Exchange 2003 to Exchange 2010/2013/2016/2019 Migration
Migrate Exchange Server 2003, once a leading email and collaboration platform, has reached its end of life and is no longer supported by Microsoft. Continuing to operate on this legacy system exposes organizations to serious security risks, compliance challenges, compatibility issues with modern clients, and limited integration with newer technologies. For businesses that still store critical data in Exchange 2003, migrating mailboxes and public folders to a modern Exchange environment such as 2010, 2013, 2016, or 2019 is essential. Since direct migration from Exchange 2003 to newer versions is not natively supported, the most dependable approach is to extract data from offline EDB files and migrate it to a live Exchange server using EdbMails EDB to Exchange Migration Tool.
EdbMails provides a secure and seamless migration experience with granular control, allowing the transfer of mailboxes, attachments, calendars, contacts, and tasks while preserving folder hierarchy and permissions. It eliminates the need for complex, multi-step upgrades and enables a direct, downtime-free migration from Exchange 2003 to the desired Exchange version without any risk of data loss.
Prerequisites to migrate Exchange 2003 Server Data
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange server setup requirements
The following links help you to set up your target Exchange server. Learn more about the network, hardware, coexistence scenarios, and operating system requirements for installing Exchange.
- Step 2: Prepare your system with the following prerequisites for Exchange
Complete the following prerequisites for Active Directory, Windows Mailbox server, and Windows Edge Transport servers before installing the target Exchange server.
- Step 3: Set up the target Exchange server for migration
Given below is a list of key points for installing and preparing the Exchange server for migration.
- Prepare the AD and domains
- Before installing Exchange Server, you need to prepare your Active Directory forest and its domains for the new version of Exchange.
- If you have a separate team to manage the Active Directory schema, you need to first extend the active directory schema, else proceed to the next step to prepare the Active Directory.
- Install Exchange server on your computer Ensure that you meet the server system requirements and prerequisites as outlined previously. Next, follow the link to install Exchange 2016 or install Exchange 2019 from the setup wizard based on which server you want to migrate to.
- Prepare a clean Exchange target environment Configuring Exchange Server for Mail Flow and Connectivity
- Create and configure a Send connector to send mail outside the Exchange organization.
- By default, Exchange automatically creates receive connectors for inbound mail flow when the mailbox server is installed. If you need to configure receive connectors manually, follow the steps in the link.
- Add accepted domains to allow recipients to send and receive email from another domain.
- Configure the default email address policy to add the accepted domain to every recipient in the organization.
- Configure external URLs (domains) on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internet (outside the organization’s network).
- Configure internal URLs on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internal network.
- Configure SSL certificates from a third-party certificate authority for services such as Outlook Anywhere and Exchange ActiveSync.
- Verify the Exchange server installation by running the command Get-ExchangeServer on the Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
- Create mailboxes and Public folders on the Exchange server
Before you migrate your mail data, ensure that you create mailboxes on the target server and assign suitable licenses to them. For the Public folder migration, create mail-enabled Public folders.
- Assign management roles to the admin account
- Application Impersonation
- View-Only Recipients
- View-Only Configuration
- Also assign the Organization Management role group to the admin user. It is an elevated permission that is required for mailbox and Public folder migration.
- Verify the mailbox of the admin account
Check to see if the admin account that has been assigned management roles has a valid and non-hidden mailbox on the Exchange server.
- Configure the throttling and message-size limits
Change the EWS throttling and message size limits manually on the Exchange server by following the steps in the link.
- Prepare the AD and domains
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange server setup requirements
Steps to migrate Exchange 2003 EDB to Exchange 2019
Step 1: Download and install EdbMails
- Download and install EdbMails on your Windows system.
