Cross forest Migration from Exchange 2013 to 2019/2016
Cross forest migration refers to moving mailboxes, data, and other Exchange resources between separate Active Directory forests. This type of migration becomes necessary during events such as mergers, acquisitions, corporate restructuring, or business consolidations, where different IT environments must be unified. Combining cross forest migration Active Directory helps centralize management, streamline resources, and boost collaboration across the organization.
Migrating mailboxes between different forests can be complex and time-intensive, particularly when using built-in tools. Native cross forest migrations often require creating trust relationships between forests or running complicated PowerShell commands. Upgrading from older Exchange versions, such as Exchange 2010 or 2013, to newer versions like Exchange 2016 or 2019 can add further steps and increase complexity.
EdbMails Exchange Migration software offers a simplified and faster solution for cross-forest mailbox migration between on-premises Exchange servers. Its user-friendly, wizard-based interface automates much of the process, minimizing manual effort and reducing the risks associated with traditional migration methods.
EdbMails Exchange Migration tool makes it easy to migrate mailboxes, public folders, archive mailboxes, and shared mailboxes between different Active Directory forests, without facing coexistence challenges. You can directly migrate from Exchange 2010 or 2013 to newer versions like Exchange 2016 or 2019 with just a few clicks, making the migration process straightforward and stress-free.
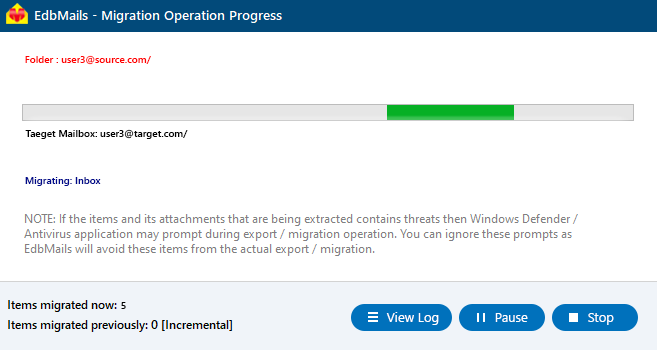
The software is built for high-performance migration. It offers incremental migration, which means after the initial transfer, only newly added or changed items are moved, saving time and reducing server load. EdbMails also manages throttling automatically to avoid slowdowns and keep the servers stable during the migration process.
For organizations handling larger migrations, EdbMails supports transferring up to 20 mailboxes at the same time, speeding up the overall move. Advanced filtering options allow you to fine-tune what gets migrated — you can filter items by date range, sender, recipient, subject, attachments, or even message status (read/unread), ensuring only necessary data is transferred.
The upcoming sections will guide you through all essential prerequisites, detailed steps for cross-forest Exchange migration, and important post-migration tasks to complete a successful migration without disruptions.
Common Challenges in Cross Forest Migration and How EdbMails Solves Them:
Exchange cross forest migration prerequisites
Exchange cross forest migration step by step
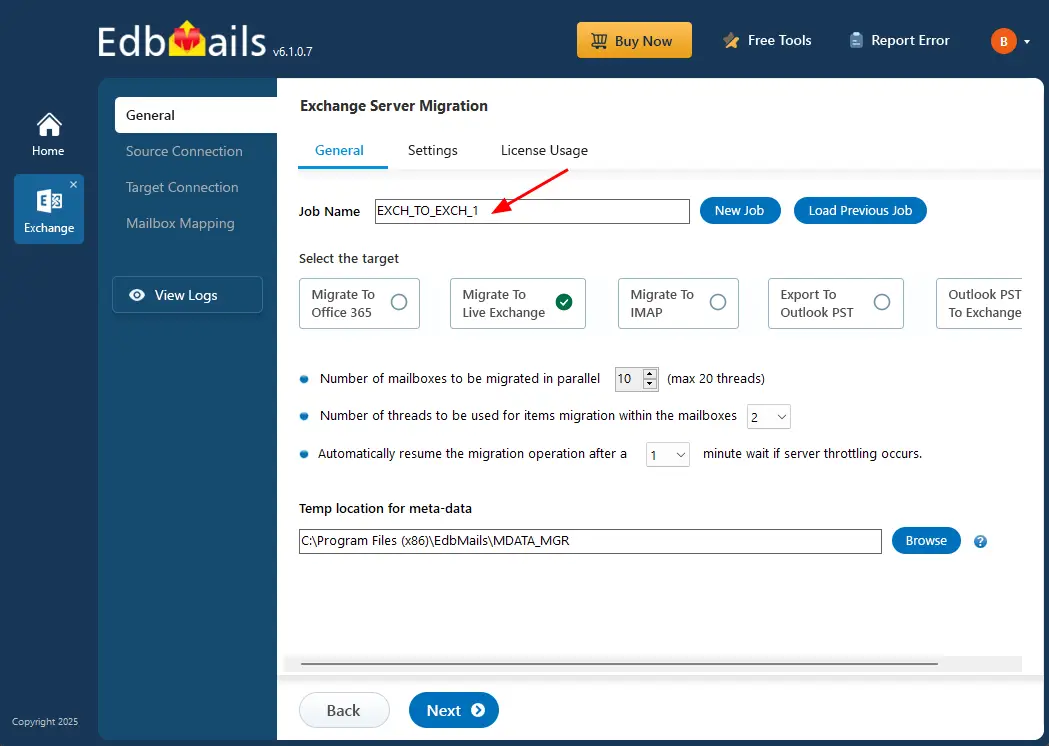
Step 1: Download and install EdbMails Exchange migration software
- Download and install the EdbMails application on Windows operating system.
