EdbMails Free EDB File Viewer to open EDB Files
When an Exchange Server goes down, unavailable, or is permanently decommissioned, accessing data stored in an EDB (Exchange Database) file can be difficult. Without suitable tools, viewing emails, contacts, and other mailbox items is often not possible. In such situations, EdbMails Free EDB File Viewer proves useful by allowing you to open and browse EDB files without requiring a live Exchange Server at no cost.
EdbMails EDB to PST Converter simplifies the process of accessing, recovering, and exporting mailbox data from offline, damaged, or dismounted Exchange EDB files. It helps restore emails after server failures, retrieve mailboxes from archived backups, or open data stored in inaccessible files without complexity. The recovered mailbox data can then be exported to PST format, making it readily available for use in Outlook.
This guide explains how to open an offline EDB file with EdbMails without requiring an Exchange Server. It allows you to preview all mailbox data such as emails, calendars, contacts, and attachments, and export only the information you need. Whether you’re performing a single recovery or managing multiple mailboxes, EdbMails ensures a smooth and efficient workflow.
What is an EDB file?
An .EDB file (Exchange Database file) is used by Microsoft Exchange Server to store all mailbox data and public folders. This file format is based on the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) and organizes data in a B-tree structure for efficient storage and retrieval. In earlier versions like Exchange 2003 and 2000, EDB files were typically named priv1.edb for private mailboxes and pub1.edb for public folders. With Exchange server 2007 and 2010, Microsoft replaced the priv1.edb with a file called Mailbox Database.edb. Starting from Exchange 2013, all mailbox data are stored in a single .edb file.