- Launch the EdbMails application and log in with your email and password, or click the Start Your Free Trial button
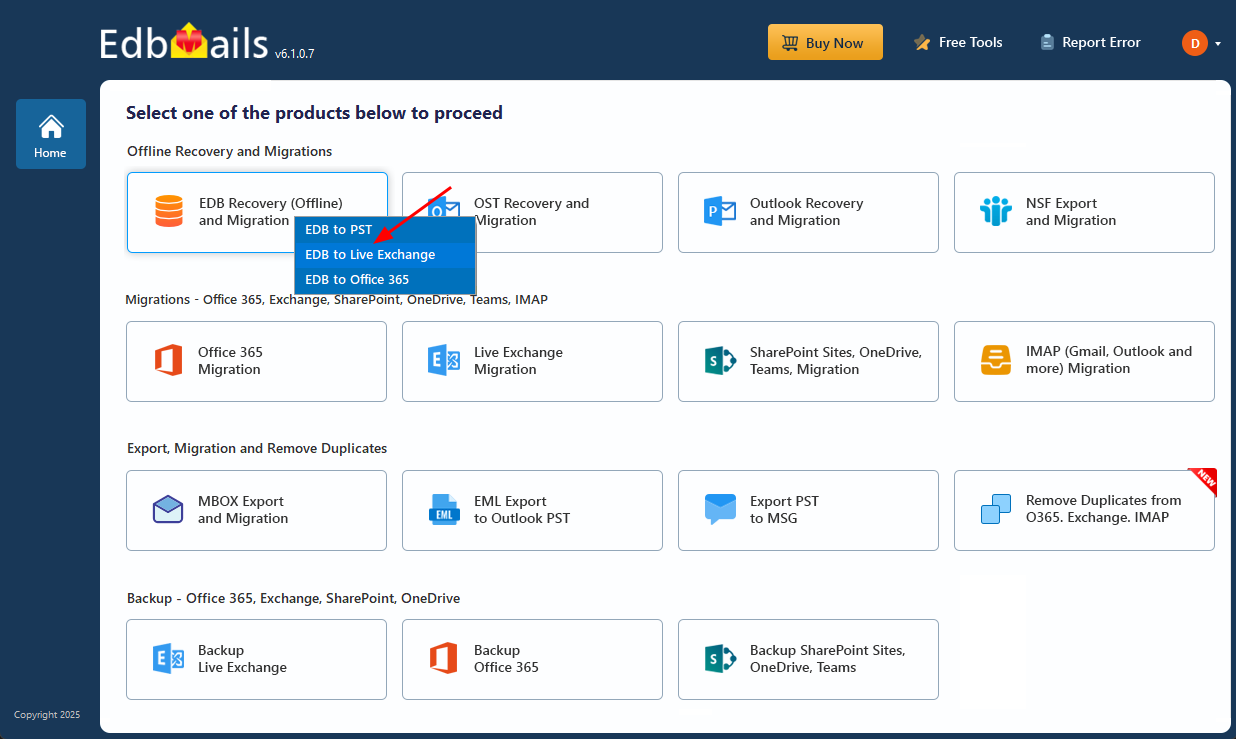
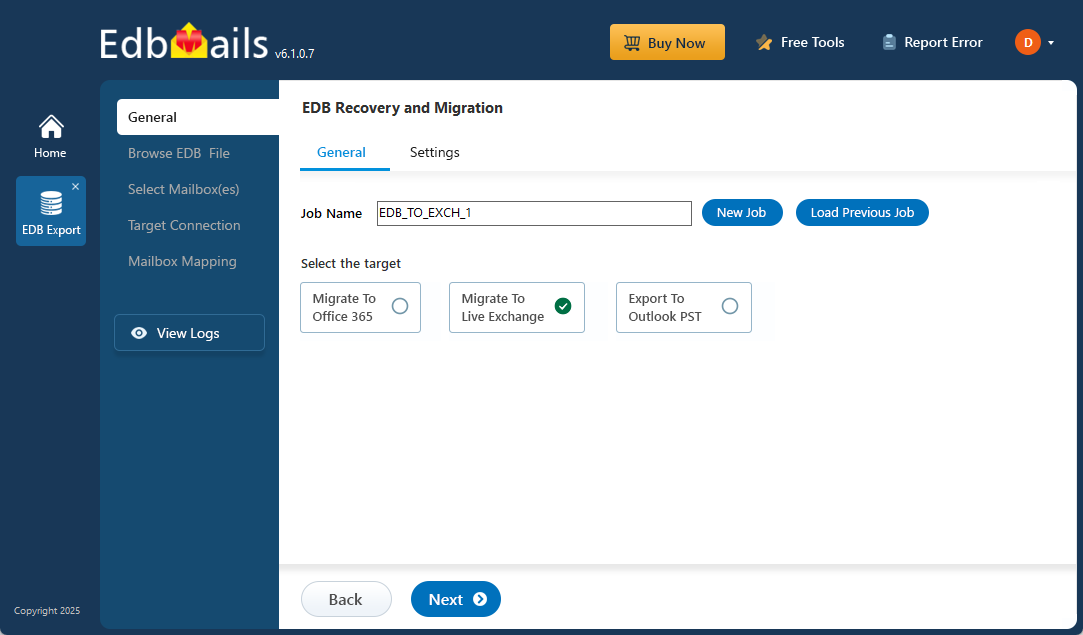
- Select ‘EDB Recovery (Offline) and Migration’ and choose 'EDB to Live Exchange'.