See a detailed list of EdbMails system requirements for cross forest Exchange migration.
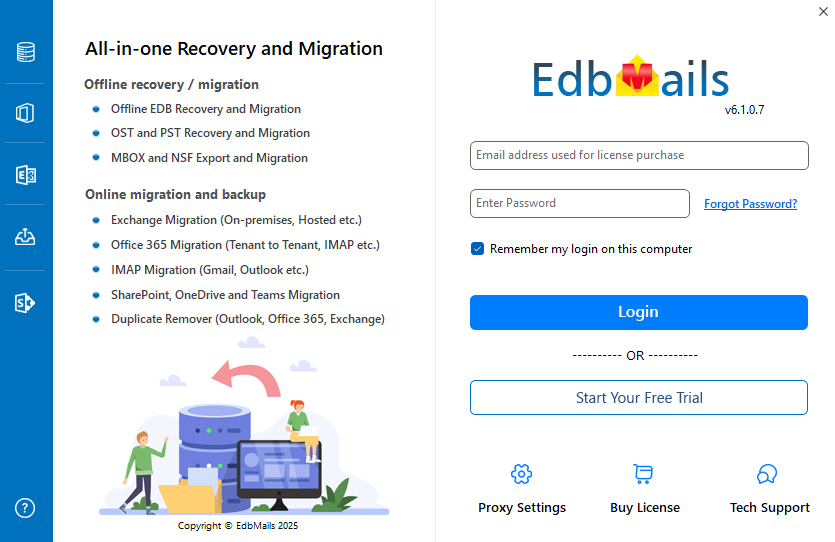
- Launch the EdbMails application and either ‘login’ with your email address and password or select the ‘Start Your Free Trial’ option to continue.
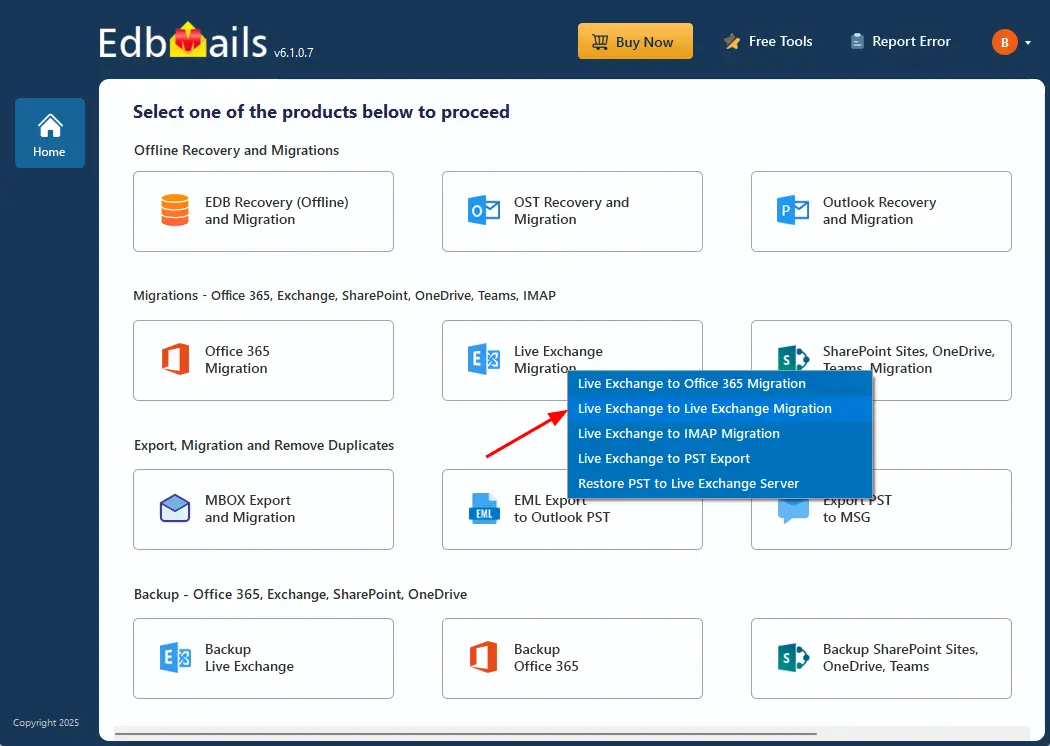
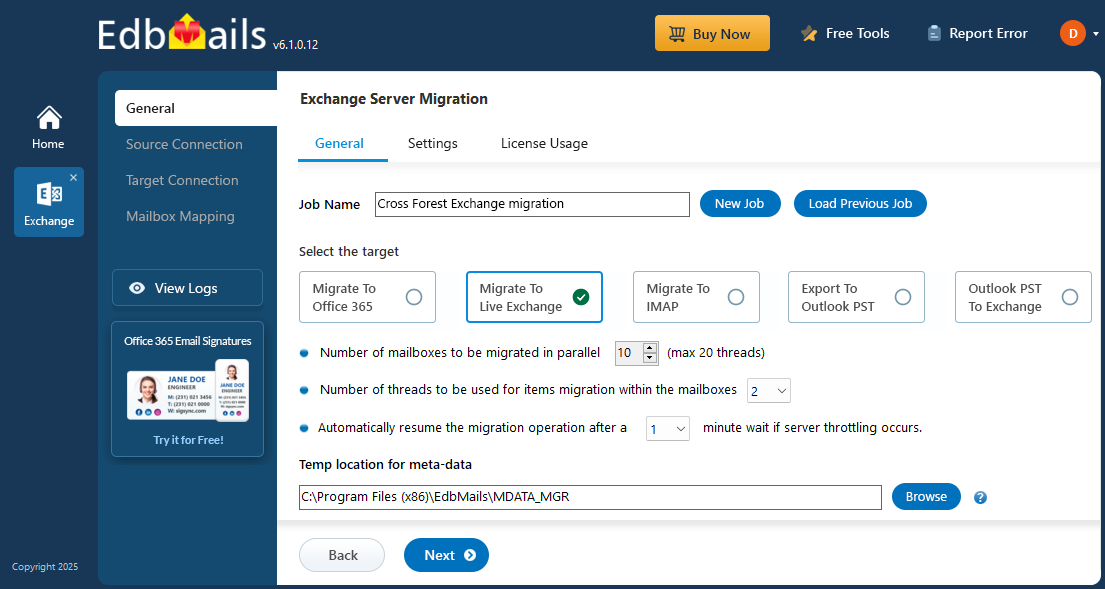
- Select ‘Live Exchange Migration’ option.
