Exchange migration checklist
Upgrading from one version of Exchange Server to another can be a complex task, even for experienced administrators. It requires careful planning, selecting the right data, and managing mailboxes on both the old and new servers. The process becomes even more challenging when the servers are located in different environments or have different configurations.
Migrating is especially important because Microsoft no longer provides support or updates for older Exchange versions, such as Exchange Server 2010. Moving to a newer version, like Exchange Server 2013, 2016, or 2019, ensures you continue to receive updates, security patches, and access to the latest features and improvements without disruptions.
This Exchange Migration Checklist serves as a practical guide for administrators, acting like a to-do list to ensure a smooth and successful migration. It provides essential tips and insights to help you plan, deploy, and migrate your Exchange migration efficiently.
Phases of an Exchange Migration
An Exchange migration typically involves three main phases:
Planning: In the planning phase, you gather all the necessary details for the migration. This includes setting up and deploying the new system, managing mailboxes and public folders, configuring mail flow, using the Exchange Management Shell, ensuring client connectivity, and making sure both the old and new Exchange servers work together.
Deployment: During deployment, you set up Exchange 2013, 2016, or 2019 and prepare for migration from Exchange 2010. This phase ensures that both old and new servers operate together without affecting existing services.
Migration: The migration phase involves transferring emails, mailboxes, and public folders from the old Exchange 2010 server to the new Exchange 2013, 2016, or 2019 server. Using reliable tools like EdbMails Exchange Migration Tool helps complete the migration securely and efficiently.
Exchange Migration 2010 to 2013 / 2016 / 2019: Thorough Checklist
Here are some useful tips to help administrators handle challenges during an Exchange Server migration from Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2013, 2016, or 2019.
Project Progression: Before starting the migration, it is important to evaluate your current environment and resources. A proper assessment helps you understand the scope of the project, allocate the right resources, and estimate timelines accurately. This step is essential for tracking progress and ensuring that the migration stays on schedule.
Key Considerations:
- Understand your business requirements, including recovery goals and migration needs, and identify how much data must be retained.
- Evaluate the total volume of data that will be migrated to plan resources effectively.
- Specify the types of data to be migrated, such as emails, contacts, calendars, tasks, and address books.
- Set a practical timeline for completing the migration — whether it can be done within a week, two weeks, or over several months.
These key points and strategies help you collect the necessary details to build a clear plan and set the right expectations for your Exchange 2010 to 2013, 2016, or 2019 migration project.
Verify System Prerequisites: After reviewing the project guidelines, release details, and other important information, the next step is to verify all system prerequisites. Collect details about the required hardware, software, operating systems, and network performance. Also, make sure coexistence scenarios between old and new Exchange servers are properly planned.
Hardware Requirements: If you plan to install Exchange Server 2010 or 2013 temporarily before moving to Exchange 2019, consider using a virtual environment. This approach makes it easier to deploy and remove servers as needed. For physical servers without virtualization support, you may need to purchase or rent a temporary server for the setup.
When setting up a new Exchange 2019 server, the requirements depend on the mailbox size and the number of users. For an organization with around 50 users, it is recommended to have at least 4 CPU cores, 32 GB of RAM, and assign approximately a quarter of the storage for the paging file.
Suggested storage allocation:
- 100 GB for the operating system
- 50 GB for Exchange installation
- 100 GB for mailbox storage
- 20 GB for the paging file
Adjust these values according to your organization’s current data and storage needs.
Active Directory Cleanup: Before migration, it’s important to clean up your Active Directory to maintain its integrity and prevent issues during the process. Remove any unauthenticated or unused references from Exchange domains and related Active Directory objects. You can use ADSI Edit to delete these entries, but always ensure you have a complete backup before making any changes.
Maintain Exchange Database Health: Keeping your Exchange databases in good condition is essential for a successful migration. If the database is corrupted or unstable, it can cause data transfer errors or service interruptions. Use the ESEUTIL tool to check and repair database integrity, and make regular backups to safeguard against unexpected issues.
Consider Server Roles: Exchange 2010 includes the following five server roles:
- Client Access Server (CAS)
- Mailbox server
- Unified messaging server
- Edge Transport server
- Hub Transport server
For migration purposes, only the Mailbox Server and Client Access Server (CAS) roles are required. Review your current Exchange setup and evaluate how these roles and changes will impact the overall migration process. This assessment helps you plan the migration flow more effectively.
Managing Public Folders: Migrating public folders can be complex, particularly when moving to modern public folders in Exchange 2013 and later versions. While it’s possible to move public folder content to SharePoint, many organizations still choose to retain them within Exchange.
Modern public folders require careful handling throughout the migration process to ensure data consistency and folder permissions are maintained. With EdbMails Exchange Migration Tool, you can easily migrate public folder data to another Exchange server while preserving folder hierarchy and permissions.