Where is the Exchange EDB file located?
Depending on the Exchange server version you’re using, an EDB file is commonly located under C:\Program Files\ in the directory where your Exchange server is installed.
In Exchange Server 2010, for instance, the EDB file is located in the following file path as shown below. Remember, that in Exchange 2010 there are two types of edb files i.e. the Mailbox Database file and the Public folder Database file (pub1.edb) which have specific paths.
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V14\Mailbox Database\Mailbox Database.edb
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V14\Public Folder Database\Public Folder Database.edb
In Exchange server 2019 for instance, the EDB is located under the following folder
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Mailbox\Database_name.edb
Common reasons to open an EDB file
Under normal conditions, Exchange Server first records changes in transaction log files before saving them to the main database. When all changes are properly saved, the database is in a Clean Shutdown state. But if the server crashes or log files are deleted before the data is written to the database, it causes a Dirty Shutdown error. In this state, the EDB file becomes unstable and can’t be accessed until it’s repaired.
When an Exchange database is in a Dirty Shutdown state, it fails to mount on the server, making all user mailboxes inaccessible. To regain access, it becomes essential to open and convert the EDB file to PST or other readable formats. If not addressed promptly, the database may suffer permanent corruption, leading to potential data loss. Below are some of the most common scenarios where opening and converting an EDB file becomes necessary.
- An EDB file can become corrupted due to a virus infection.
- Abrupt shutdown of Exchange server making the mailboxes inaccessible.
- When the Exchange server undergoes extended maintenance.
- To export Exchange emails to PST by a specific date for legal requirements.
- To recover and restore deleted Exchange mailboxes.
- To create a backup by extracting and converting the EDB.
- When the EDB file is in Dirty Shutdown and fails to mount to the server.
- When the log files go missing before they are committed to the database.
EdbMails Free EDB Viewer allows you to open and preview offline Exchange EDB files without needing an Exchange Server. It also helps you recover data from corrupted EDB files and export the contents to PST format. Also, you can directly migrate mailboxes from the EDB file to Office 365 or a live Exchange Server.
How to open and view an EDB file on Windows?
To access an EDB file on an Exchange server, you can use Microsoft's built-in command-line tool Eseutil to try mounting the database. However, if the EDB file is corrupted or fails to mount due to a Dirty Shutdown error, a more effective solution is to use EdbMails EDB to PST Converter. This tool allows you to open the EDB file and easily convert its mailboxes into Outlook PST format
Steps to open Exchange EDB file using free EDB file viewer