- Select 'Live Exchange to Live Exchange Migration' option.
- Keep the existing job name or select ‘New Job’ if you want to enter a different name.
- Download and install the EdbMails application on Windows operating system.
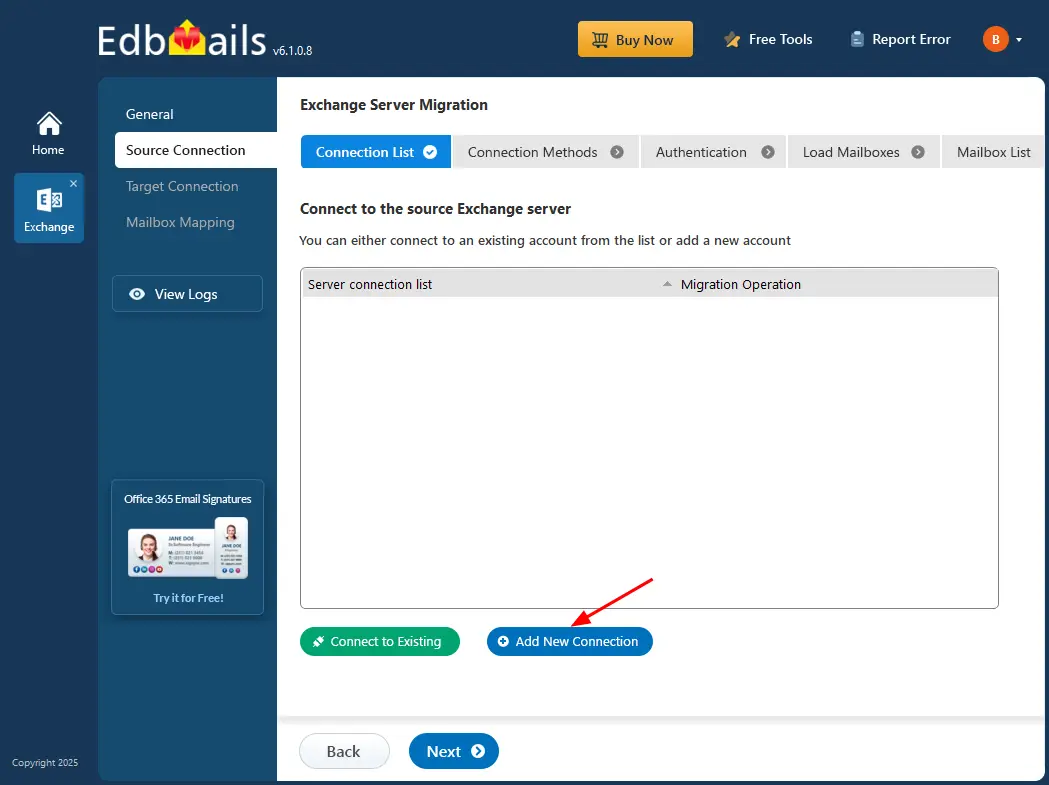
Step 2: Connect to the source Exchange server
- To establish a new connection to the source Exchange server, click on ‘Add New Connection’. If you have an existing connection, simply select it from the list and click ‘Connect to Existing’ to continue.
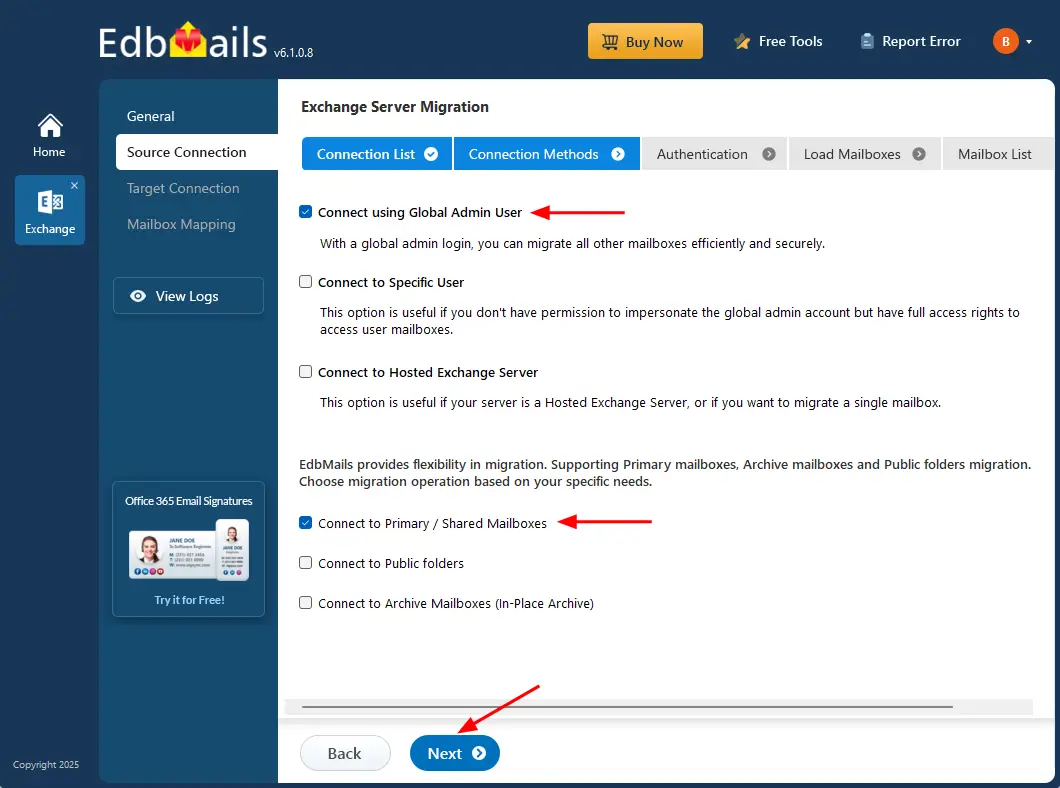
- Select the required connection options and click the ‘Next’ button.
