IMAP to Exchange migration
Migrating from IMAP to Exchange Server is an important step for organizations aiming to improve email management, security, and collaboration within their environment. While IMAP offers basic access to emails, it lacks essential enterprise features such as shared mailboxes, centralized administration, integrated calendaring, contact synchronization, data loss prevention (DLP), and multi-layered security. Microsoft Exchange provides all these capabilities along with complete Active Directory integration, making it the ideal platform for businesses that require reliability, compliance, and advanced communication features.
However, performing an IMAP to Exchange migration can present challenges such as preserving folder structures, maintaining message metadata, accurate mailbox mapping, minimizing downtime, and transferring large mailboxes efficiently. These complexities make it essential to use a dependable migration solution that ensures data accuracy, security, and continuity.
EdbMails IMAP migration software simplifies the entire process with a script-free, automated, and user-friendly interface. It supports migrations to all Exchange Server versions (2007–2019) and handles user mailboxes, shared mailboxes, archive mailboxes, and public folders. With features like incremental migration, advanced filtering, parallel mailbox transfer, and an intuitive step-by-step wizard, EdbMails ensures zero data loss, complete consistency, and minimal disruption.
Whether migrating a few mailboxes or performing a large-scale migration, EdbMails IMAP to Exchange migration tool provides a secure, efficient, and reliable solution that helps businesses achieve seamless collaboration, enhanced productivity, and business continuity.
IMAP to Exchange migration plan
Planning is one of the most important steps before you begin migrating your IMAP data to Exchange. Prepare the target environment to avoid potential risks and data loss. Here is a brief checklist of points to consider before you migrate.
- Remove unused mailboxes, mail items and duplicate files from the source.
- Make an inventory of items before you make the move. These should include but are not limited to the following items.
- User accounts, email addresses and login credentials
- The source and target details, browser and operating systems used
- Network settings, DNS configurations, MX records, firewall settings
- Outlook settings and version you are using in your organization.
- Licensing plans on your current source server
- Active Directory configuration and other dependencies associated with it.
- List of data and permissions from the source server that you want to transfer.
- Determine the size of the data and number of mailboxes you want to migrate.
- Decide if you want to migrate everything at once (cutover migration) or plan to migrate your data in stages (staged migration).
- Decide if you plan to migrate your source mailboxes to Public folders, In-Place Archive or Shared mailboxes.
- Create user mailboxes on the target Exchange server and assign licenses to them.
- Ensure you have enough network capacity and bandwidth to migrate.
- Consider the throttling and message size limits for the migration.
- Communicate the migration plan and changes to your end users and stakeholders.
- Run a test migration from the source to the target environment before starting the full migration
- Start the actual migration, verify the endpoints and update the MX records.
- Check for correct mail flow and configure Outlook for all the users.
- Decommission unused apps and their settings post migration.
IMAP to Exchange migration prerequisites
On source IMAP server:
- Make sure you have the IMAP server hostname, port number, email address, and password ready.
See how to find IMAP server Host name
- To migrate multiple users, download the sample CSV file from the EdbMails application and update it with the IMAP server hostname, port number, email address, and password for each user's mailbox you wish to migrate.
- If you're migrating from Gmail, create an app password and use it in place of your regular password.
On target Exchange server:
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange server setup requirements.
Note: Exchange 2010 and 2013 reached the end of support . Therefore it is highly recommended that you migrate your mailbox data to Exchange 2016 or 2019.
If you are planning to migrate IMAP to a Hosted Exchange server, skip to ‘Create mailboxes and Public folders on the Exchange server’ in the following section.
The following links help you to set up your target Exchange server. Learn more about the network, hardware, coexistence scenarios, and operating system requirements for installing Exchange.
- Step 2: Prepare your system with the following prerequisites for Exchange
Complete the following prerequisites for Active Directory, Windows Mailbox server, and Windows Edge Transport servers before installing the target Exchange server.
Set up the target Exchange server for migration
Given below is a list of key points for installing and preparing the Exchange server for migration.
- Step 1: Prepare AD and domains
- Before installing the Exchange server you need to prepare your Active Directory forest and its domains for the new version of Exchange.
- If you have a separate team to manage the Active Directory schema, you need to first extend the active directory schema, else proceed to the next step to prepare the Active Directory.
- If you have multiple domains you need to additionally prepare the Active Directory domains.
- Step 2: Install Exchange server on your computer
Ensure that you meet the server system requirements and prerequisites as outlined previously. Next, follow the link to install Exchange 2016 or install Exchange 2019 from the setup wizard based on which server you want to migrate to.
- Step 3: Prepare a clean Exchange target environment
- Create and configure a Send connector to send mail outside the Exchange organization.
- By default, Exchange automatically creates receive connectors for inbound mail flow when the mailbox server is installed. If you must configure receive connectors manually, follow the steps in the link.
- Add accepted domains to allow recipients to send and receive email from another domain.
- Configure the default email address policy to add the accepted domain to every recipient in the organization.
- Configure external URLs (domains) on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internet (outside the organization’s network).
- Configure internal URLs on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internal network.
- Configure SSL certificates from a third-party certificate authority for services such as Outlook Anywhere and Exchange ActiveSync.
- Verify the Exchange server installation by running the command Get-ExchangeServer on the Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
- Step 4: Create mailboxes on target Exchange server
- Before migrating your mail data, ensure that mailboxes are created on the target server. You can use EdbMails to automatically create mailboxes on the target Exchange server. Alternatively, if you prefer to create mailboxes manually, refer to the link below:
- If you want to migrate to public folders, ensure that mail-enabled public folders are created and that the necessary permissions are assigned to the admin user.
Steps to create Public folder in Exchange server and assign permissions to the admin user.
- Step 5: Assign management roles to the admin account
- If you are using a global admin account to connect to the Exchange server, ensure to set impersonation rights to the global admin user.
- Step 6: Configure the throttling and message-size limits
Create custom throttling policies for EWS and configure message size limits manually on the Exchange server by following the steps in the link.
- Make sure you have the IMAP server hostname, port number, email address, and password ready.
Steps to migrate IMAP to Exchange server using EdbMails
Step 1: Download and install EdbMails IMAP migration tool
- To get started, Download and install EdbMails on your computer.
