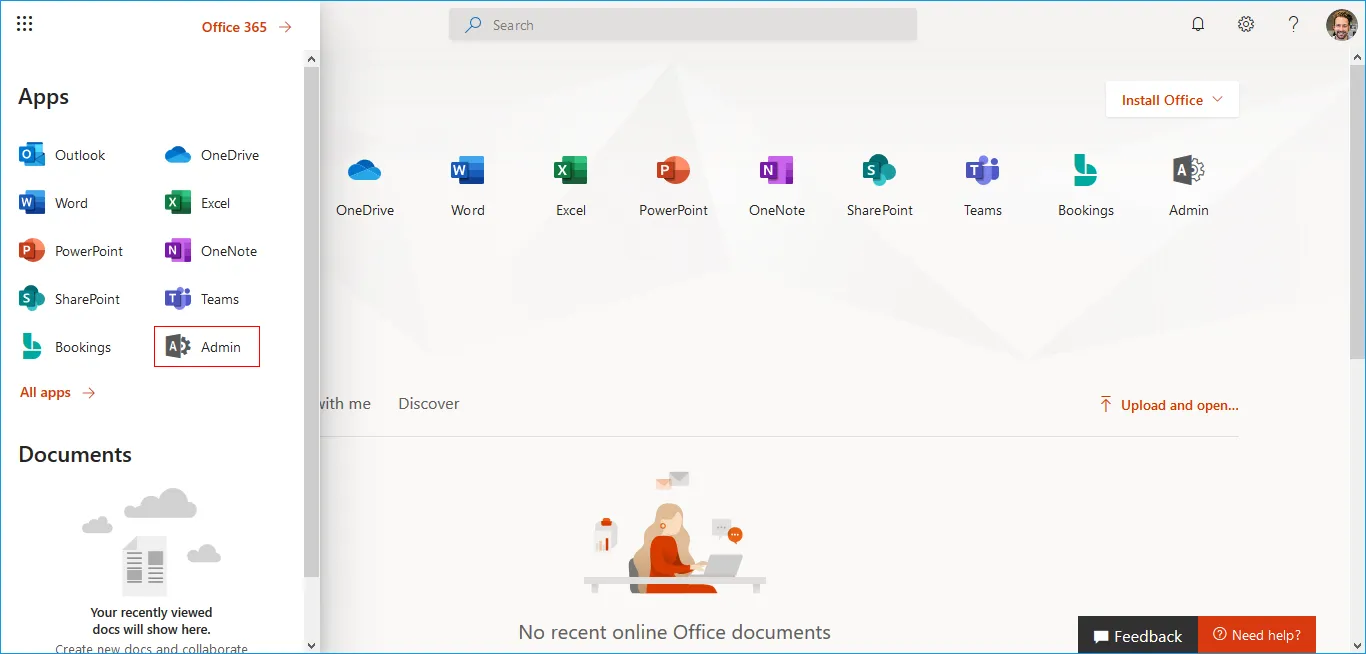
- Step 2: Click on 'Admin' (gear icon) from the left panel.
