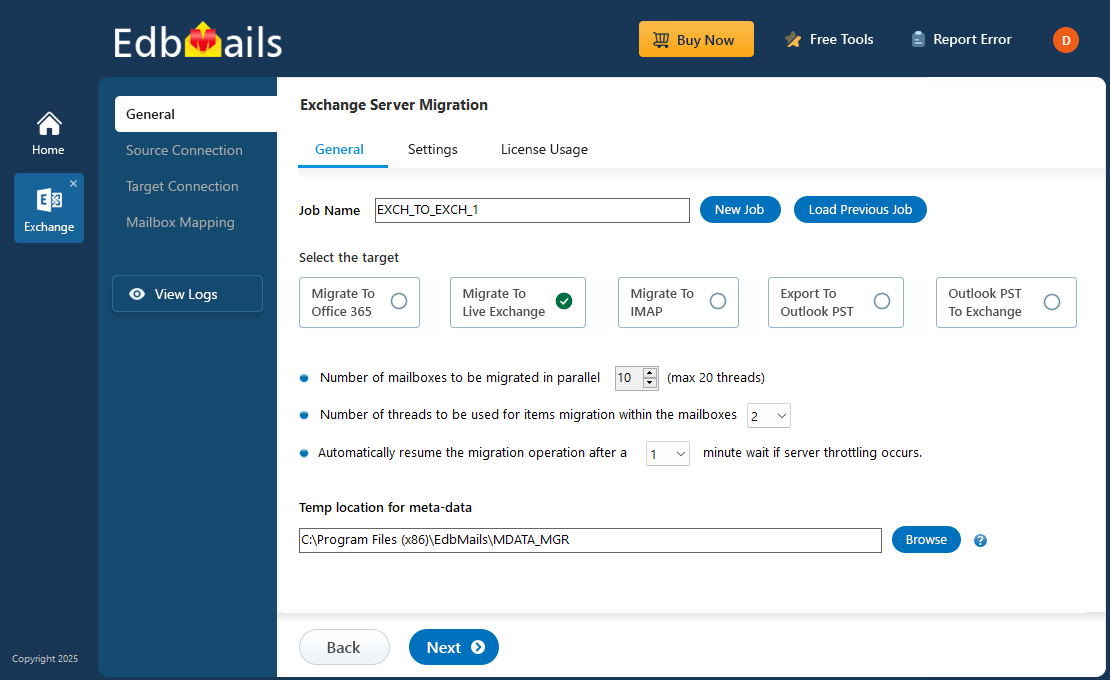
Exchange to Exchange Migration
Exchange to Exchange migration is an important process for organizations looking to migrate user mailboxes, public folders and other data between Microsoft Exchange servers. This migration enables system upgrades, resource consolidation, and enhanced organizational efficiency by streamlining data access and management. Achieving a smooth migration requires careful planning to ensure compatibility, preserve data integrity, and minimize downtime.
EdbMails Exchange migration stands out as the perfect solution designed to facilitate migration between Exchange servers. With its user-friendly interface and powerful capabilities, EdbMails simplifies the migration of mailboxes while eliminating the need for advanced technical skills or complex scripting. The software supports all Exchange server versions such as Exchange 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010 and 2007, ensuring that organizations can easily migrate to the most suitable environment without compatibility concerns. EdbMails automates essential tasks, streamlines migration workflows, and provides real-time monitoring and reporting features, allowing users to oversee the migration process with confidence. The software tool not only helps organizations achieve a seamless migration but also preserves the integrity of their data, making it an invaluable asset for any organization undergoing an Exchange to Exchange migration.
Simplified cross-domain and cross-forest migration
For organizations managing multiple domains or Active Directory (AD) forests, EdbMails provides a straightforward solution for complex cross-domain and cross-forest migrations. The software simplifies the typically challenging process into a quick, three-step method: installing the application, connecting to both source and target Exchange servers, and configuring a migration job via an intuitive, user-friendly interface. This streamlined approach eliminates the need for complex scripting or advanced technical skills, making the software accessible to users of all backgrounds. EdbMails handles intricate configurations in the background, ensuring smooth data transfer between domains and AD forests without extensive manual input, which saves time and minimizes the potential for errors. The result is a highly efficient and reliable migration experience, even for organizations with intricate, multi-domain setups.
Complete solution for Exchange to Exchange migration
EdbMails is a complete solution designed to handle all aspects of Exchange to Exchange migrations, supporting not only user mailboxes and public folders but also archive mailboxes (In-Place Archives). This feature enables smooth migration of archived data, offering flexibility to move data into archive mailboxes, primary mailboxes, or public folders in the new Exchange environment. By preserving both current and historical data, EdbMails ensures that users maintain access to their complete mailbox history post-migration, eliminating the need for multiple tools to handle different data types. This all-encompassing approach ensures that every element of your Exchange environment is fully transferred, allowing your organization to migrate smoothly to the new server with all essential data intact and readily accessible.
Essential features for effective migration
EdbMails Exchange to Exchange migration features include a suite of advanced tools designed to make migrations faster, more efficient, and precise. Its automatic mailbox mapping intelligently aligns source mailboxes with their corresponding targets, reducing manual work and ensuring accurate data transfer. Concurrent mailbox migration boosts performance by allowing multiple mailboxes to be migrated simultaneously, significantly cutting down migration time for large-scale projects.
Automatic mailbox creation feature allows the software to automatically create mailboxes directly on the destination Exchange server, eliminating the need for manual configurations. The incremental migration transfers only new or modified items after the initial migration, effectively managing data volumes and preventing duplication. EdbMails also supports cross-version compatibility, allowing smooth migrations across various Exchange environments without compatibility issues. Together, these high-performance features ensure minimal disruptions and help organizations maintain productivity throughout the migration process.
Key Benefits of EdbMails Exchange Migration:
EdbMails Exchange Migration offers several key advantages that make it a reliable solution for organizations upgrading or consolidating their Exchange environments.
- The software ensures zero downtime, allowing users to continue working during the migration without service interruptions.
- It automatically manages Exchange throttling limits and reconnects sessions in case of connection breaks, ensuring uninterrupted data transfer.
- All folder, mailbox, and delegation permissions are preserved, maintaining access consistency across mailboxes.
- EdbMails also supports the migration of public folders and archive mailboxes between Exchange servers, enabling complete data transfer.
- Administrators can monitor progress in real time through detailed migration logs and summary reports, ensuring full visibility and accountability.