Different options to connect to Exchange server in EdbMails.
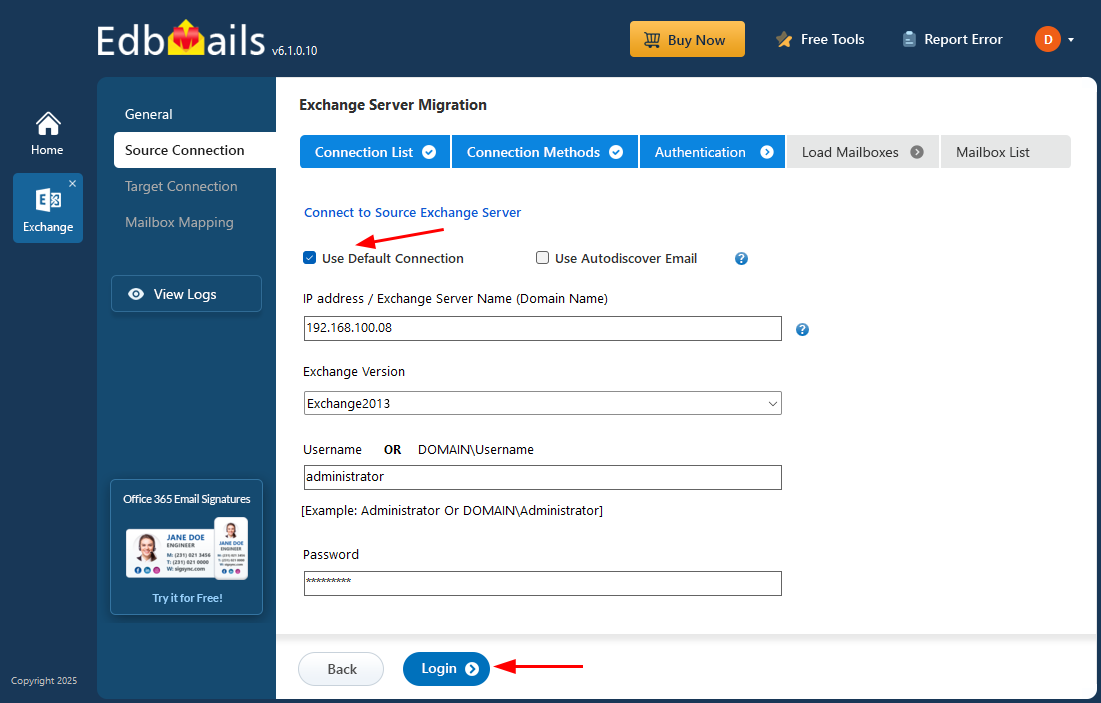
- Enter the source Exchange server details and click the ‘Login’ button.