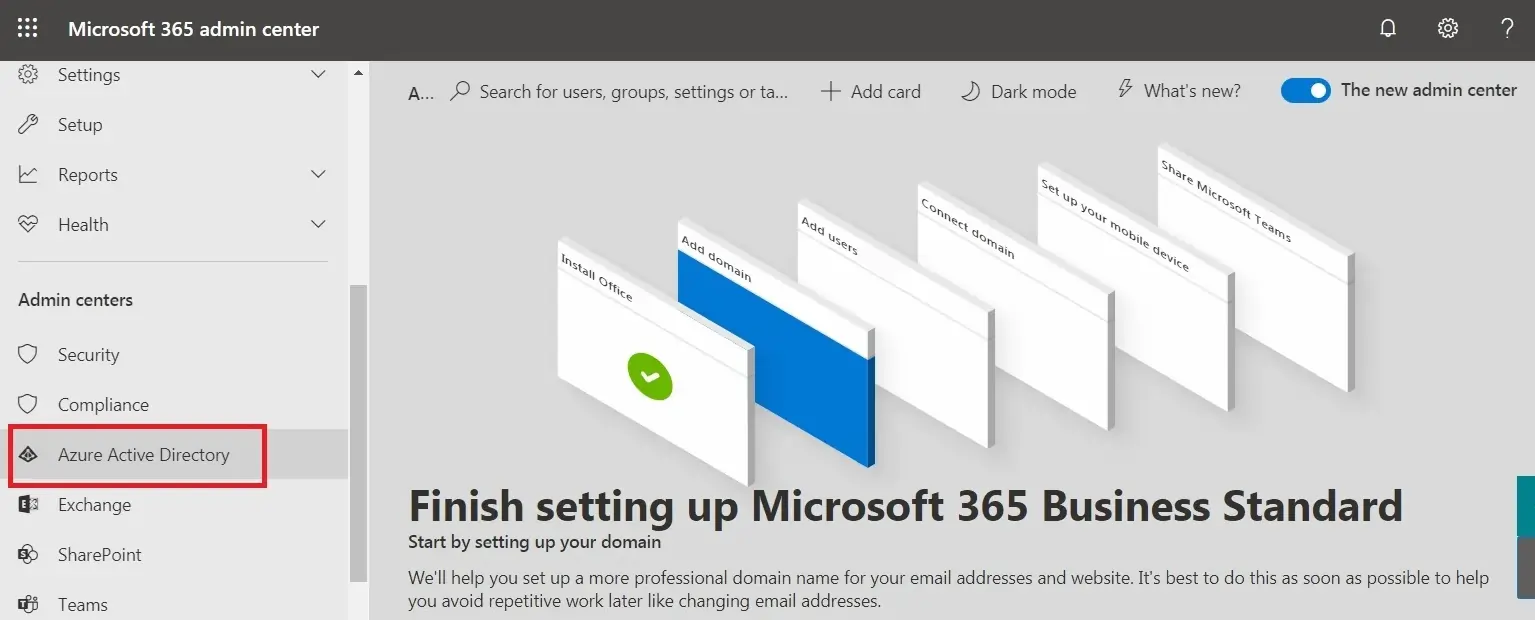
- Step 3: From the Admin centers section, select Azure Active Directory to proceed.
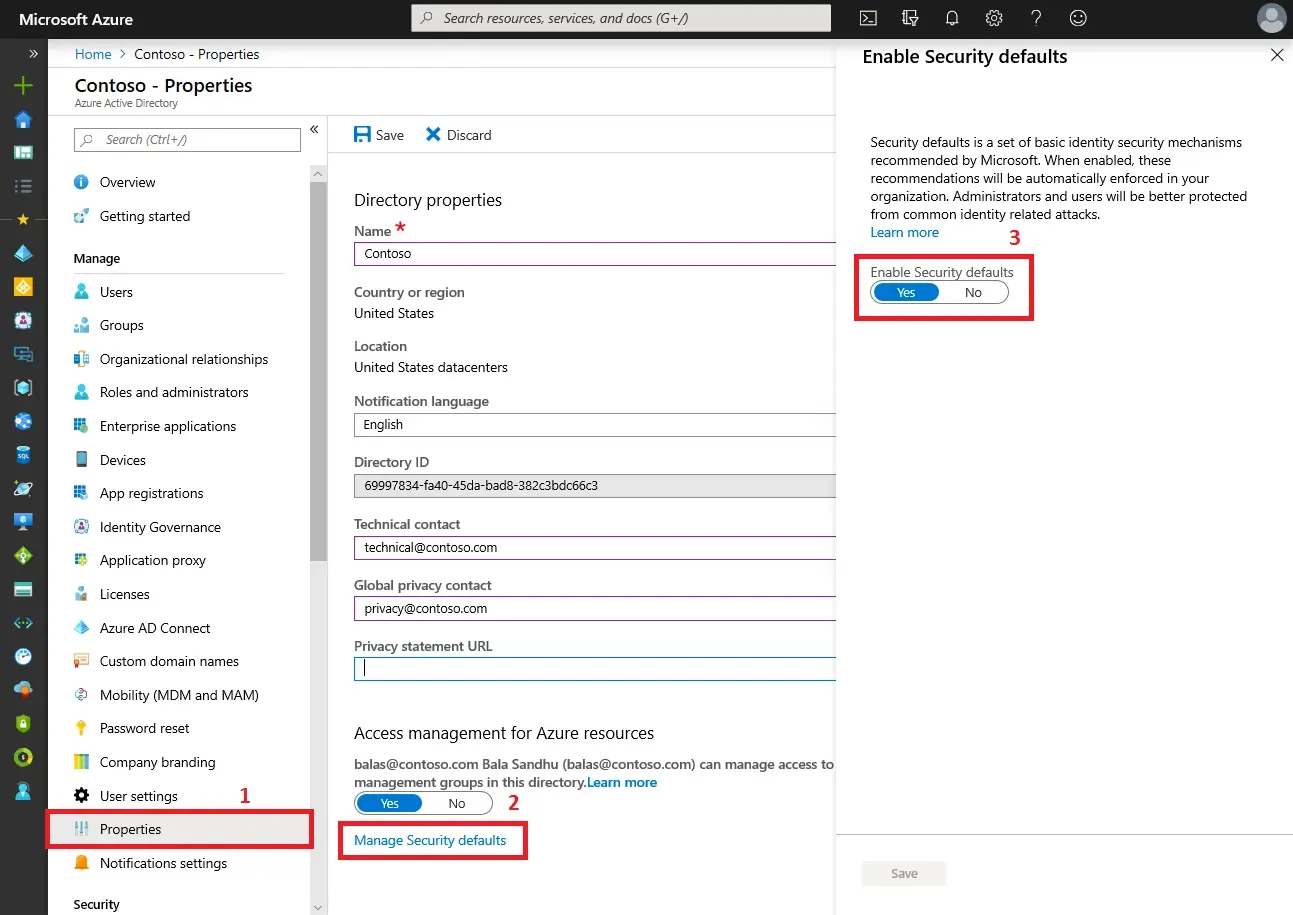
- Step 4: In the left-hand panel, open Properties.
- Step 5: Scroll down and select the Manage Security defaults option.
- Step 6: Adjust the toggle for Security defaults.
Set Enable security defaults to No and save your changes. (Switch it to Yes if you want to turn the settings back on.)
Once the security defaults are disabled, users will no longer be prompted to configure MFA during sign-in.