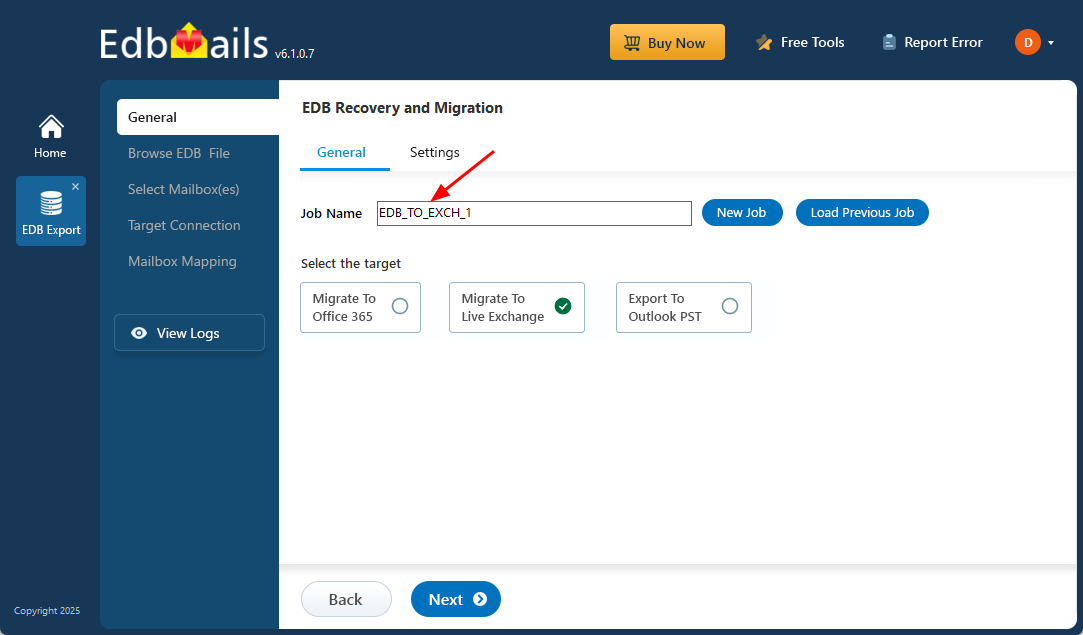
- Enter a job name by clicking the New Job button or use the default name.
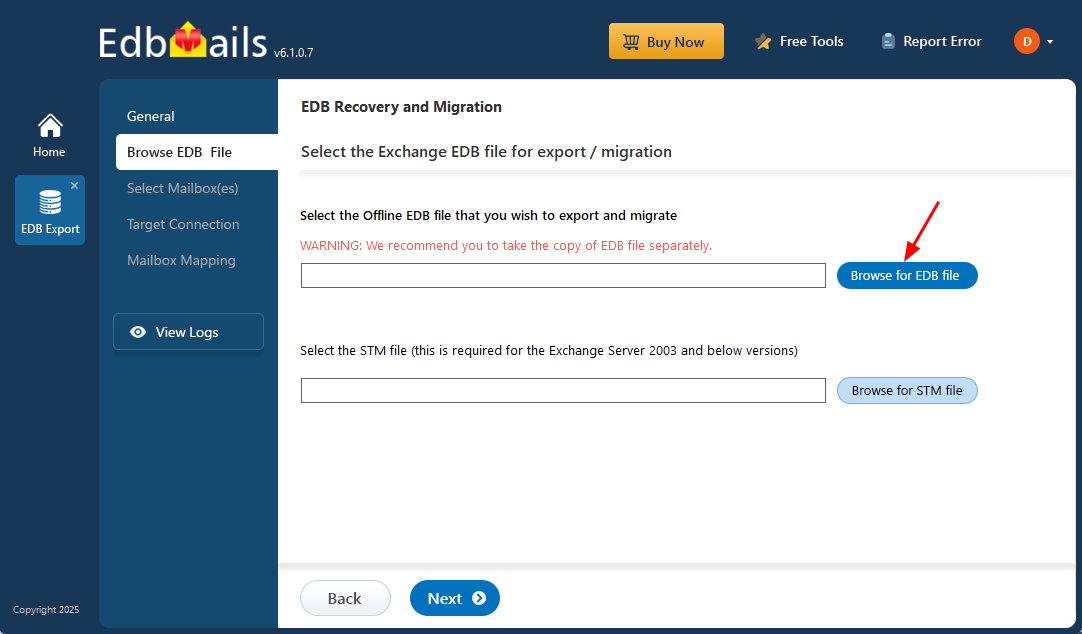
Step 2: Load the Offline Exchange 2003 EDB File
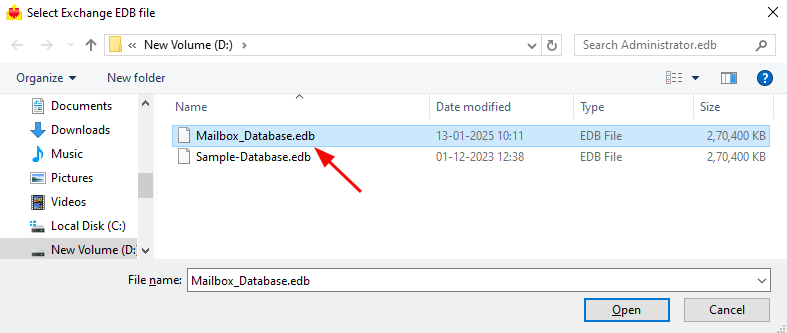
- Click ‘Browse for EDB file’ and select your offline EDB file.