See EdbMails system requirements for IMAP to Exchange migration
- Open the application, then either log in with your email and password or click 'Start Your Free Trial' to begin
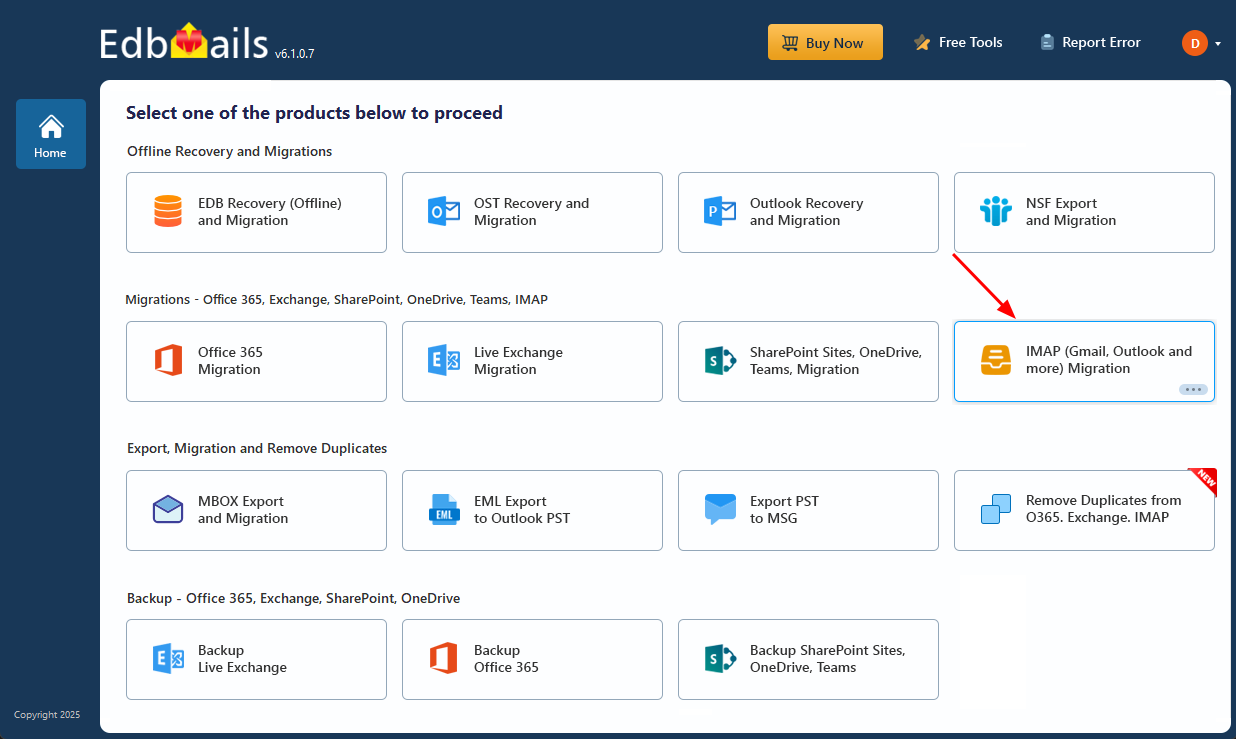
- Select the option ‘IMAP (Gmail, Outlook & more) Migration’
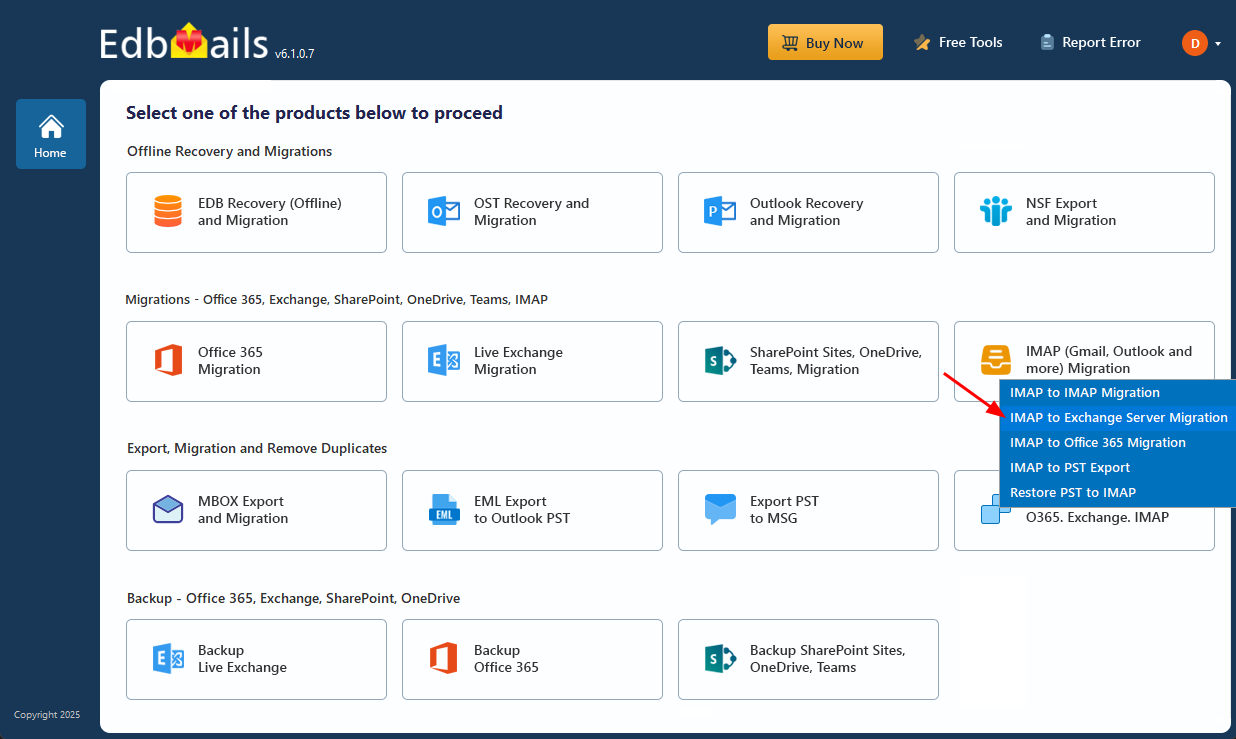
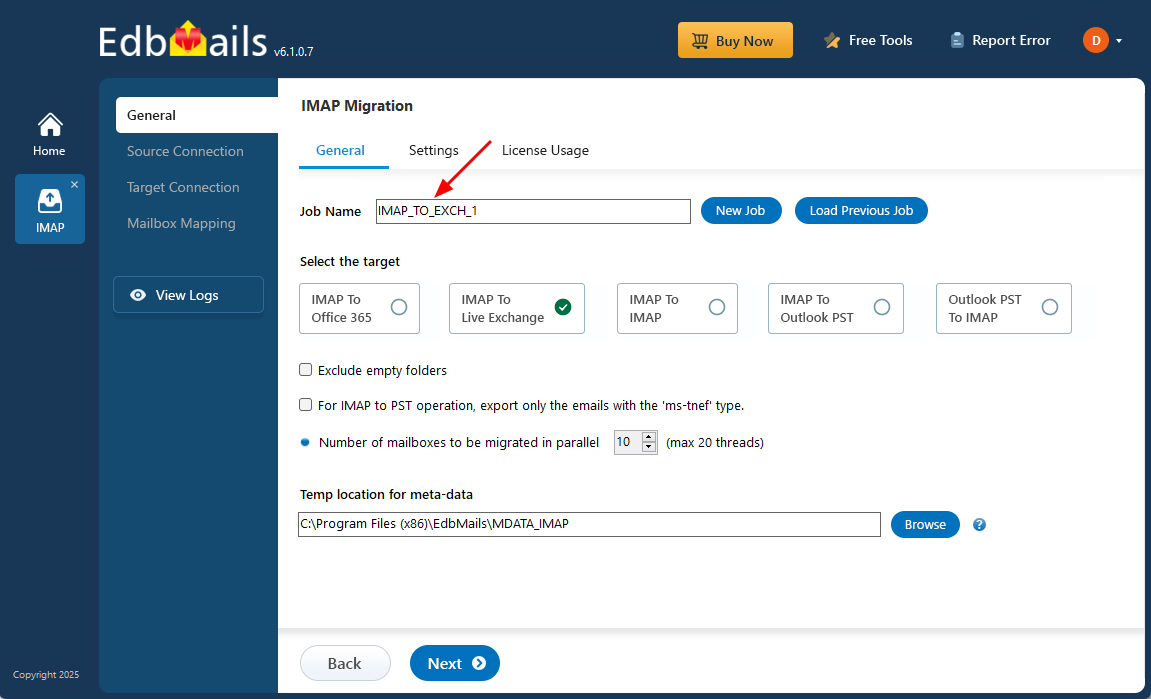
- Select ‘IMAP to Exchange Server Migration’.