Enable Access to Basic Authentication Protocols
If you are unable to connect your IMAP or POP accounts (such as Gmail, Hotmail, or Outlook) to your email clients, you may need to enable legacy authentication protocols. Follow the steps below to configure this setting:
- Step 1: Login to Office 365 using global administrator credentials.
- Step 2: From the left panel, click on Admin (gear icon).
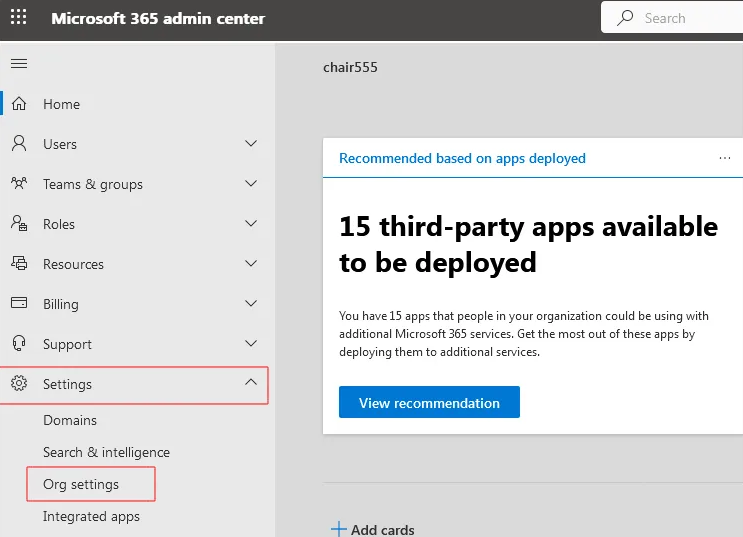
- Step 3: Open the navigation menu in the top-left corner, select Show All, expand Settings, and then click on Org Settings..