- Select the offline EDB file from your computer drive, then click the ‘Next’ button to continue.
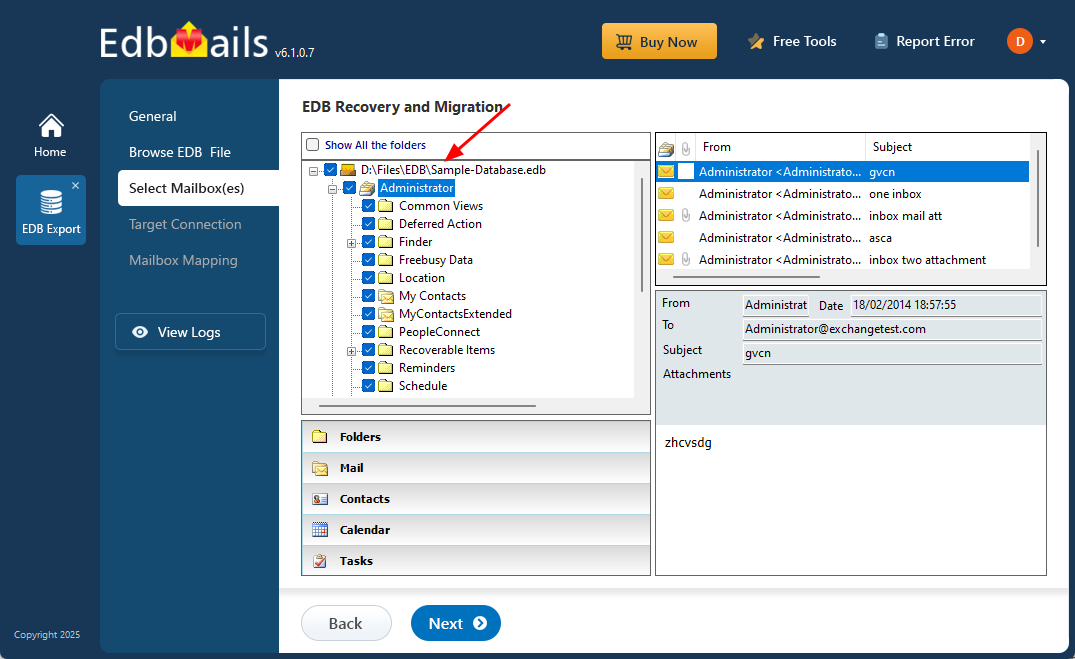
- EdbMails will scan and recover data from corrupted files if needed.
- Once scanned, preview the mailbox items and select the required mailboxes and folders to migrate.