Migration Roadmap: A well-defined migration roadmap is essential for completing the process efficiently. Each newer version of Exchange introduces specific steps and procedures for migrating from Exchange 2010 to 2013, 2016, or 2019. Review the latest Exchange Server migration checklist and assess how the changes affect your organization. This evaluation helps you plan and execute a clear, organized, and successful migration strategy.
Moving to Exchange 2013 / 2016 / 2019
Conduct a final verification by consolidating all your existing messaging system data and transferring it to the new version. Once you're confident that all the Exchange components are functioning well, you can proceed with making Exchange 2013 / 2016 / 2019 your active platform.
However, don't overlook the post-migration tasks. After successfully migrating to Exchange 2013 / 2016 / 2019 , it's crucial to ensure that everything, including mail flow and mailboxes, is operating smoothly.
Administrators can follow the steps mentioned above for a reliable and secure migration.
Replace the Exchange Migration checklist with the EdbMails Exchange Migration tool
Alternatively, you can bypass the complex manual migration process by utilizing a user-friendly and secure third-party software i.e. EdbMails Exchange Migration tool.
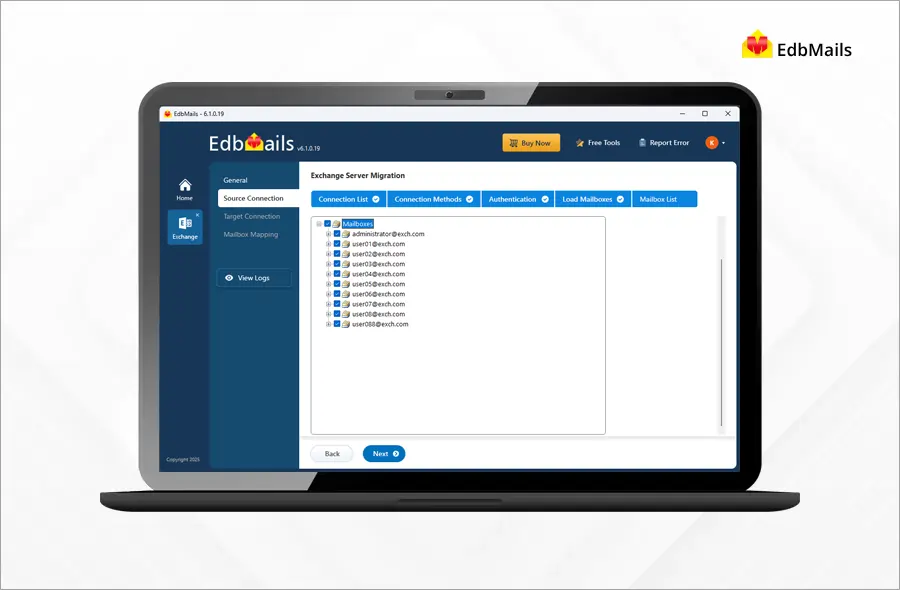
EdbMails is a reliable choice for various recovery and migration needs. You can start the migration operation within a few clicks. Simply connect to your source and the target Exchange servers, select the option to load the mailboxes, and configure settings. The software will automatically map the mailboxes between the source and target servers.
EdbMails facilitates seamless migration between different versions of Exchange and Office 365 within the same domain or across domains. It covers all the migration scenarios required for successful Exchange migration.
Steps to perform Exchange Migration using EdbMails
EdbMails is the best software for Exchange server migration. The software adeptly manages the migration of mailboxes, public folders, archive mailboxes, and shared mailboxes from the source Exchange server to different target servers such as live Exchange, Office 365, and Hosted Exchange servers. Furthermore, it supports migration in hybrid environments.
EdbMails allows direct migration of mailbox data between different Exchange servers, regardless of their versions. It facilitates data migration across Exchange 2019, Exchange 2016, Exchange 2010, Exchange 2013, and Exchange 2007.
Navigate through the below link for steps to perform the Exchange migration using EdbMails
- Exchange 2010 to 2019 migration
- Exchange 2013 to 2019 migration
- Exchange 2016 to 2019 migration
- Exchange 2010 to Office 365 migration
- Exchange 2013 to Office 365 migration
- Exchange 2016 to Office 365 migration
- Exchange 2019 to Office 365 migration
Benefits of using the EdbMails Exchange Migration tool
- EdbMails supports an incremental migration process to avoid duplicating items during successive migration operations to the target server.
- Utilize advanced include and exclude filters for selective mailbox items and folders.
- Enable the migration of Exchange Public folders and Shared Mailboxes.
- Data consistency with no downtime and data loss.
- Establish direct mailbox mapping between the source and target servers.
- Achieve migration to Exchange and Office 365 without requiring technical expertise.
- Ensures quick migrations with full data consistency between the source and target servers.
- Direct migration from any Exchange version (2010-2019) without coexistence issues.
- Compatible with all Windows server and client operating systems.