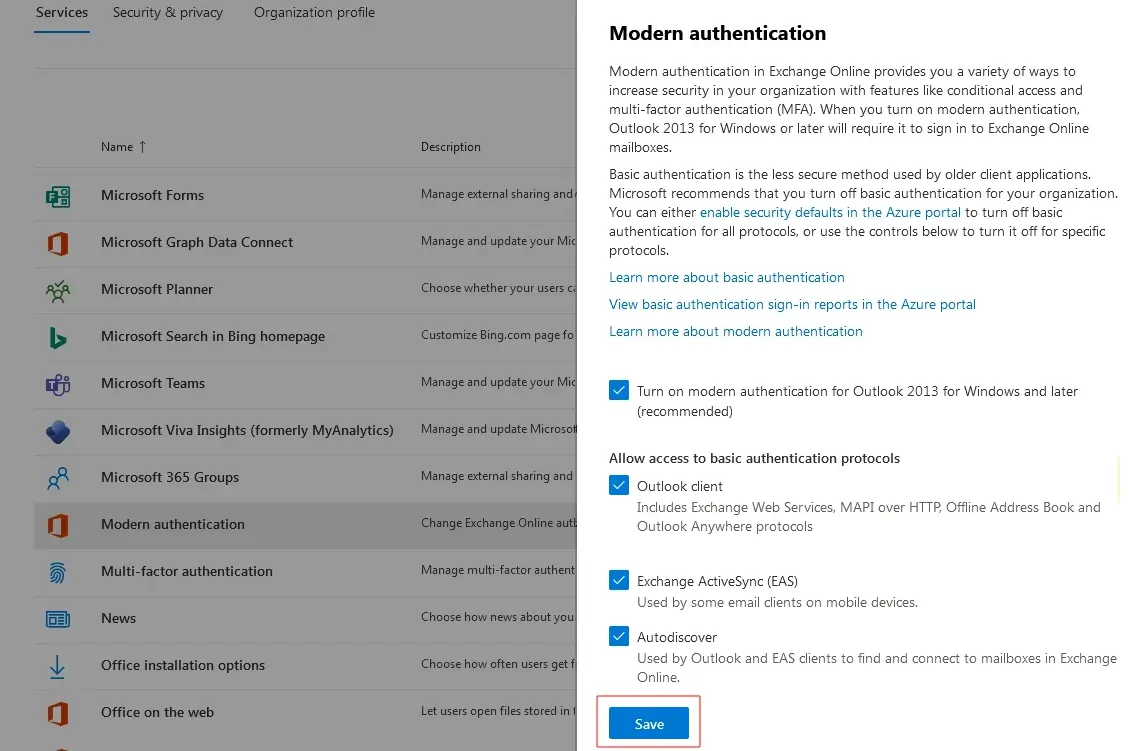
- Step 4: In the Modern authentication section, choose the protocols you want to enable and then click Save to apply the changes.
Now, your email clients will be able to access your account or connect using IMAP.
If you need to migrate from one Office 365 tenant to another, EdbMails Office 365 Migrator allows you to seamlessly transfer emails, contacts, mail items, and folders without relying on manual methods like PowerShell scripts. In addition, EdbMails supports secure OAuth 2.0–based modern authentication for Office 365. Simply download and install the latest version to take advantage of this feature. With modern authentication enabled, turning off security defaults in Office 365 is no longer necessary.