- You can either proceed with the default job name provided or click on ‘New Job’ to customize the job name according to your preference before continuing with the process.
- To get started, Download and install EdbMails on your computer.
Step 2: Connect to source IMAP server
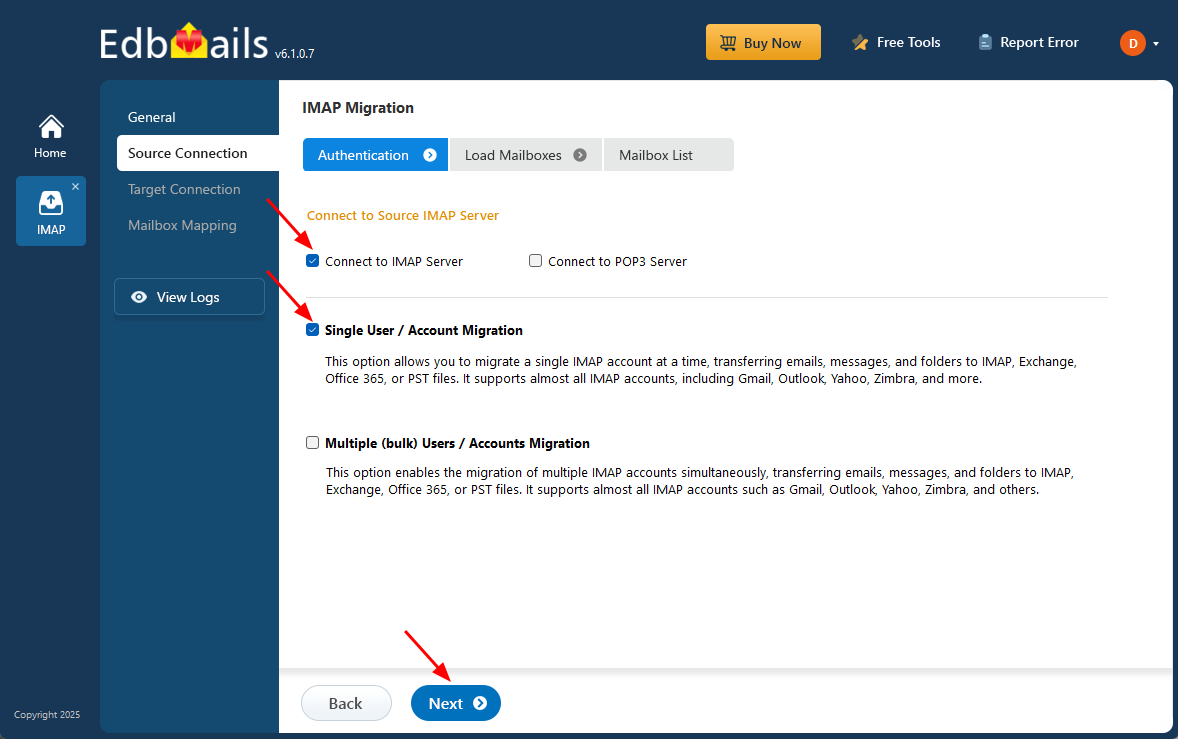
- To connect a single user account, select ‘Single User / Account Migration’ Then, choose the required protocol, such as ‘Connect to IMAP Server’ or ‘Connect to POP3 Server’ and click ‘Next’ to proceed.
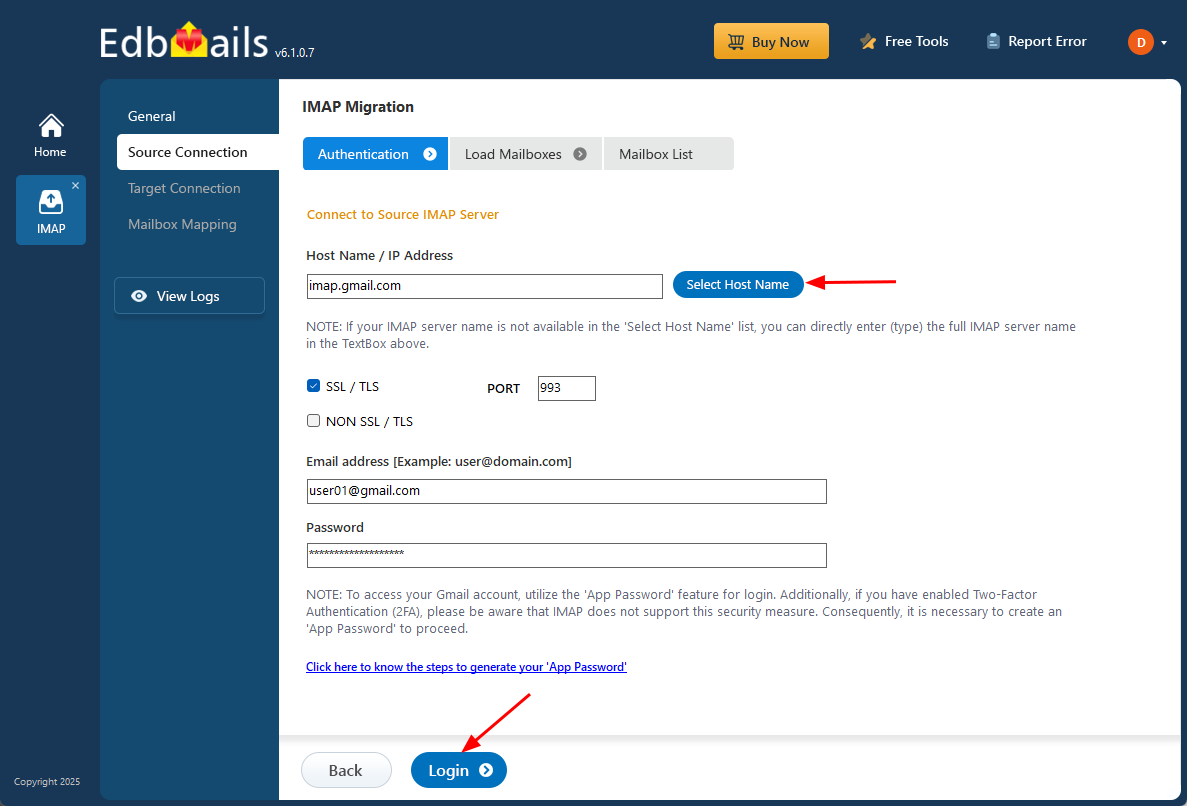
- For single-user login, select the appropriate IMAP host name from the list or enter it manually. Then, provide the email address and password. To connect to a Gmail account, ensure you create an app password and use it as the password.