EdbMails EDB to PST Converter is an easy-to-use tool that helps you repair corrupted EDB files from various Exchange versions, including 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007, and 2003. Once the EDB files are repaired, you can convert them to PST format for use in Outlook. EdbMails also allows you to migrate mailboxes to another Exchange server or Office 365. Additionally, you can export mail items from the EDB file in formats such as HTML, MHT, and EML.
Step 1 : Download EdbMails EDB recovery software
- Download and install EdbMails on any computer. If you need to view, recover, or convert an EDB file, you can also install EdbMails on a system that doesn't have an Exchange server. The software is designed to recover offline and corrupted EDB files without the need for an Exchange server or Active Directory.
- Open the EdbMails application on your system.
- Sign in using your email address and password, then click ‘Login’. If you don’t have an account yet, select ‘Start Your Free Trial’ to get started.
Note: The Free Trial allows you to export all mailboxes, but limits the export to 30 items per folder. To remove this restriction and export all items, a valid license is required.
Click here to purchase the license from the EdbMails website.
Once the purchase is complete, close and relaunch the application, then log in using the same email address and password to activate your license.
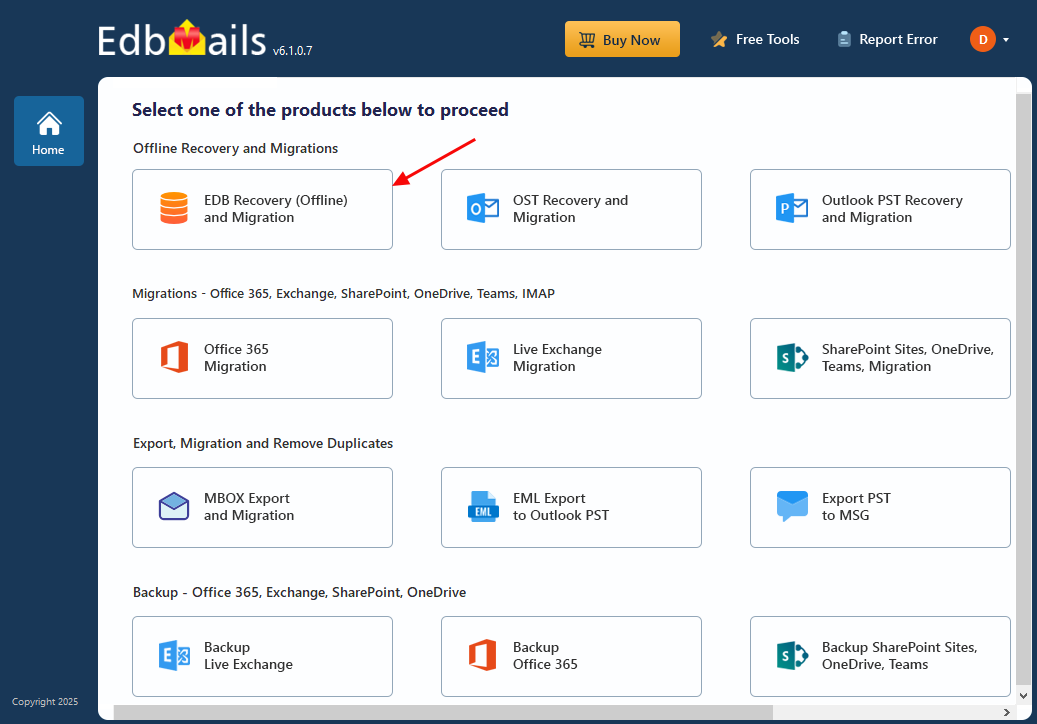
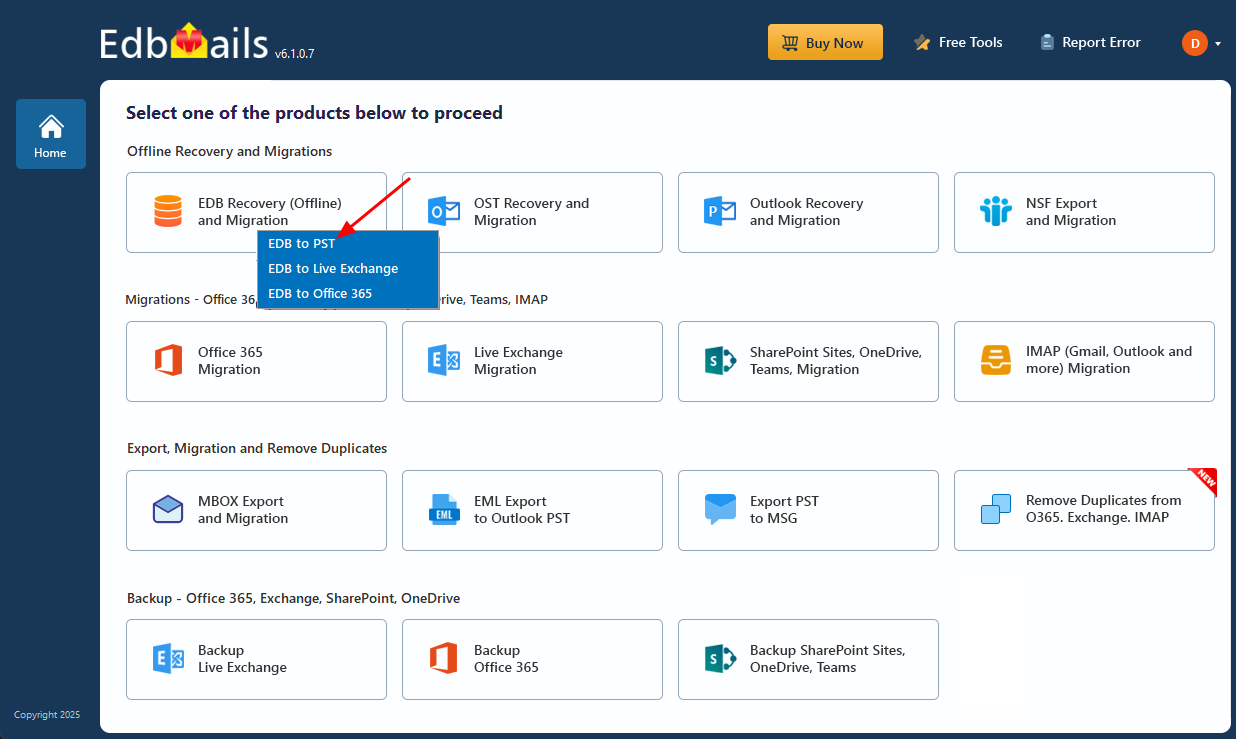
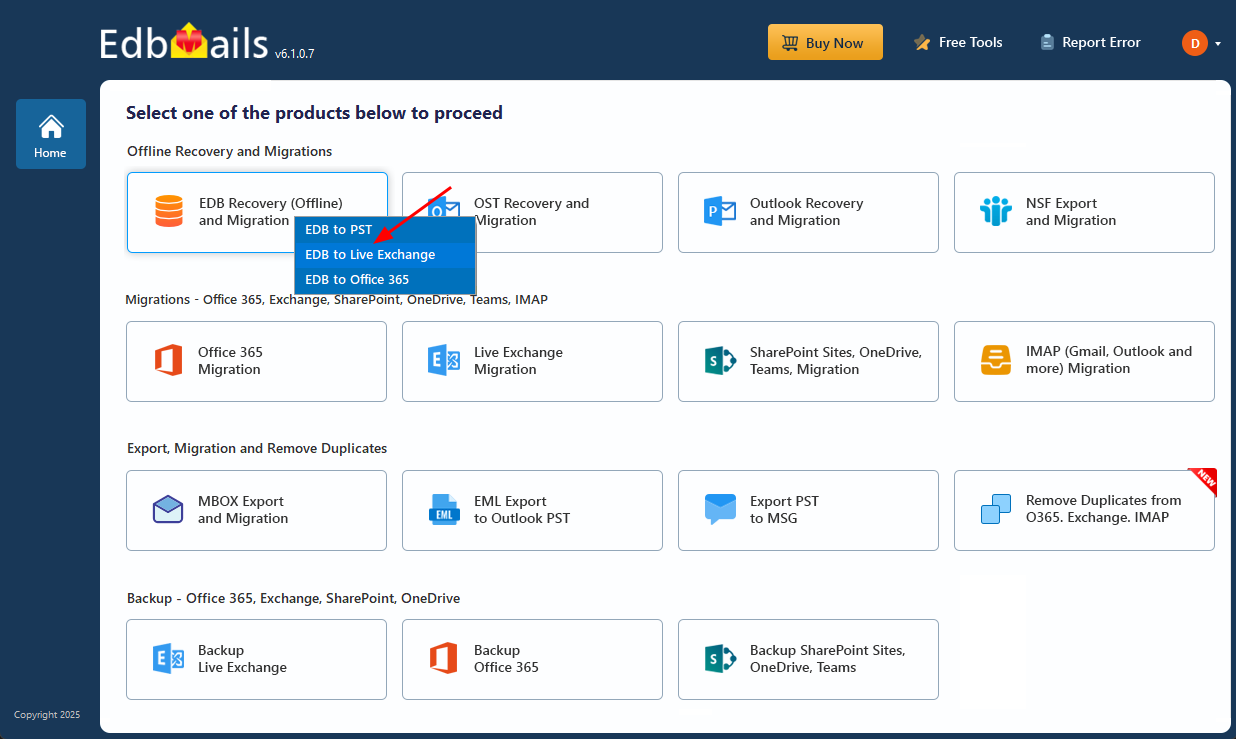
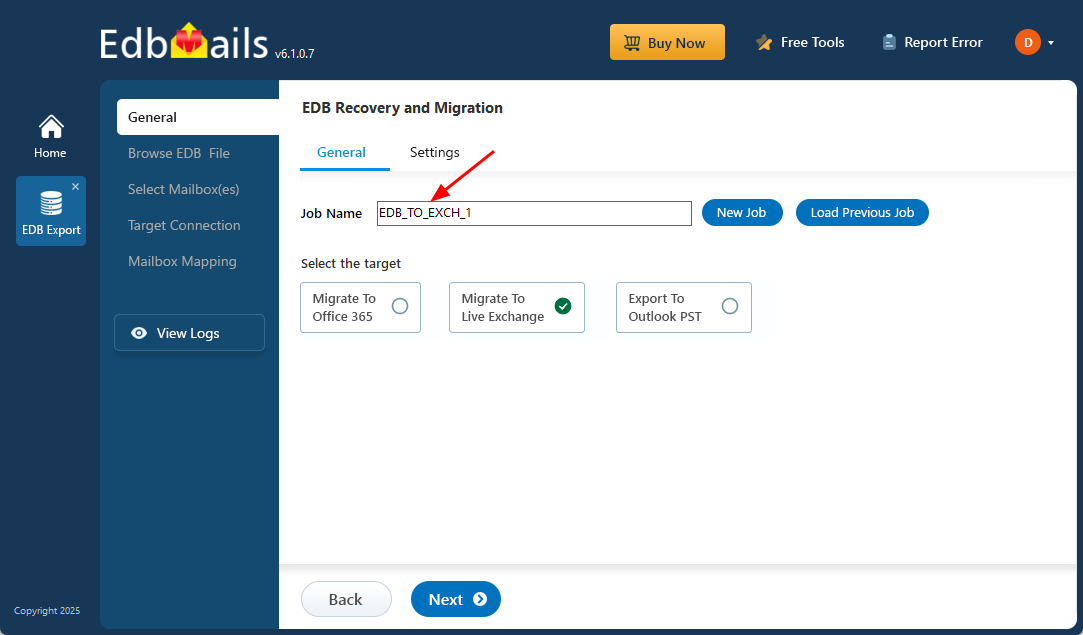
- From the product list, select ‘EDB Recovery (Offline) and Migration’