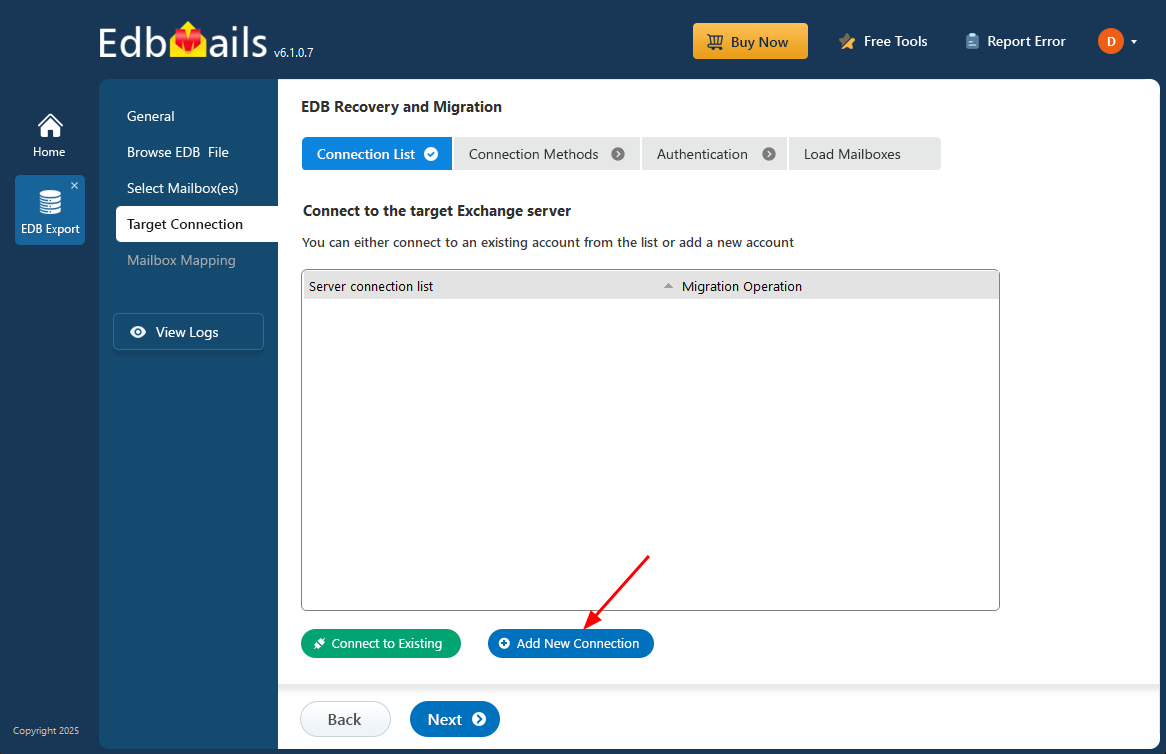
Step 3: Connect to the target Exchange Server 2019
- Click the ‘Add New Connection’ button to establish a new connection to the target Exchange server. To use a previous connection, select it from the connection list and click the ‘Connect to Existing’ button to proceed.
- Select the required connection options and click the ‘Next’ button.
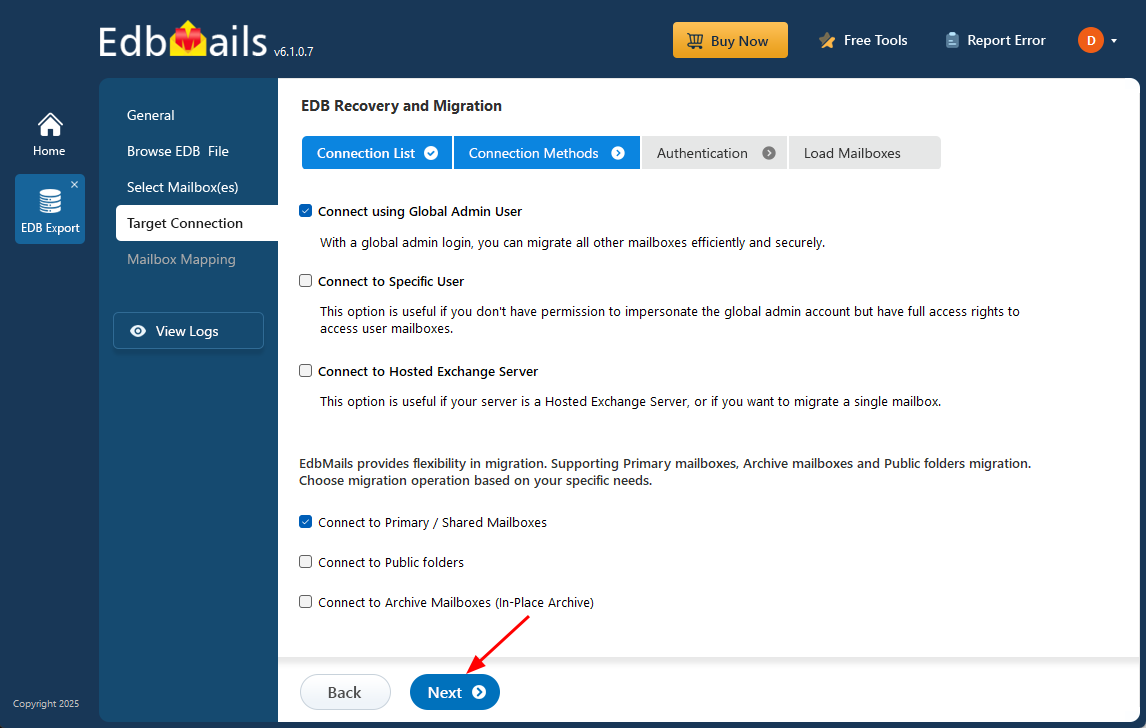
Different options to connect to Exchange server in EdbMails
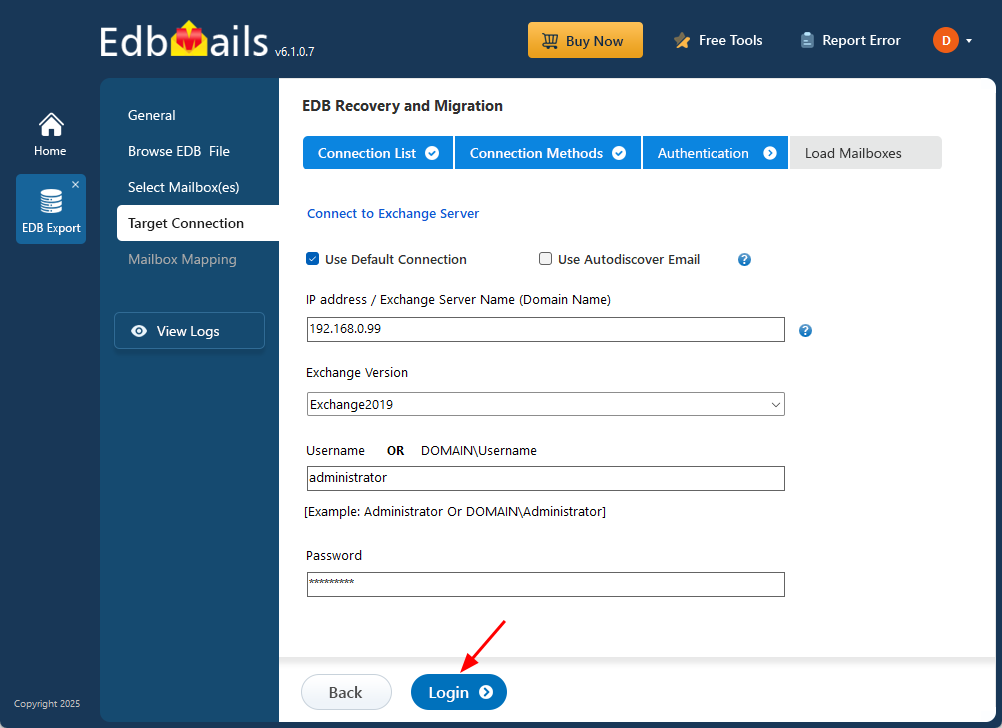
- Enter the target Exchange server details and click the ‘Login’ button
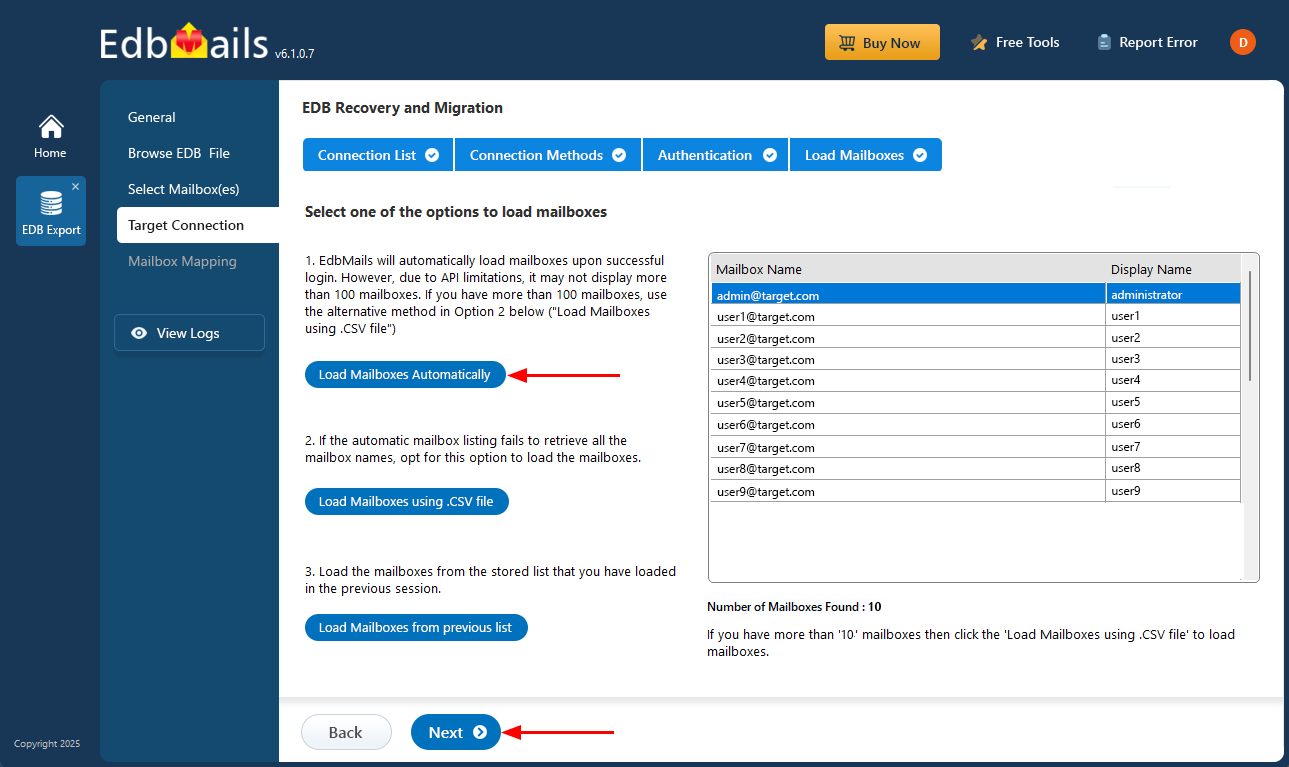
- Select one of the methods to load the mailboxes. You can also load mailboxes using CSV files.