- Click the ‘Login’ button.
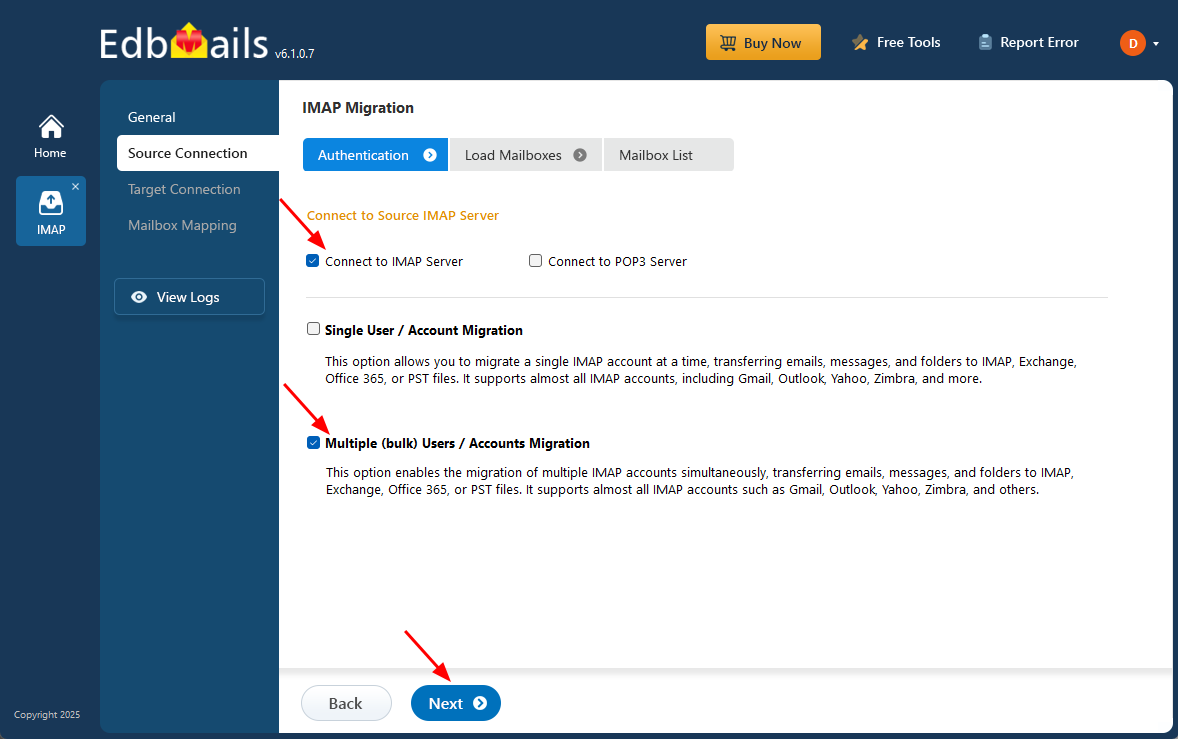
- For migrating multiple mailboxes, select ‘Multiple (Bulk) Users/Accounts Migration and click ‘Next’.
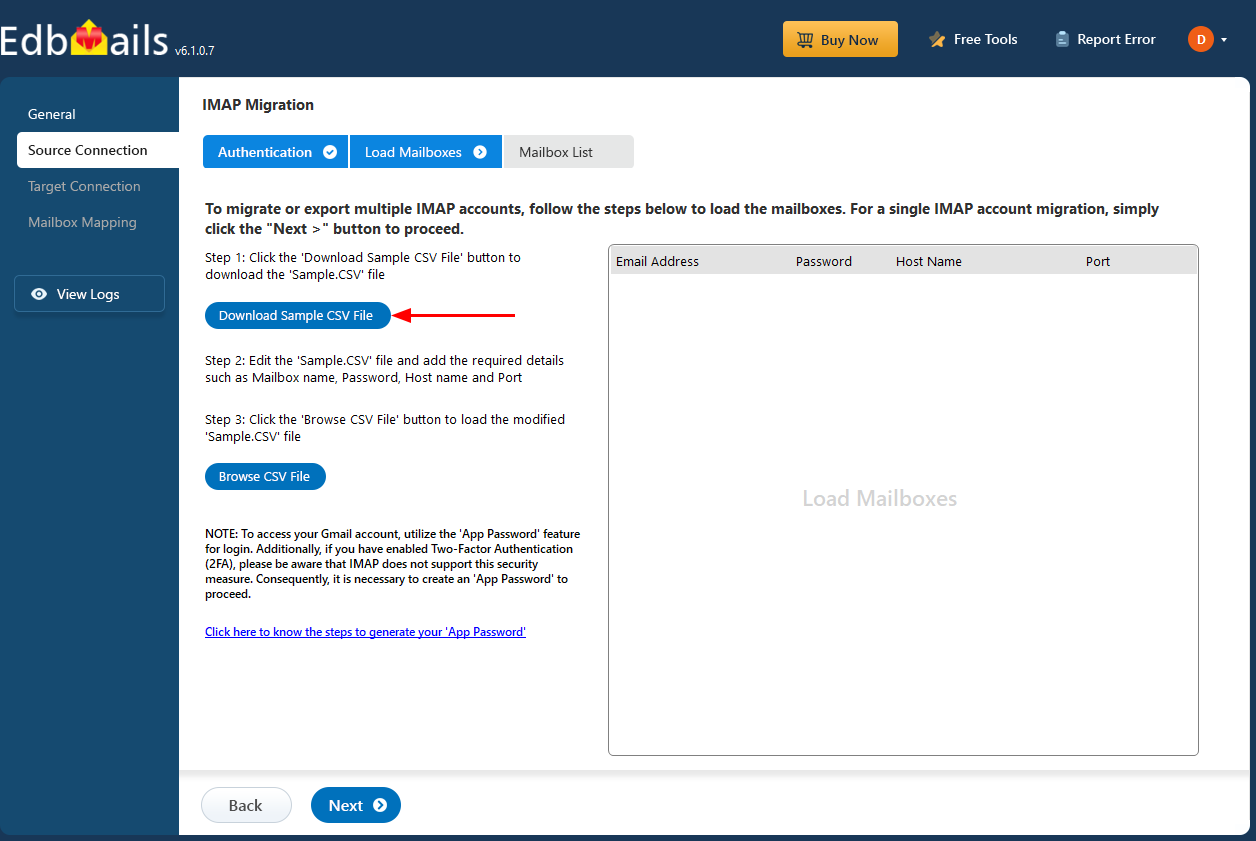
- Click ‘IMAP Migration CSV File’
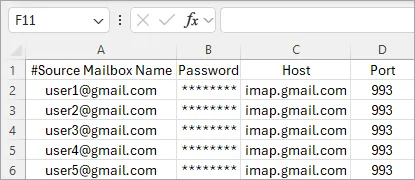
- Update the CSV file by entering the necessary details—like email address, password, host name, and port number—then save your changes.