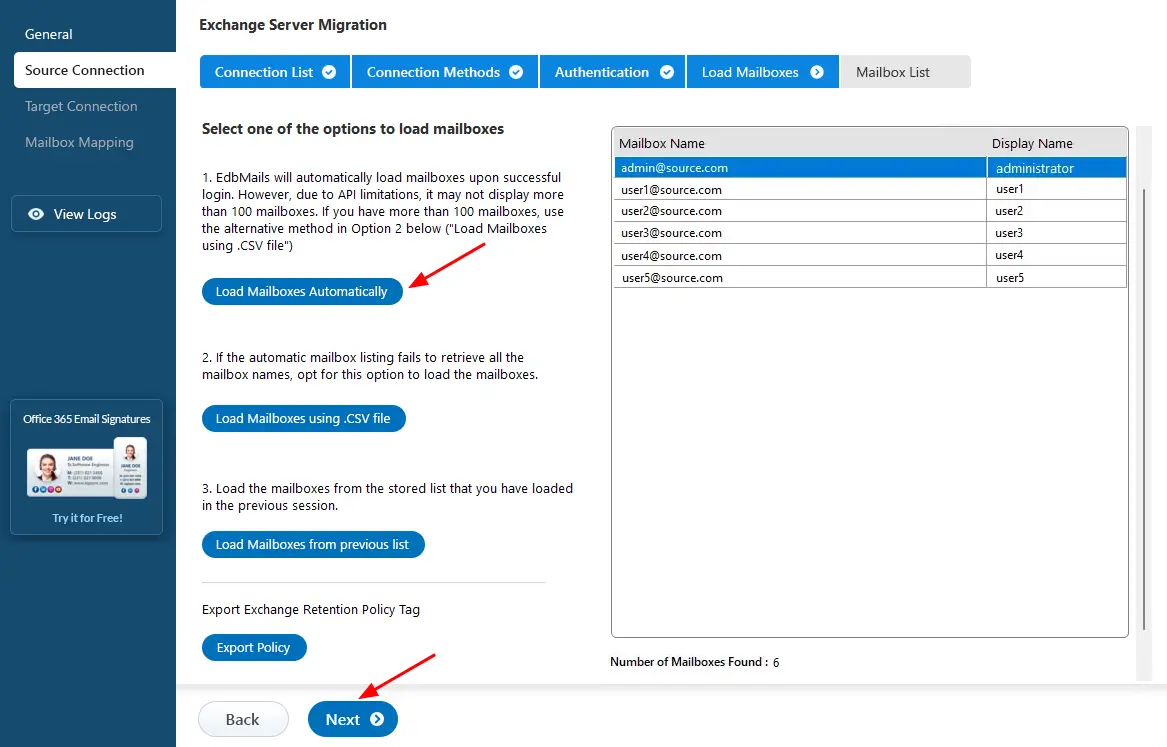
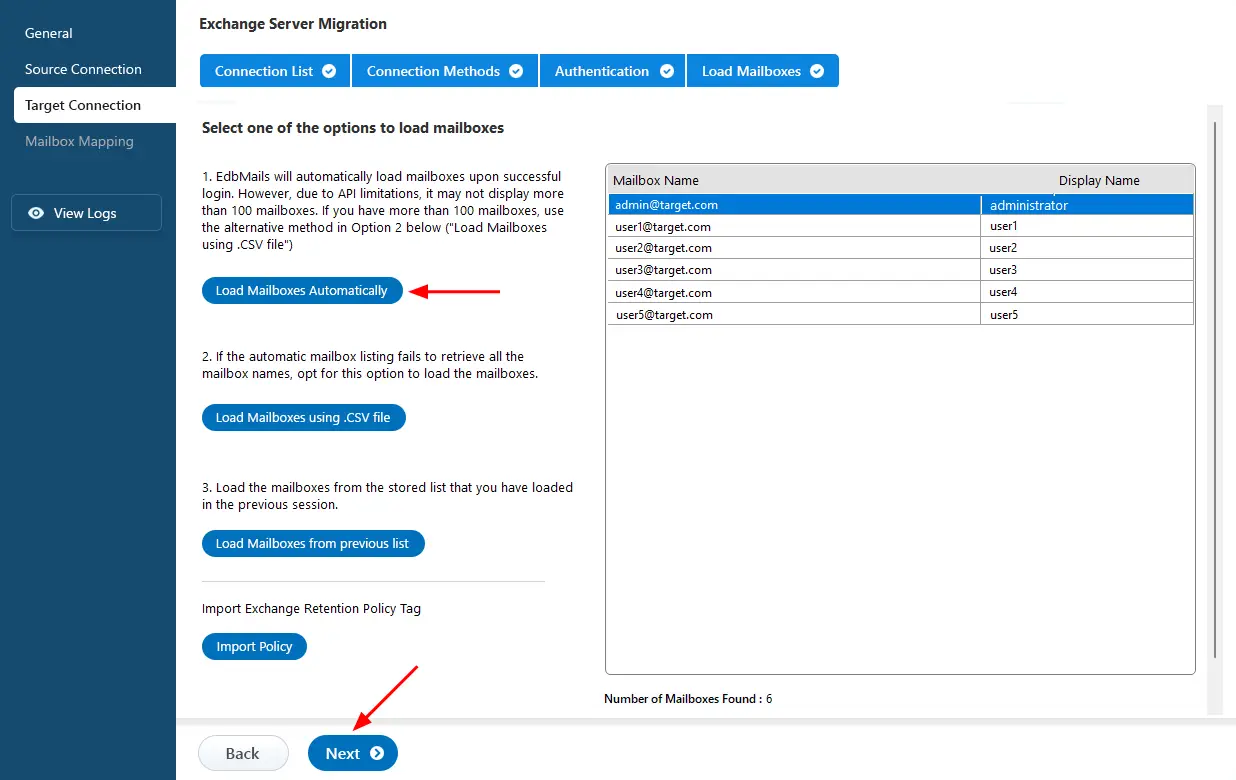
- After logging into your source Exchange server, choose a method to load the mailboxes. EdbMails will automatically load them, but due to Microsoft API limitations, it may not display more than 100 mailboxes. If you have more than 100, you can use the ‘Load Mailboxes using .CSV file’ option to load them all.