- Select ‘EDB to PST’
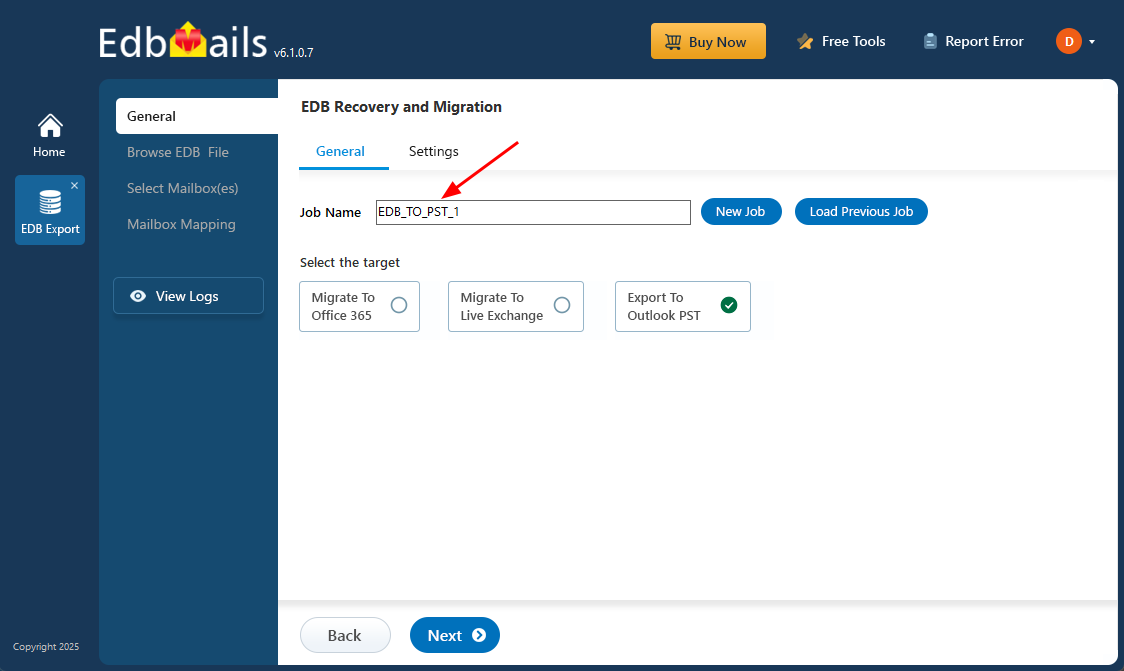
- You may retain the default job name or choose the 'New Job’‘ option to rename it.
- After that, click ‘Next’ to proceed further.
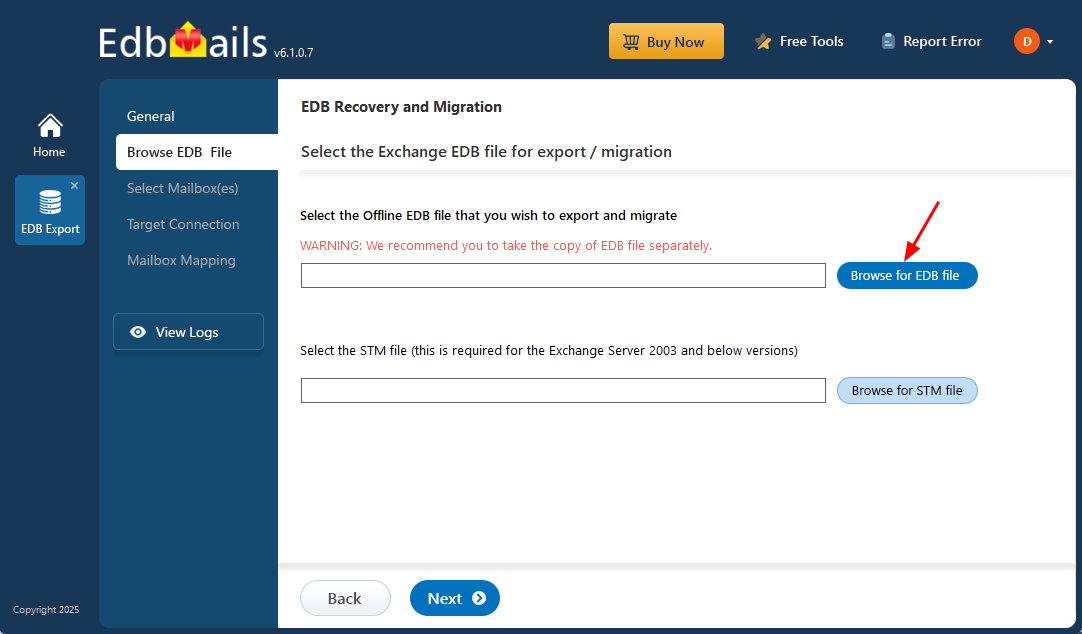
Step 2: Select the offline EDB file
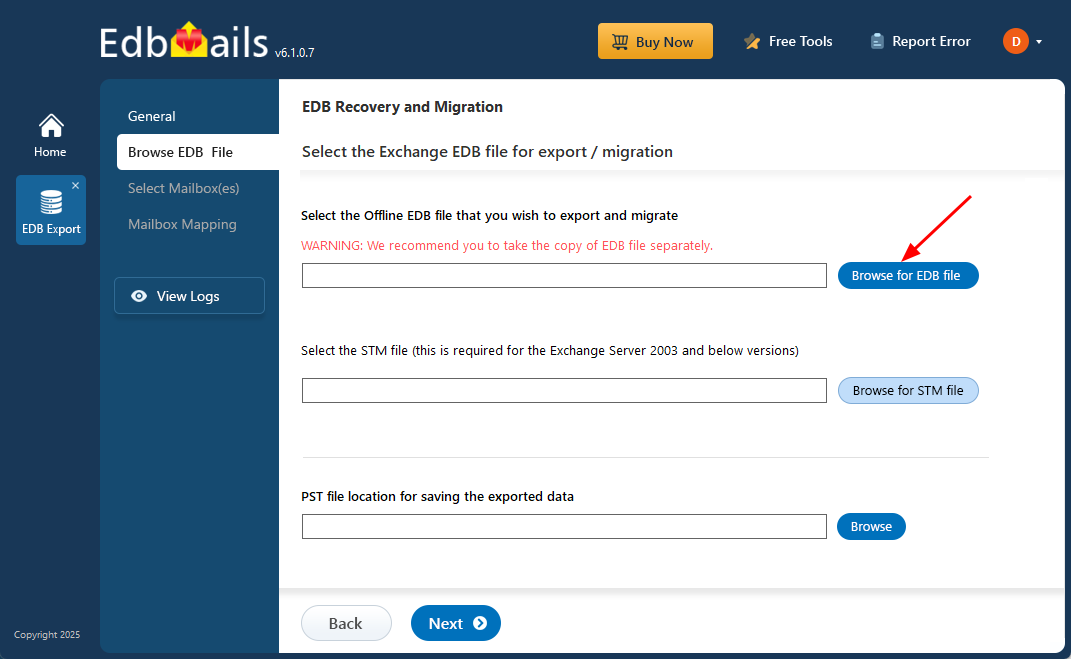
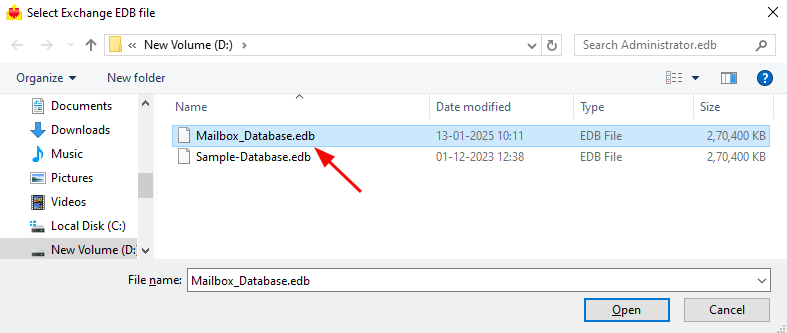
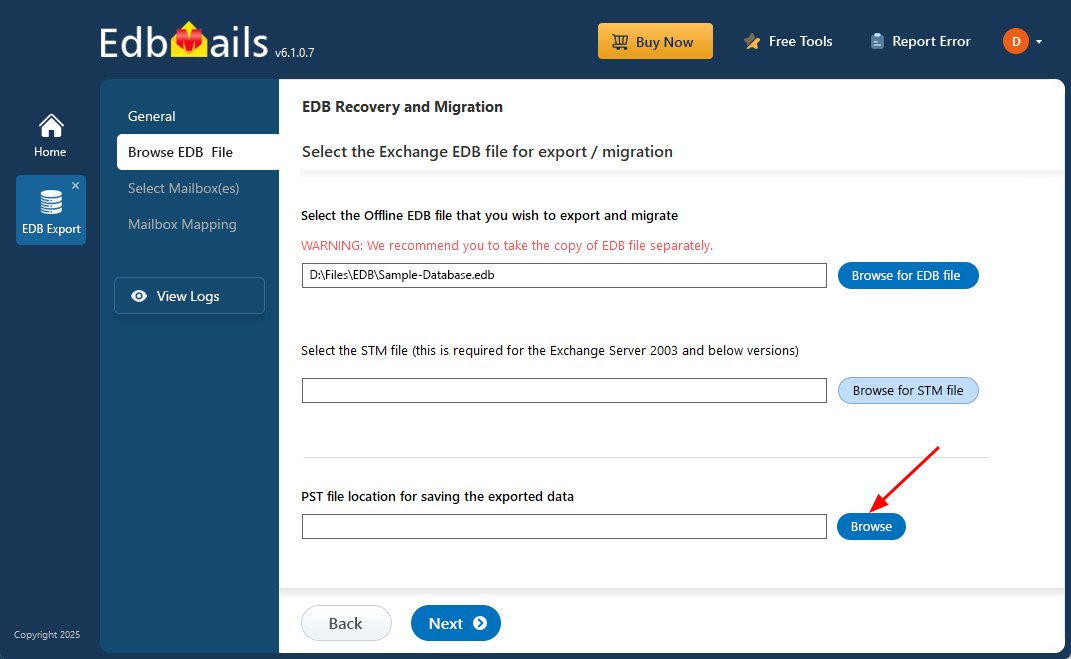
- Click ‘Browse for EDB file’
- Browse your local drive to select the offline Exchange EDB file, then click ‘Next’ to continue. If the file is stored on a shared network location, make sure you have the required access permissions before proceeding.
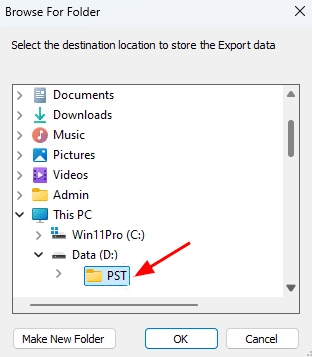
- Click the ‘Browse’ button.
- Select a destination folder for the exported PST files and ensure the drive has sufficient available space to store them successfully.
- EdbMails thoroughly scans EDB files and recovers mailbox data, even from virus-infected, orphaned, or corrupted EDB files of any type.
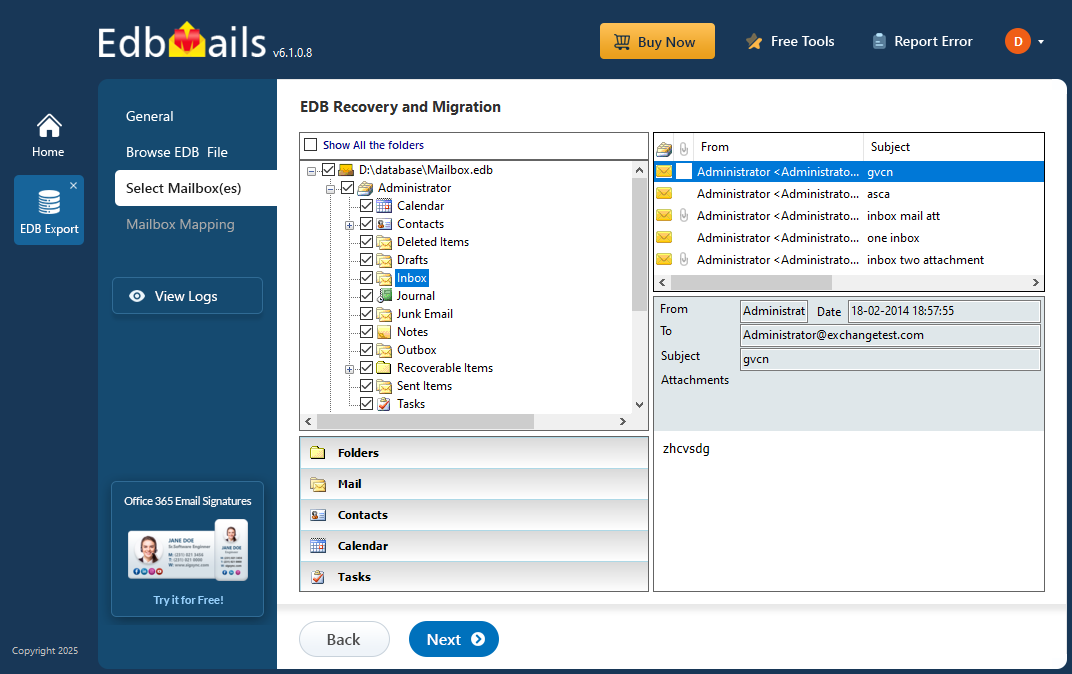
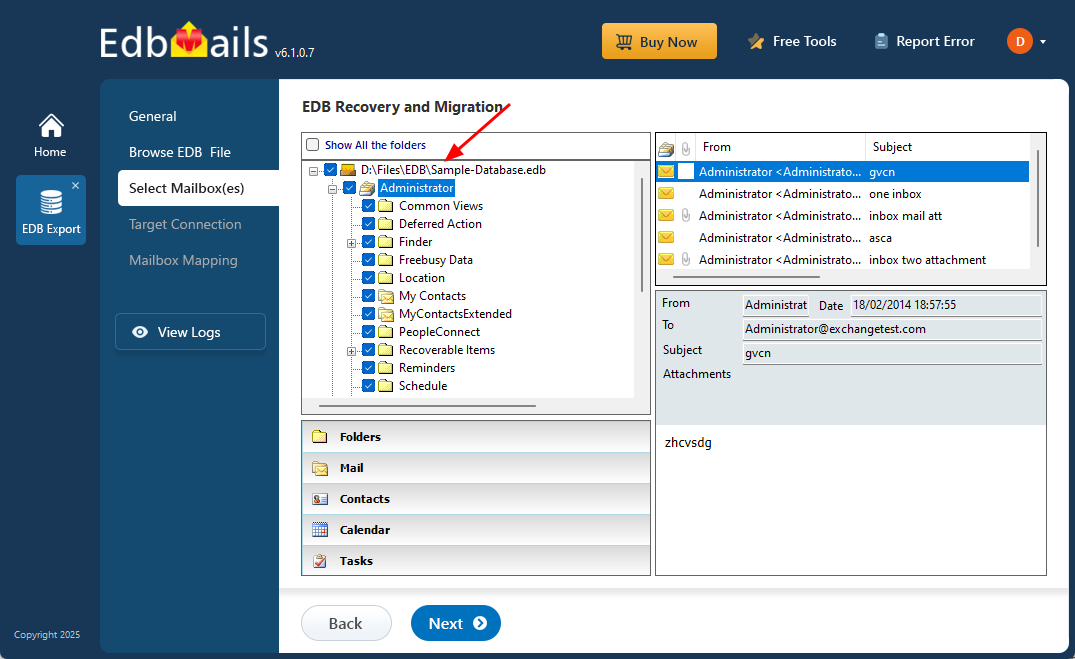
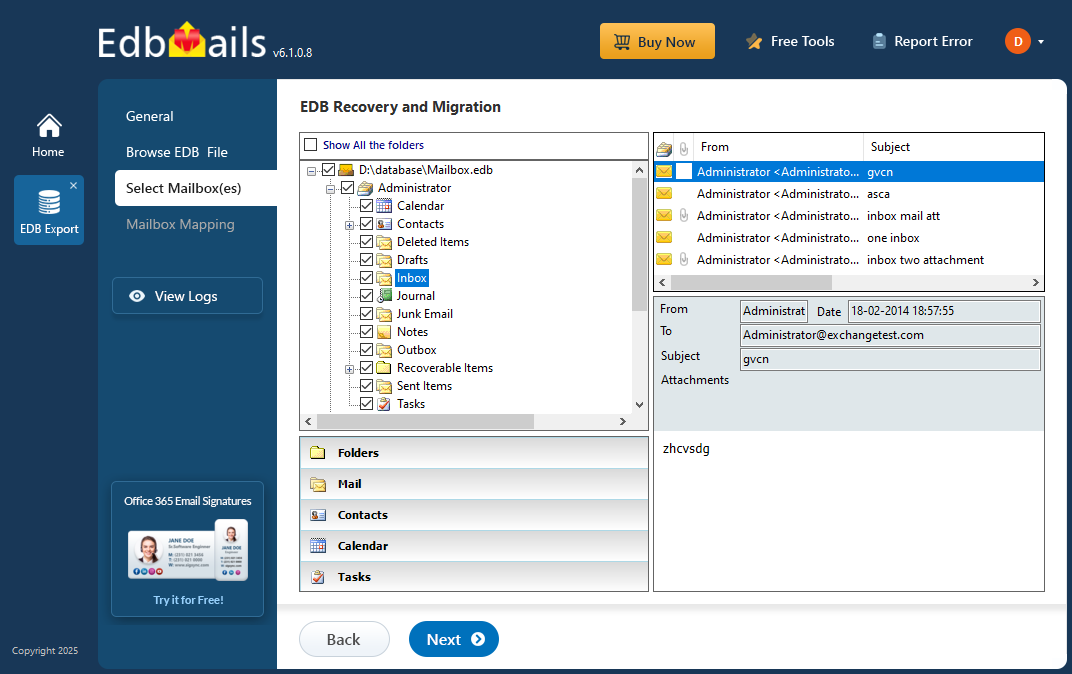
Step 3: Select the mailboxes to export EDB to PST
- After the recovery process finishes, EdbMails will list all your mailboxes and let you preview each email, including deleted items. You can browse through messages, view their details, and ensure everything is intact before proceeding.
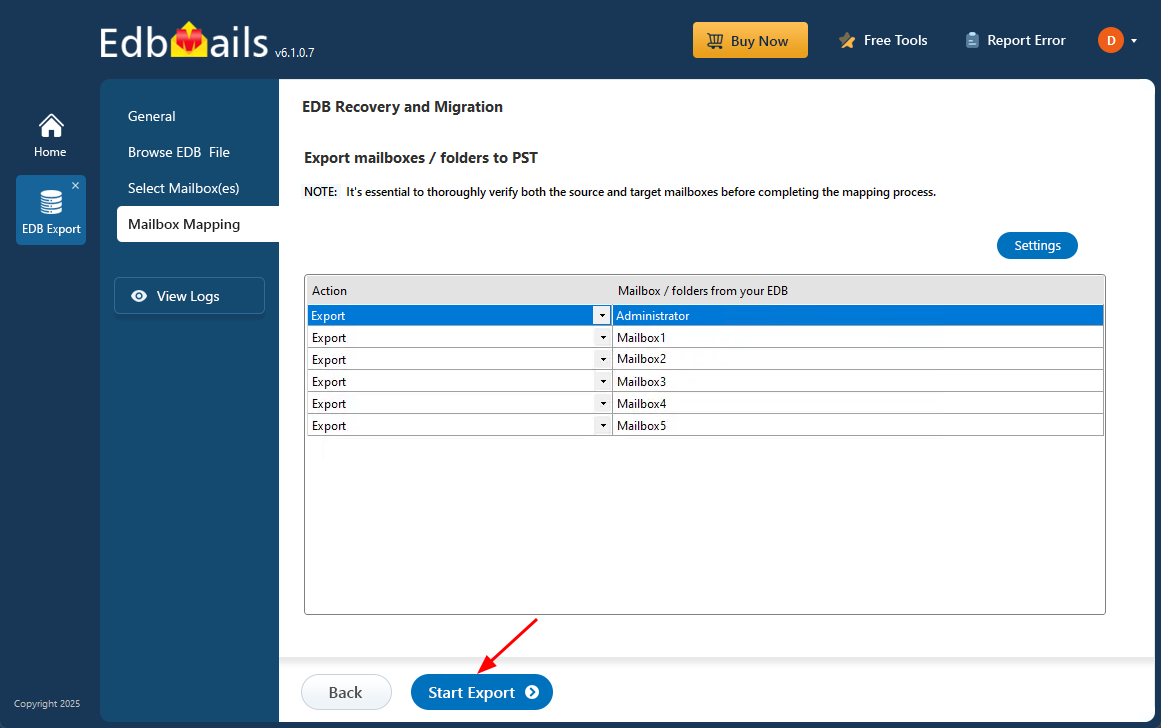
Step 4: Convert EDB to PST
- Check the mailboxes and folders selected for export operation. Make sure the 'Action' column shows 'Export', then click on 'Start Export' to begin the export process.