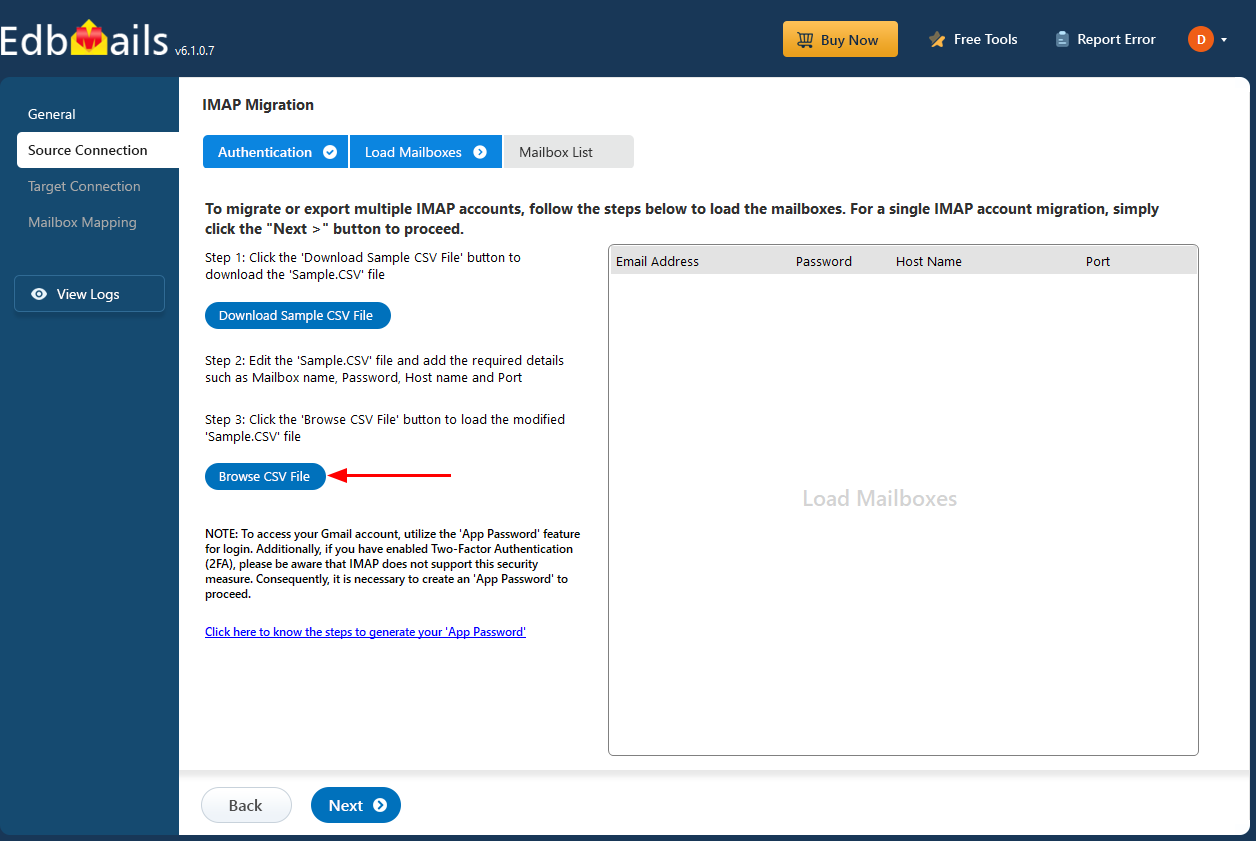
- Close the CSV file, click the 'Load Modified CSV File' button , select the modified CSV file.
- Verify the mailboxes, and click 'Next'.
Refer to the EdbMails detailed steps on connecting to single and multiple users during IMAP migration.
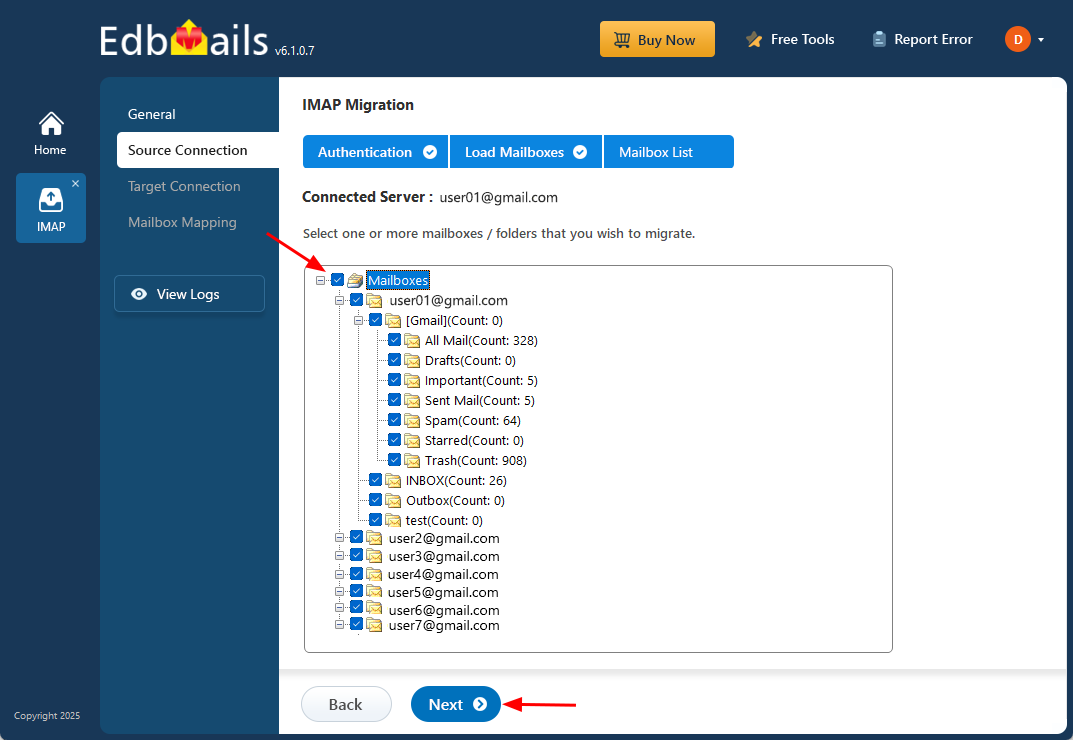
Step 3: Select source IMAP server mailboxes
- Choose the specific mailboxes or individual folders you want to migrate, and once your selection is complete, click ‘Next’ to proceed.