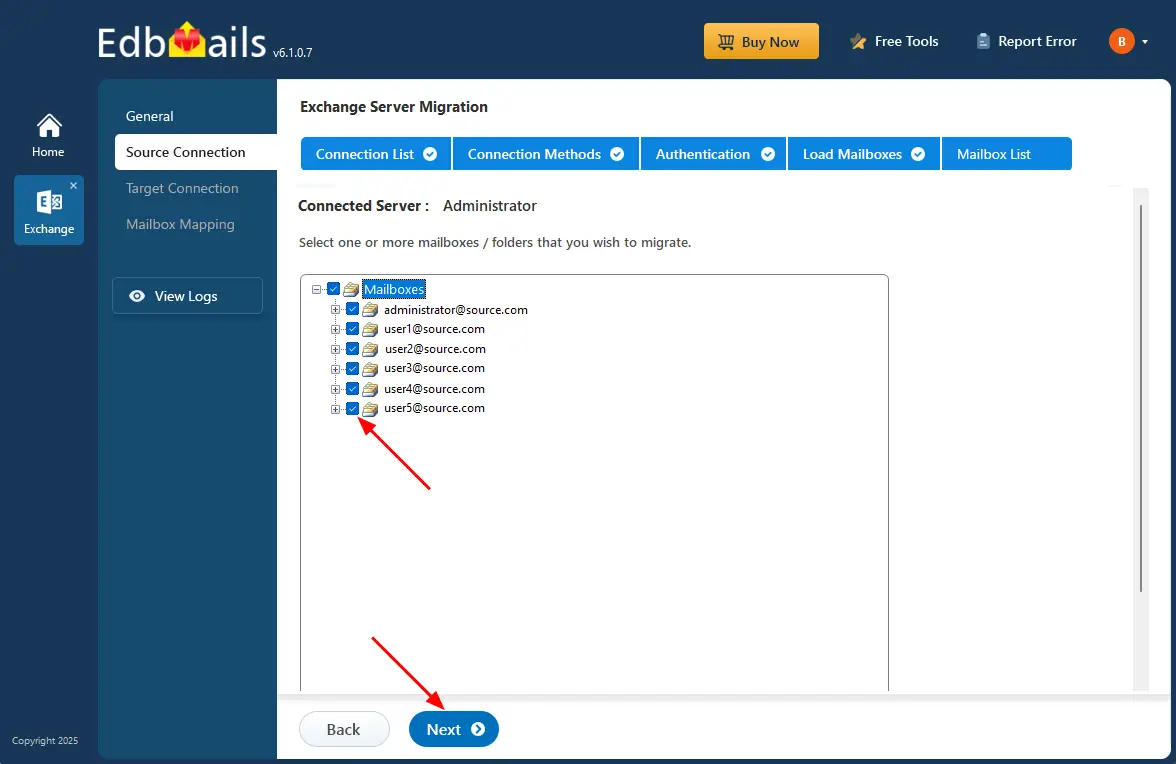
Step 3: Select the source Exchange mailboxes
- Select the mailboxes/folders from the source Exchange server that you intend to transfer to the target server.
- Click the ‘Next’ button.
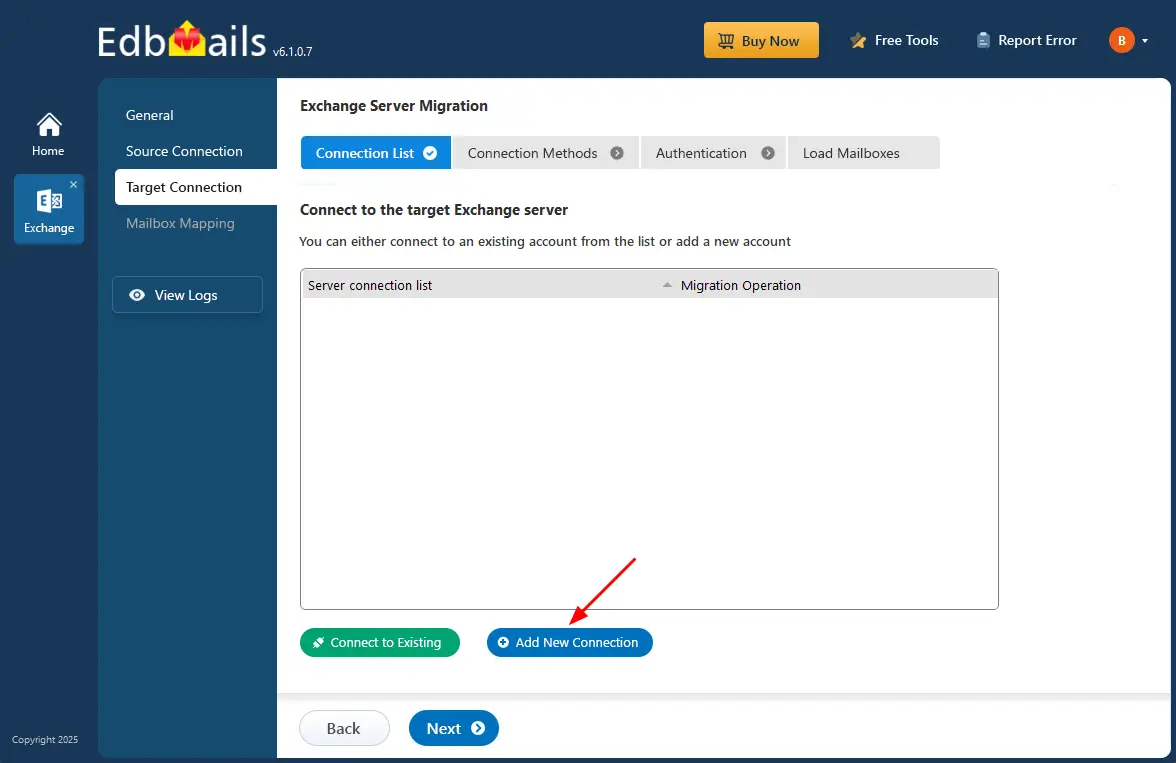
Step 4: connect to the target Exchange server
- To establish a connection to the target Exchange server, click on ‘Add New Connection’ for a fresh connection. If you wish to use an existing connection, simply select it from the list and click ‘Connect to Existing’.