- EdbMails allows you to use filters to tailor your EDB to live Exchange migration, ensuring that only the required mailboxes or specific items are transferred. For example, date-based filters help you migrate emails from a selected time range, which reduces migration time and improves efficiency. These filters can be easily configured by clicking the ‘Settings’ option on the right side of the interface.
Click here to learn more about setting date filters for EDB to live Exchange Migration.
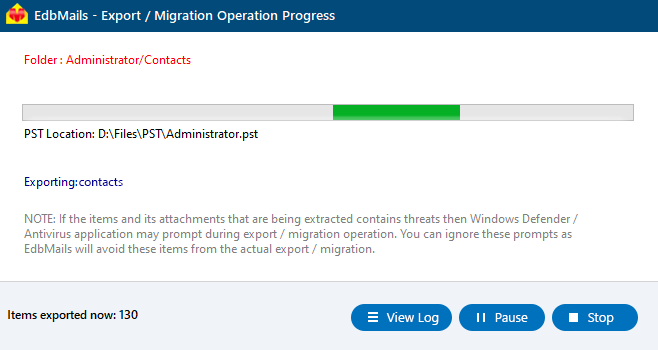
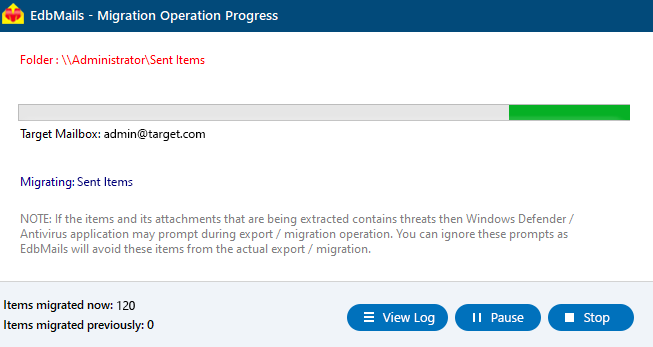
- EdbMails includes a built-in progress bar that allows you to monitor the export process in real time. After the export is successfully completed, a confirmation message is displayed to notify you that the process has finished.
- Click the ‘View Logs’ button to view the export operation report
Steps to migrate EDB file to live Exchange server
With EdbMails, you can easily open an EDB file and directly import it to another on-premises Exchange server, Hosted Exchange, or Office 365.
Step 1 : Download and launch EdbMails EDB Exchange and Recovery software application
- Download EdbMails and install the application on any Windows system to access, recover, or convert EDB files, even when Microsoft Exchange Server is not installed on the computer.
- Open the EdbMails application on your system.
- Sign in using your registered email address and password, then click ‘Login’. If you don’t have an account yet, select ‘Start Your Free Trial’ to proceed.
- Select ‘EDB Recovery (Offline) and Migration’ from the product list.
- Select 'EDB to Live Exchange'
- You can either use the default job name or click ‘New Job’ to assign a custom name.
- Then, click ‘Next’ to continue.
Step 2: Select the offline EDB file to migrate to the live Exchange server
- Click the ‘Browse for EDB file’ button.
- From local drive choose the offline EDB file, and then click ‘Next’ to proceed with the process.
- Recovery process is underway
- Select the required mailboxes or folders you want to migrate and click the 'Next' button to proceed.
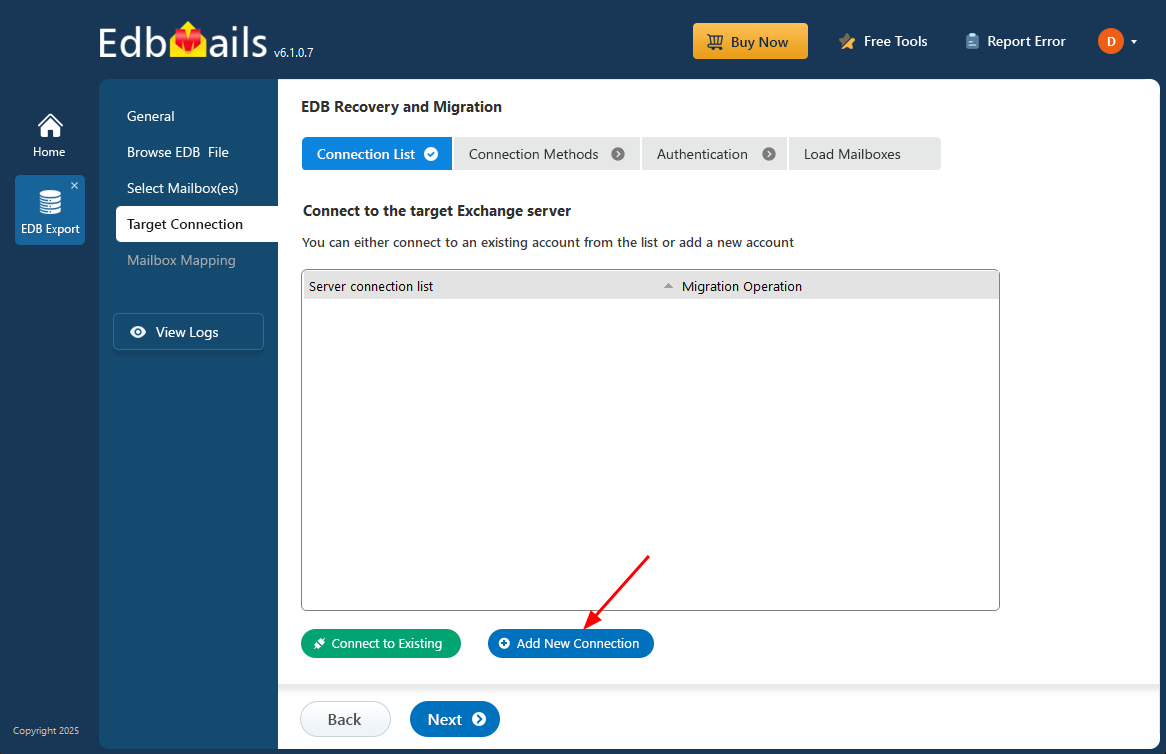
Step 3: Connect to target Exchange server
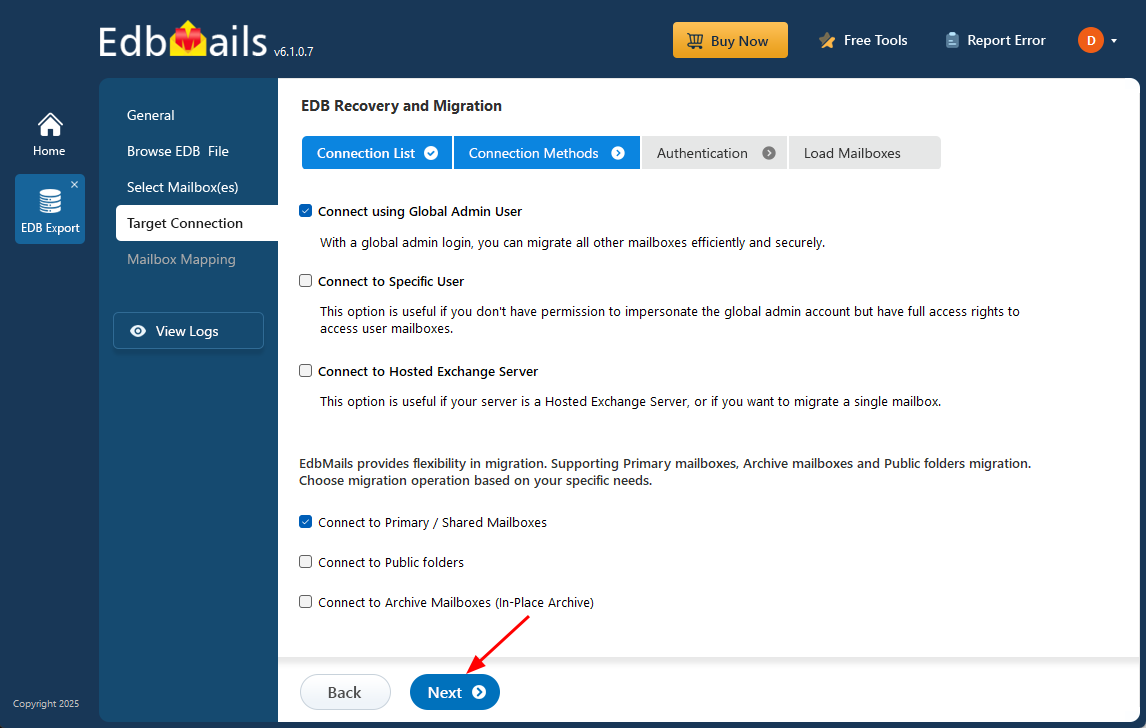
- Click the 'Add New Connection' button to create a new connection to the source Exchange server. If you wish to use an existing connection, simply choose it from the list and click 'Connect to Existing' to continue.