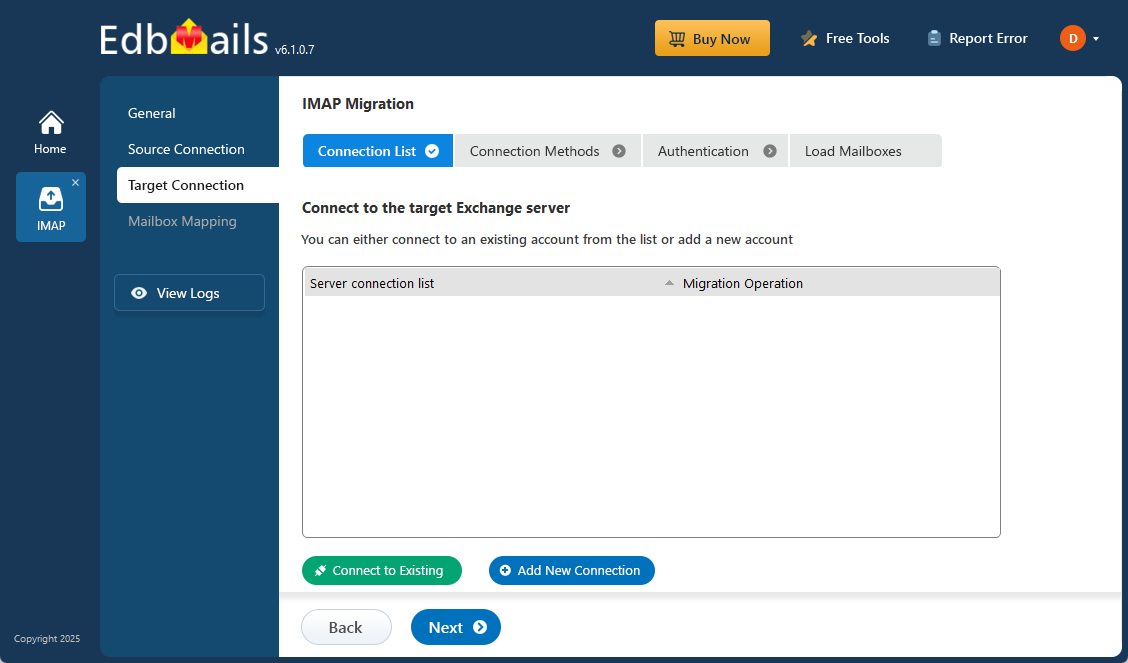
Step 4: Connect to target Exchange server
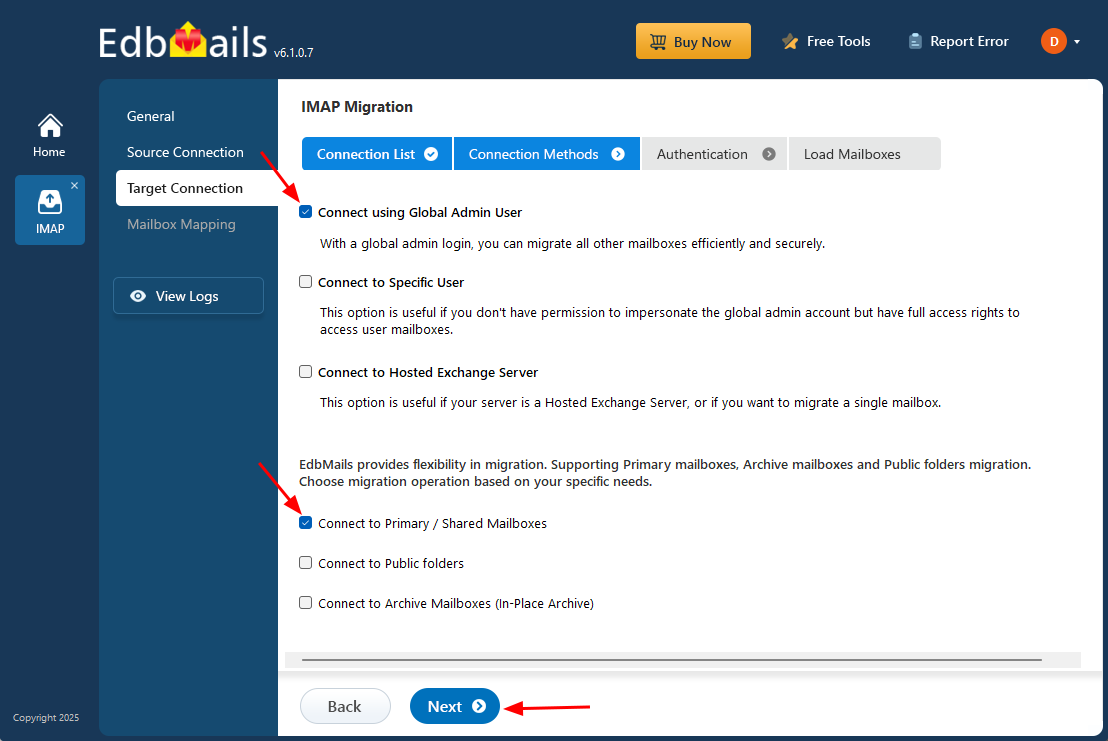
- Click the ‘Add New Connection’ button to establish a new connection to the target Exchange Server. To use the previous connection, select it from the connection list and click the 'Connect to Existing' button to proceed.
- Select the required connection options and click the ‘Next’ button.