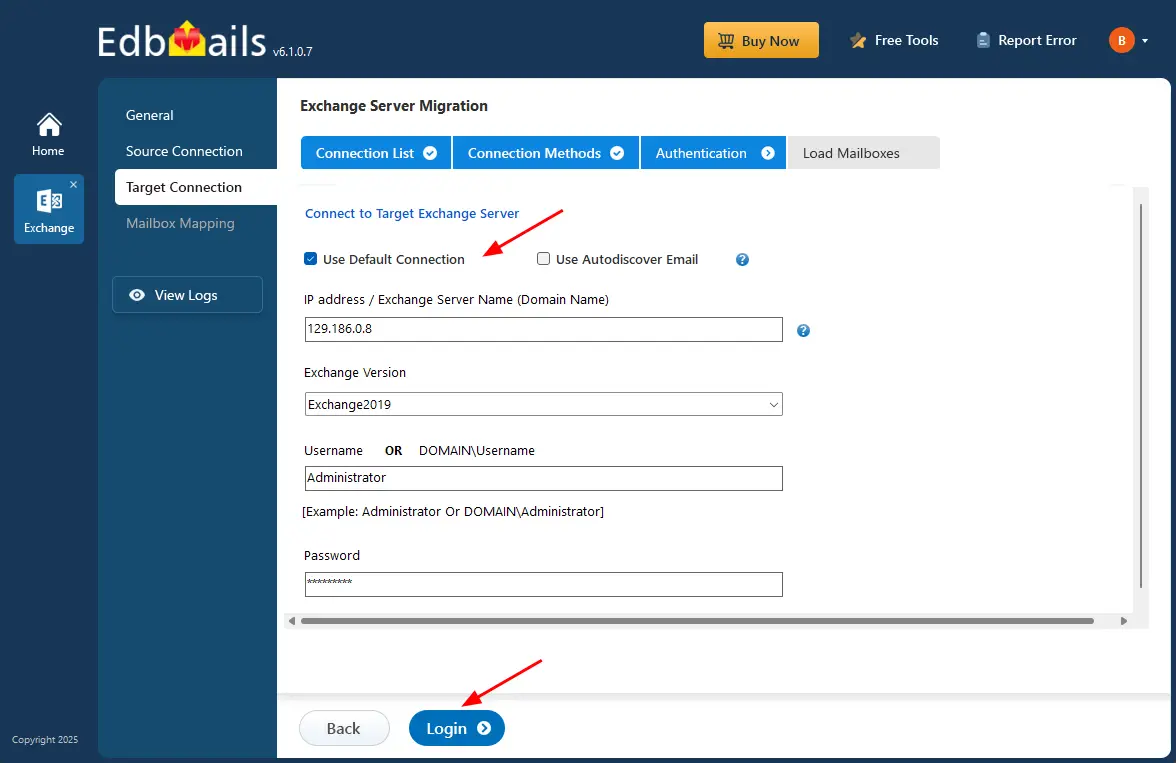
- Choose the required options to connect to your target Exchange server and click the ‘Next’ button.
- Enter the target Exchange server details , and then click the ‘Login’ button to proceed.
- Select one of the methods to load the target Exchange server mailboxes.
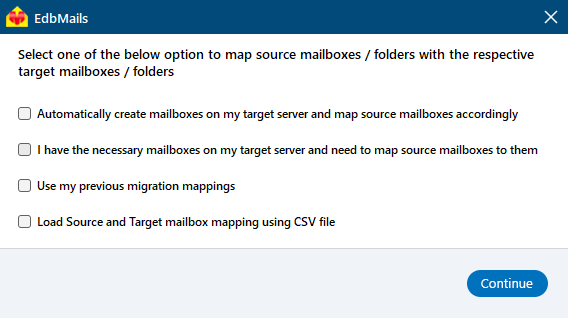
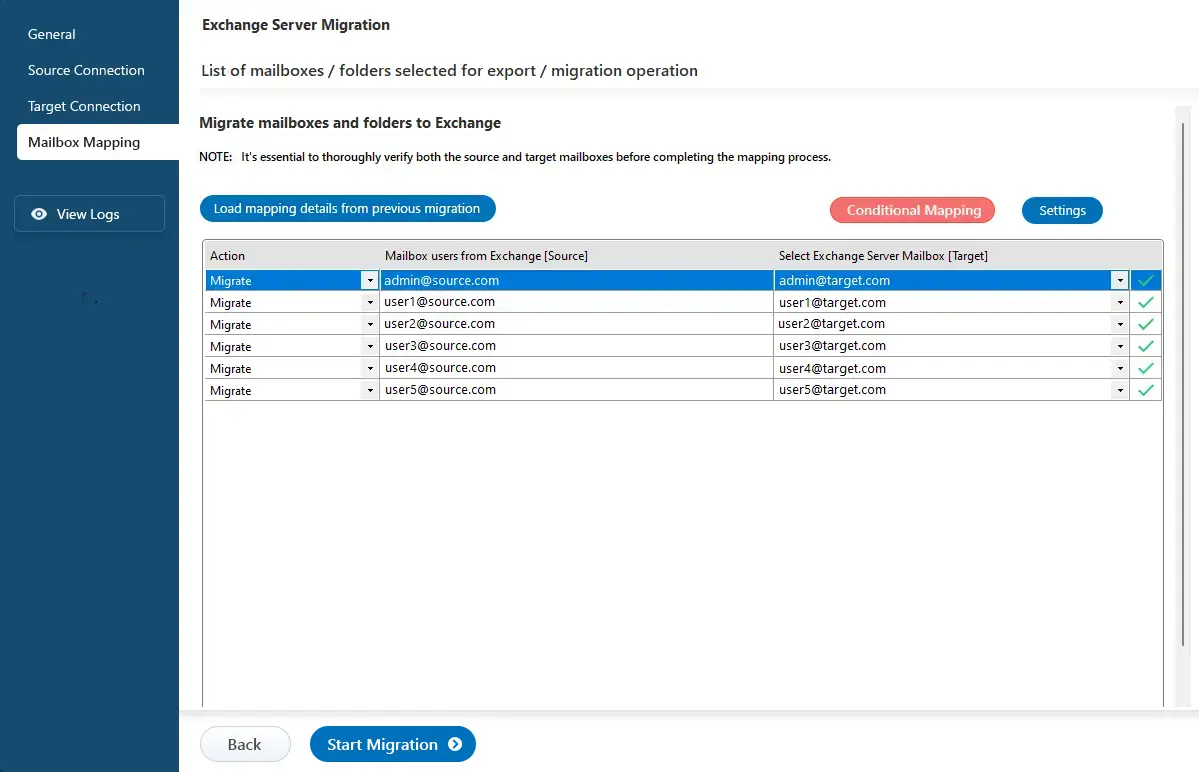
Step 5: Map the mailboxes between the source and the target servers
- Select the required mapping option.