- Select the required connection options and click the ‘Next’ button.
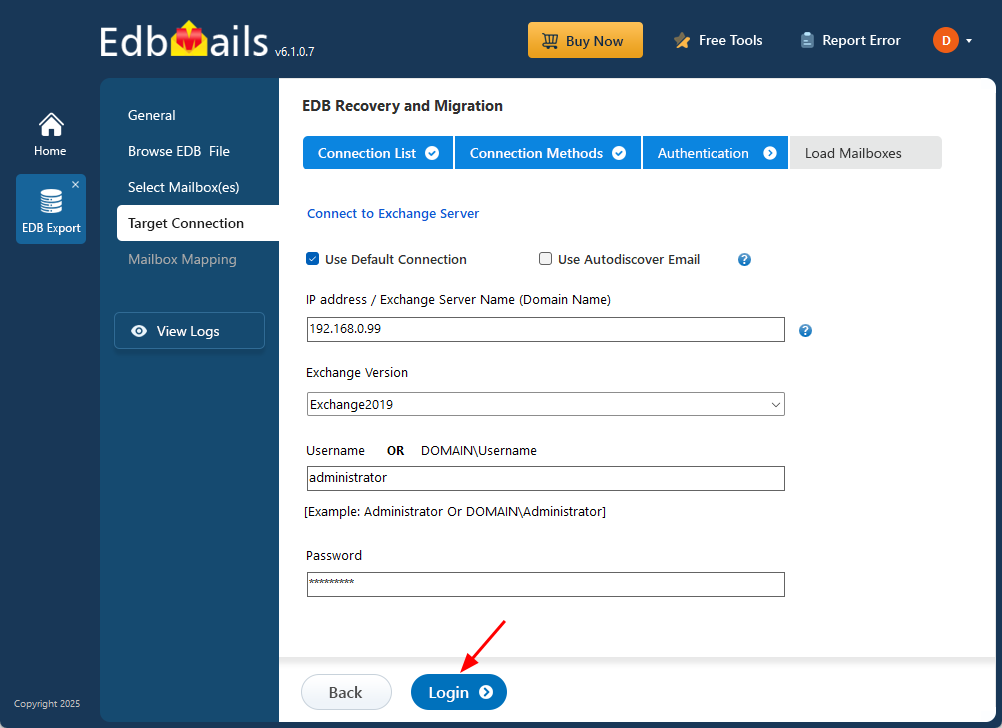
- You can use the ‘Default Connection’ or ‘Autodiscover Email’ to connect to your Exchange server
- Enter your target Exchange server details and click the ‘Login’ button
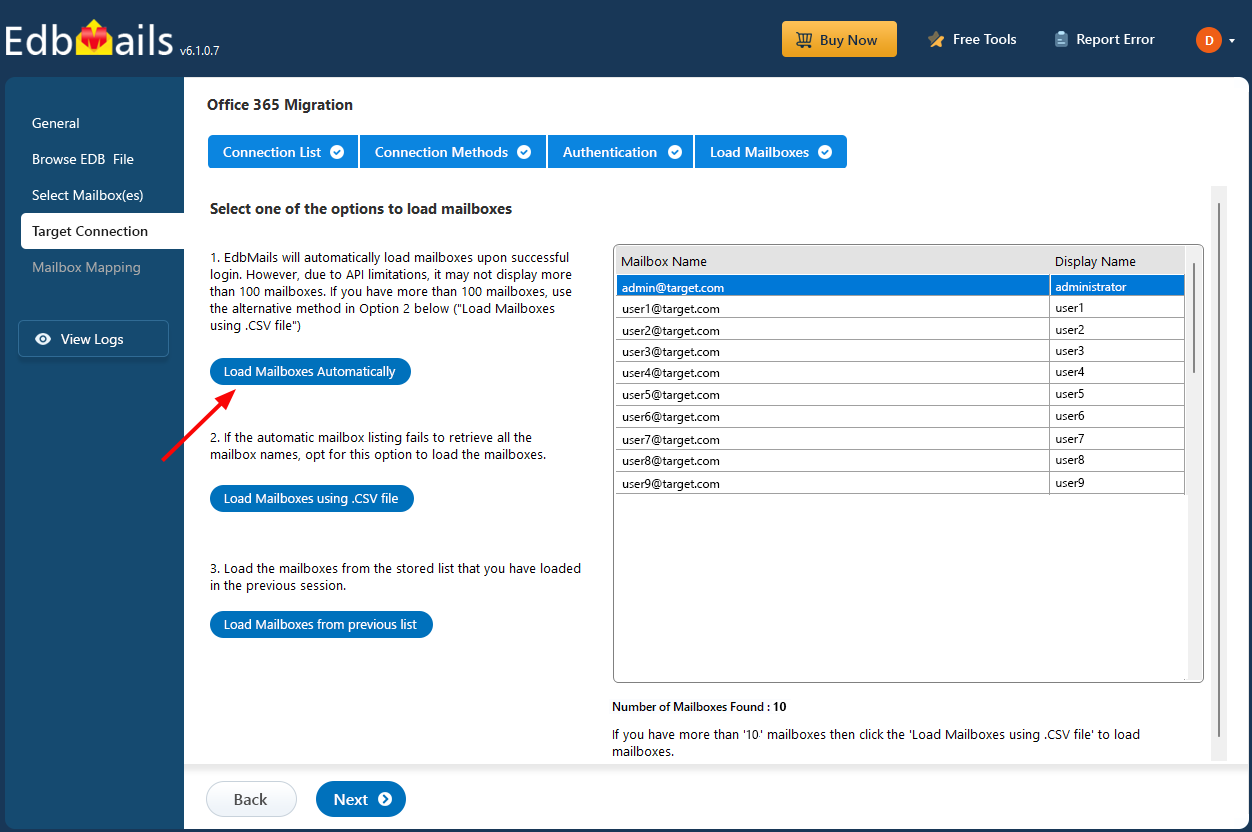
- Choose a method to load the mailboxes. EdbMails can automatically load up to 100 mailboxes using Microsoft’s API, which is subject to certain limitations. If you need to load more than 100 mailboxes, you can use the CSV file option to manually list and load all the required mailboxes without restrictions.