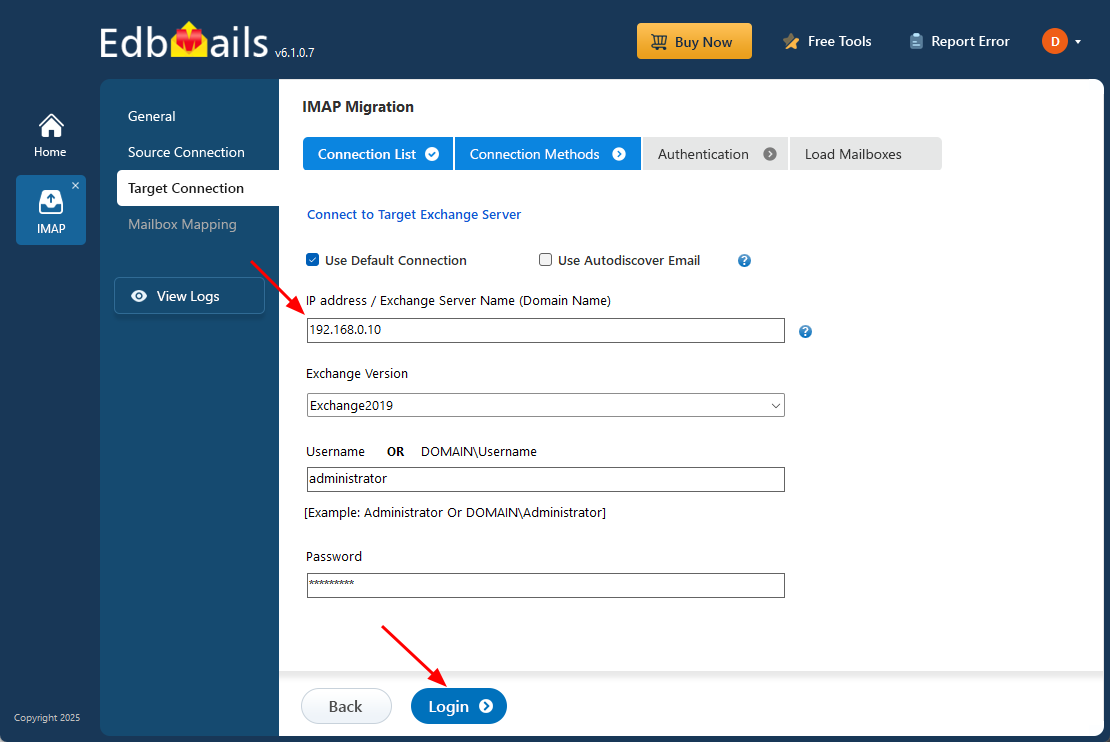
- Enter the target Exchange server details and click the ‘Login’ button
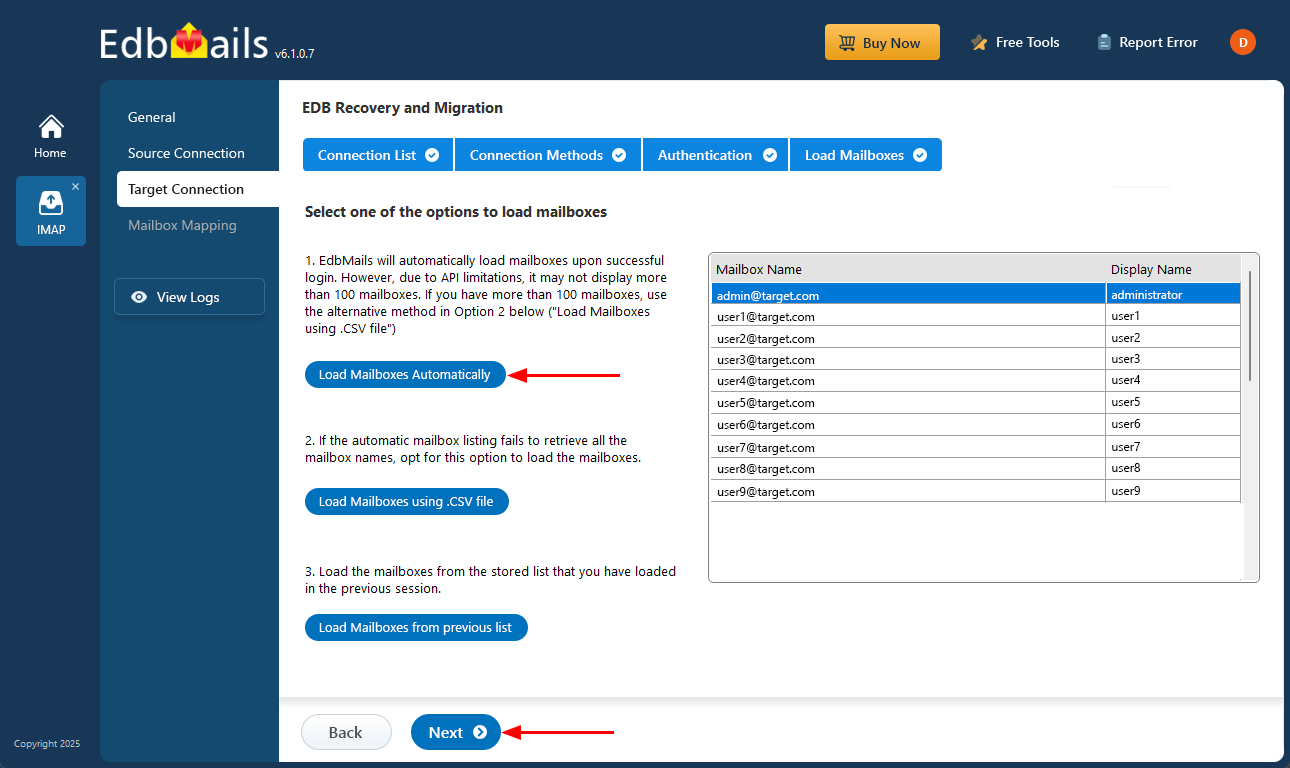
- EdbMails automatically loads mailboxes for a quick and easy setup. However, due to Microsoft API limitations, only up to 100 mailboxes may be displayed when using this method. To avoid this limitation, you can choose to load the mailboxes using a CSV file instead. Once you've selected your preferred method, click ‘Next’ to continue.
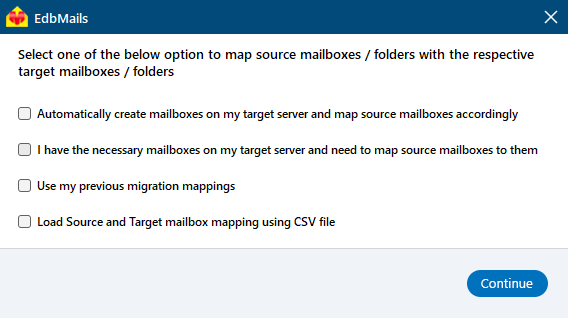
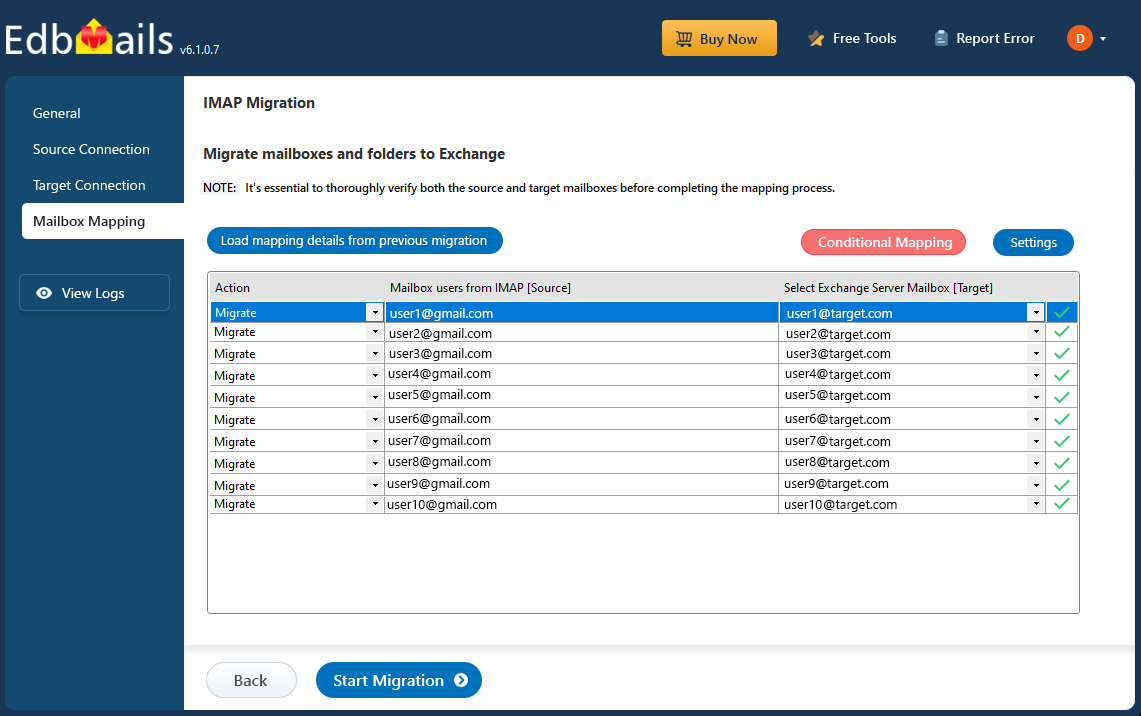
Step 5: IMAP to Exchange server mailbox mapping
- Choose the required mailbox mapping option
- EdbMails automatically creates target mailboxes in Exchange Server and maps source IMAP mailboxes and folders, making it easy to manage large-scale migrations.