- If EdbMails is installed on your target Exchange server, you can choose to let it automatically create the mailboxes on the target server.
- EdbMails automatically maps mailboxes between the source and target Exchange servers, making it especially helpful for migrating large numbers of mailboxes. This feature minimizes manual work.
Step 6: Start Exchange cross forest migration
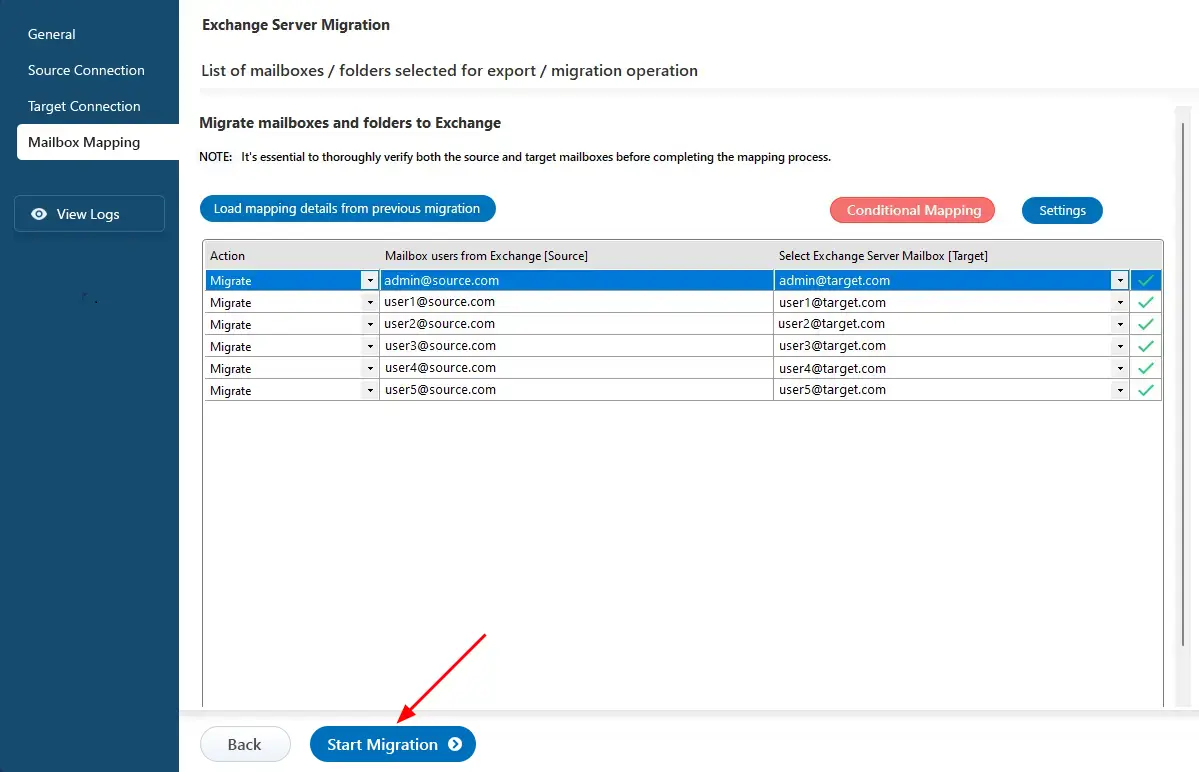
- After completing the mailbox mapping, click the ‘Start Migration’ button to initiate the migration process.
- The cross forest migration has now started. You can track the progress through the progress bar. Once the migration is finished, EdbMails will display a completion message. Click on the ‘View Logs’ button to check the migration report.
Exchange Cross forest Post Migration Tasks
Exchange cross domain migration troubleshooting
Benefits of EdbMails for Exchange cross forest migration
- Support for all Exchange server versions: EdbMails supports seamless migration from Exchange 2003, 2007, 2010, and 2013 to both Exchange 2016 and 2019.
- Cross forest migration capabilities: The software effectively manages cross-forest domain migration without encountering coexistence issues.
- Incremental migration: Incremental migration is designed to prevent the migration of duplicate items during subsequent operations.
- Granular brick-level migration: With the granular brick-level migration feature, users can precisely select individual mailboxes and specific items for migration.
- Public folders and Shared mailbox migration: EdbMails support for Exchange public folders and shared mailbox migration.
- Support for all migration types: EdbMails Exchange migration software accommodates a variety of migration types, such as cutover, staged, and hybrid migrations.
- User-friendly interface: EdbMails features an intuitive interface that simplifies the navigation process for performing migration operations, requiring no technical expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I migrate shared and archive mailboxes across forests?
Do I need coexistence or trust setup between forests?