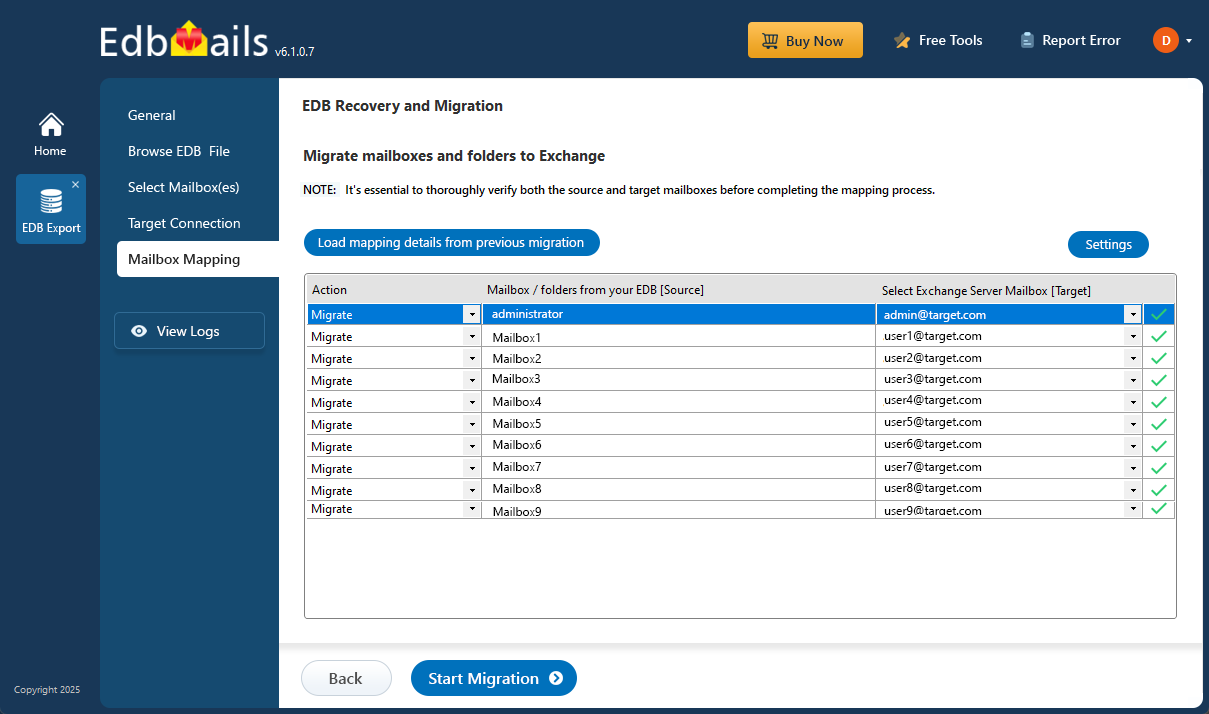
Step 4: Map source and target mailboxes
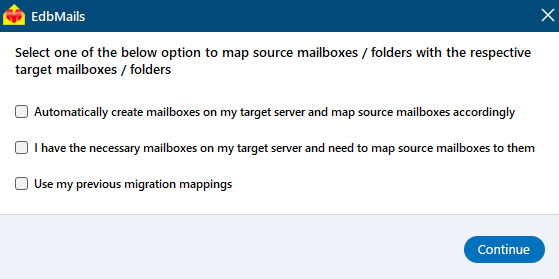
- Select the required mailbox mapping option
- EdbMails automatically maps mailboxes and folders between the source and target servers. You can also manually map source mailboxes to their corresponding target mailboxes if required.
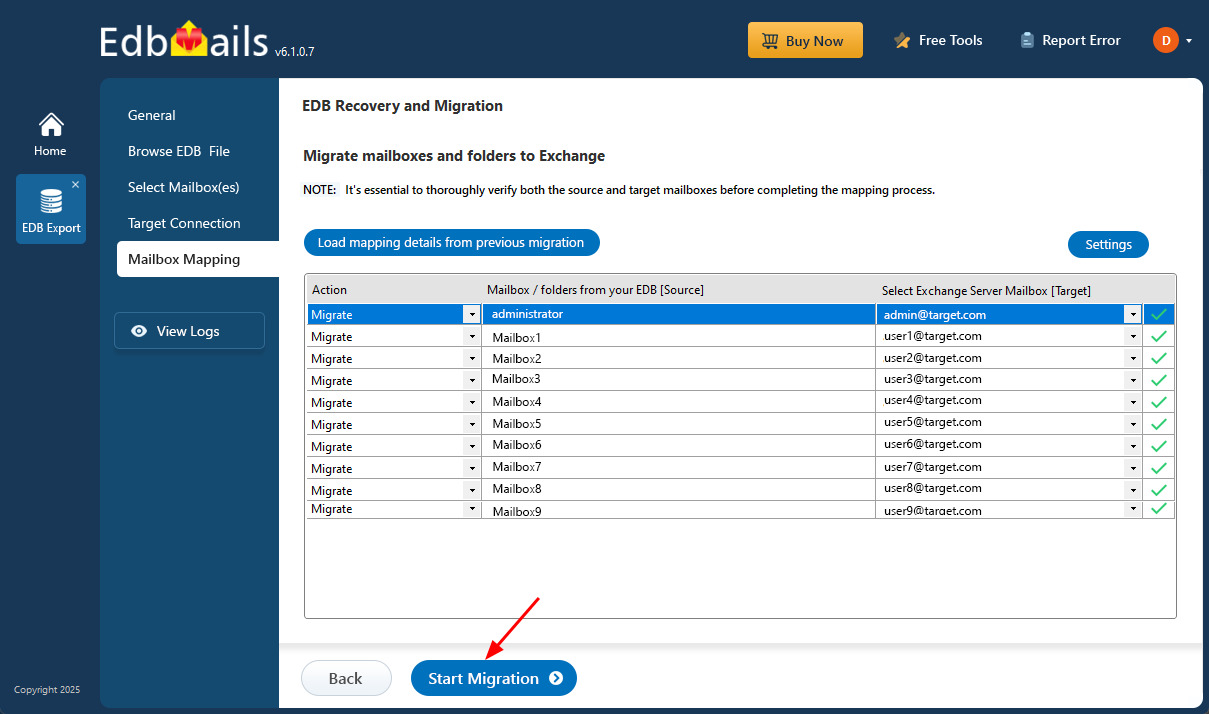
Step 5: Start EDB to live Exchange migration
- Verify the mailbox mapping
- Click the ‘Start Migration’ button to migrate your mailbox data and folders from the EDB file to the Exchange server.
- When the migration is successfully completed, EdbMails will display a confirmation message.
- To view the migration report, click the ‘View Logs’ button.
Conclusion
An Exchange database file (EDB) plays a crucial role in an Exchange server by storing essential data such as emails, folders, contacts, calendars, and other messaging-related information. To open and manage an Exchange EDB file, tools like Eseutil can be used to repair and mount the database on the server. However, if the Exchange server crashes or the EDB file becomes severely corrupted, it is highly recommended to use a Microsoft-partnered tool like EdbMails EDB to PST Converter to open offline EDB files.
One of the key benefits of EdbMails is that it allows you to access and view your mailboxes without requiring an Exchange server, Active Directory (AD), or transaction log files. Additionally, EdbMails makes it easy to migrate mailboxes directly from the EDB file to another Exchange server or Microsoft 365 tenant, providing a comprehensive and efficient solution for managing and recovering Exchange data.