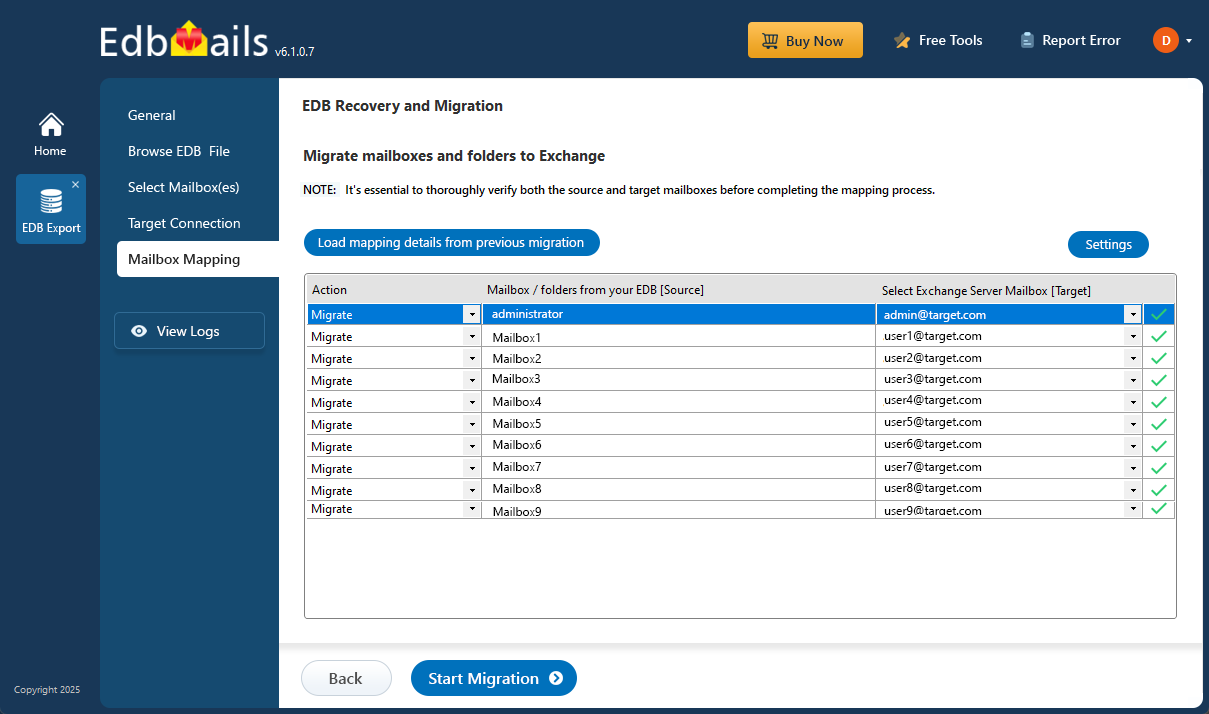
Step 4: Map source and target mailboxes
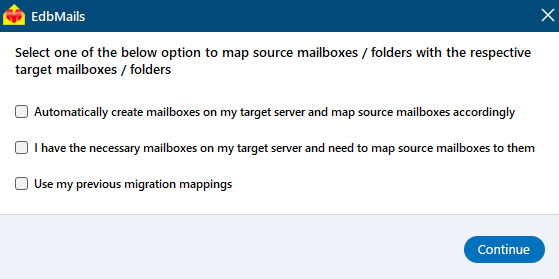
- Choose the required mailbox mapping option
- EdbMails automatically maps source mailboxes to target servers.
- You can adjust mappings manually and apply filters to migrate specific data based on date, subject, or folder, etc..
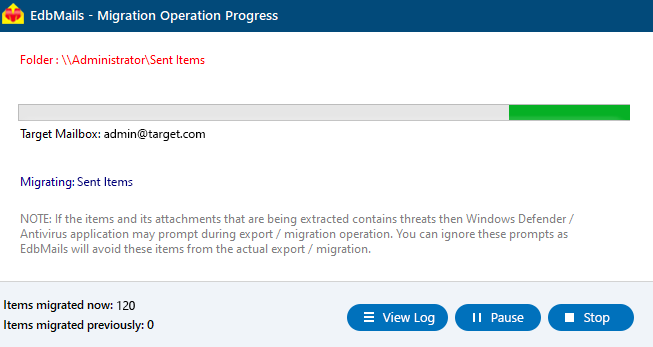
Step 5: Start the Exchange 2003 to Exchange 2019 migration
- Click ‘Start Migration’ to begin. Monitor progress in real time. After completion, review the migration log report to verify item counts and ensure all data has been successfully migrated.
Advantages of Migrating from Exchange 2003 to the Latest Exchange Server
Upgrading from Exchange 2003 to a modern Exchange environment brings significant improvements in performance, security, and manageability. Key advantages include:
1. Enhanced Security
The latest Exchange versions include advanced security protocols, encryption, and threat protection features that safeguard against modern cyberattacks and vulnerabilities.
2. Improved Reliability and Performance
The Latest Exchange servers, such as Exchange 2013, 2016, and 2019, deliver better stability, faster data processing, and higher uptime, ensuring smooth communication and reduced maintenance efforts.
3. Compliance and Data Protection
Newer versions are designed to meet current compliance standards such as GDPR and HIPAA, helping organizations maintain legal and regulatory requirements.
4. Better User Experience
Enhanced Outlook integration, web-based access through Outlook on the Web (OWA), and improved mobile synchronization make email management more convenient for users.
5. Simplified Administration
The Exchange admin center (EAC) and PowerShell management tools simplify mailbox administration, monitoring, and reporting tasks.
6. Larger Mailbox Support and Storage Efficiency
Latest Exchange servers support larger mailboxes and offer better database management, backup, and recovery options.
7. Long-Term Support and Updates
Upgrading ensures continued support from Microsoft, access to regular updates, bug fixes, and new feature enhancements.