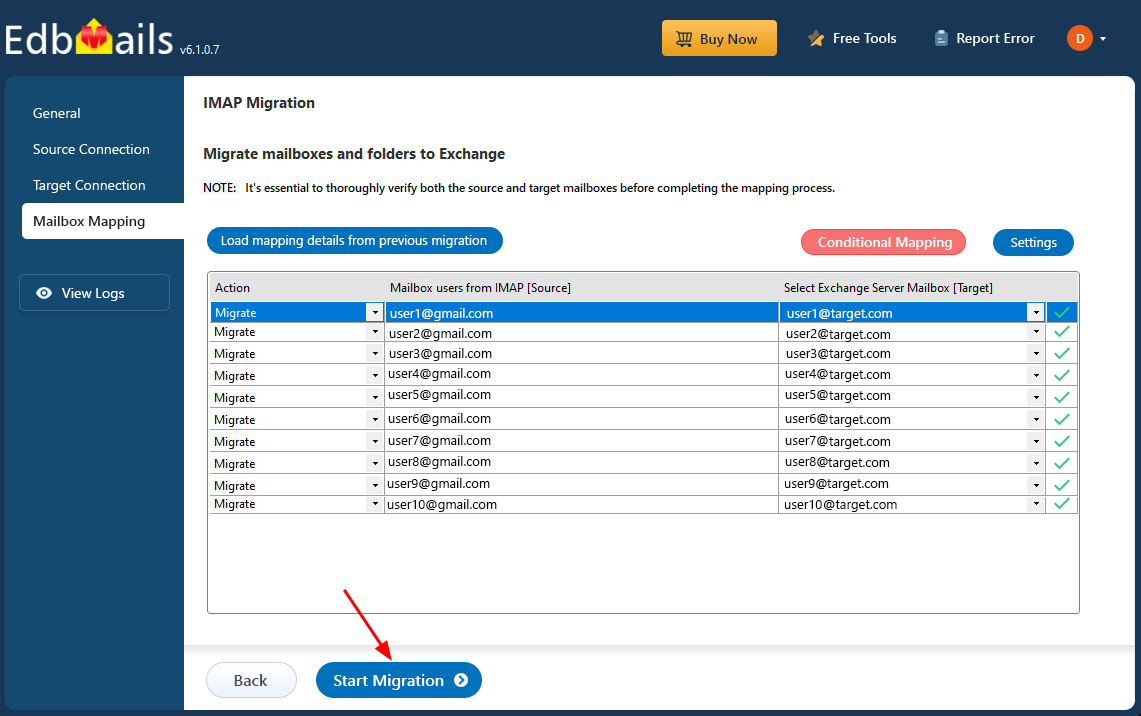
Step 6: Start IMAP to Exchange server migration operation
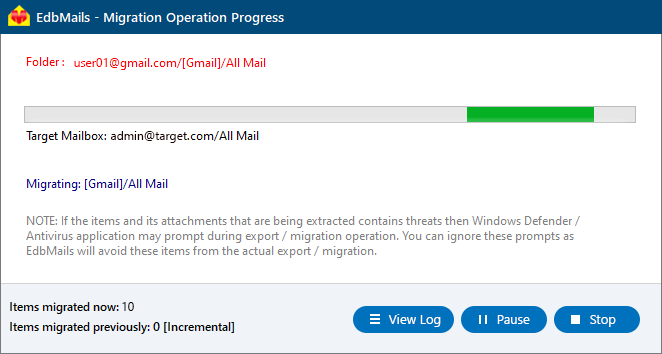
- After mapping the mailboxes, click the ‘Start Migration’ button to initiate the migration process
- Click the ‘View Log’ button to access the IMAP Export operation report, which provides a detailed summary of the export process, including the total number of items exported and the count of items exported from each folder.
IMAP to Exchange post migration tasks
- Step 1: Update DNS records (MX record) to point to the new server
Change the MX records to enable and receive email messages on the target server. In addition to this setup, configure the Autodiscover record to allow Outlook to connect to the migrated mailboxes.
- Step 2: Create a new Outlook profile for users in the new domain
Remove any previous instances of the email account you may have on Outlook to avoid conflicts with Exchange. Configure and recreate the Outlook profile for each user in your domain after you complete the migration.
- Step 1: Update DNS records (MX record) to point to the new server
IMAP to Exchange migration troubleshooting
Refer to the migration troubleshooting guide for solutions to common errors encountered during the process. For additional insights and detailed answers regarding EdbMails IMAP migration, visit the frequently asked questions section.
Benefits of EdbMails for IMAP to Exchange migration
- Delta migration
EdbMails' incremental (delta) migration feature ensures only new or modified data is transferred during migration, minimizing bandwidth usage and reducing migration time. This allows for efficient, partial migrations without duplicating existing data, ensuring seamless and optimized transitions.
- Automated mailbox mapping
EdbMails’ automated mailbox mapping feature eliminates the need for manual configuration, ensuring accurate mapping of IMAP to Exchange mailboxes. This reduces human error, enhances efficiency during the migration process while ensuring data consistency and integrity across all mailboxes.
- CSV-based mailbox import
EdbMails supports CSV-based mailbox imports, making it easy to migrate multiple mailboxes in bulk. By specifying mailbox details in a CSV file, users can streamline large-scale migrations, ensuring an efficient, organized, and scalable process—ideal for businesses with numerous email accounts.
- Cost-effective solution
EdbMails offers a cost-effective solution for IMAP to Exchange migration, combining powerful features in one platform. It provides exceptional value by eliminating the need for additional tools or consultants, ensuring businesses achieve a seamless migration at a fraction of the cost.
- Zero downtime
EdbMails guarantees zero downtime during the IMAP to Exchange migration process, ensuring uninterrupted access to email services. This approach allows businesses to continue their operations without experiencing email service disruptions. Users can maintain productivity and communication throughout the migration, ensuring seamless business continuity.