Check Exchange database health
The health of your Exchange database is crucial for maintaining seamless email communication and the stability of your IT environment. As the central repository for user mailboxes and emails, the Exchange database (EDB) supports day-to-day operations. However, over time, issues such as corruption or database dismounts can compromise accessibility, leading to downtime and potential data loss. Regular checks and maintenance are essential to ensure your database remains in optimal condition and minimize the risk of disruptions.
When faced with database corruption or mounting issues, EdbMails EDB to PST converter provides a reliable solution. This tool allows you to recover mailbox data directly from an offline EDB file, converting it to PST format and ensuring you can access important emails, contacts, and calendar items. With EdbMails, you can restore access to your data and reduce downtime, even when the database itself is not operational.
This article offers a comprehensive step-by-step guide for checking the health of your Exchange server database. You’ll learn how to run diagnostic checks, detect early signs of trouble, and perform necessary repairs. Additionally, we’ll cover how to leverage tools like EdbMails to recover data when issues arise, ensuring that your Exchange server remains healthy and your data remains accessible.
Advantages of EdbMails:
EdbMails is the best application to maintain the health of your Exchange database. It allows you to export all your mailboxes to PST format, helping you recover valuable space on your Exchange server. The recovery and export process with EdbMails ensures there is no downtime or data loss, making it an efficient and reliable solution for Exchange database management. Additionally, EdbMails offers the ability to recover your Exchange database even without log files or the need for advanced technical expertise.
Tip: The application also enables you to export Public folders to PST, reducing IT administrators manual efforts.
If you require further assistance, contact EdbMails 24x7 support. Try the free trial version today for Exchange backup, recovery and Exchange migration.
How to check the health of the Exchange database?
The following methods will guide you in identifying issues with Exchange server services and help you repair the database if corruption occurs, applicable to Exchange Server 2019, 2016, 2013, and 2010.
Method 1: Restart the Exchange server services
If Exchange server services are not running, you may encounter errors such as Database status is unknown, preventing users from connecting to their mailboxes. To resolve this, simply check whether all Exchange server services are running. Restarting any necessary services should restore normal operation and allow users to access their mailboxes again.
- Press 'Window Key + R' and type 'services.msc'
- Find the service named Microsoft Exchange Information Store and Microsoft Exchange Mailbox Replication. Right click on the item and select 'Start'. If the service has been disabled or stopped, click 'Restart'
Method 2: Check Exchange database health with PowerShell
For the second method, you must open the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) as an administrator and run the following cmdlets.
- To get the information about the mailboxes in the Exchange server, use the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet. The following example returns the mailbox statistics for all the mailboxes on MailboxServer02.
Get-MailboxStatistics -Server MailboxServer02
- To get information about a single user mailbox, run the following cmdlet
Get-MailboxStatistics -Identity JohnDoe
- The Test-ServiceHealth cmdlet checks if all the Exchange server services have started running which is analogous to manually starting the services described in method 1.
Test-ServiceHealth
- Run the Test-Mailflow cmdlet to check whether you can send and receive emails from the mailboxes. For example, the following cmdlet tests the mail flow from mailbox 1 to mailbox 2 on the Exchange server.
Test-Mailflow MBX1 -TargetMailboxServer MBX2
- The Test-MAPIConnectivity checks for the server functionality
Test-MAPIConnectivity
- The Get-MailboxDatabase cmdlet returns one or more database objects from a server. The following example returns the information for the mailbox database MBX01.
Get-MailboxDatabase -Identity MBX01 -Status | Format-List
- To get the information about the mailboxes in the Exchange server, use the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet. The following example returns the mailbox statistics for all the mailboxes on MailboxServer02.
Method 3: Check the database status with Eseutil
Eseutil is a Microsoft-built command-line utility that helps you check the status of your Exchange database and perform repair operations when issues are detected. If the database is in a Dirty Shutdown state, a soft repair is required to return it to a Clean Shutdown state before it can be mounted to the Exchange server. Let's explore the cmdlets you can use with Eseutil to repair the database and restore normal operation.
- Step 1: Launch eseutil.exe on your Windows computer
The Eseutil is located in the bin directory where you have installed the Exchange server.
- Step 2: Run the following cmdlet to check the database status
eseutil/mh
- Step 3: Check the database status for Clean or Dirty Shutdown
If the database is in the Clean Shutdown state, you can remount it easily. If it is in the Dirty Shutdown state, it means that the log files are missing and you most likely have to perform the Soft and Hard Recovery operations.
- Step 4: Perform the repair operation on the database with eseutil
To perform the soft recovery, run the cmdlet eseutil/r
In the following cmdlet, r stands for recovery, l stands for the location of the transaction log files and d stands for the database path. E01 is the missing log file you need to copy into the log file folder for the soft recovery operation.
eseutil /r E01 /l C:\Exchange\EDB /d C:\Exchange\EDB\DB02
Note that after you perform soft recovery, you can check the database status with eseutil/mh command. If the database fails to mount to the server, you need to perform a hard recovery operation with the cmdlet eseutil/p
. See how to repair Exchange database with Eseutil
One limitation of using Eseutil for hard recovery is that it may fail to repair a severely corrupted database and requires familiarity with PowerShell cmdlets. Additionally, the hard recovery operation purges all data that cannot be recovered, resulting in permanent data loss.
Along with Eseutil, you can use the New-MailboxRepairRequest cmdlet to detect and resolve mailbox corruption issues. This method provides a more targeted approach to fixing problems without risking widespread data loss. For comprehensive database management, also explore how to check and monitor mailboxes in Exchange server 2019 and 2016, as well as the best practices for managing user accounts.
- Step 1: Launch eseutil.exe on your Windows computer
Method 4: Repair Exchange database with EdbMails Exchange recovery tool
EdbMails EDB to PST converter is a Microsoft-partnered Exchange recovery solution that simplifies the process of fixing all types of Exchange database issues without requiring complex PowerShell scripts. With EdbMails, you can easily convert EDB files to PST format and create regular backups of your mailboxes. It supports a wide range of Exchange versions, including Exchange server 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007, and 2003. As an essential tool in every Exchange administrator's toolkit, it also allows for seamless migration of mailboxes to Office 365 and other Exchange servers. In the next section, we’ll walk you through the steps to repair a corrupted Exchange database using EdbMails and restore your mailboxes efficiently.
Step 1: Download and install EdbMails Exchange recovery tool- Download and install the EdbMails Exchange recovery tool on any computer that has access to both the source and target environments. Alternatively, you can perform the recovery process by installing EdbMails on a computer that is not running Exchange Server.
- Launch the application and click on 'Login' to sign in to your account. If you haven't registered yet, select 'Start Your Free Trial' to begin your trial and explore all the available features.
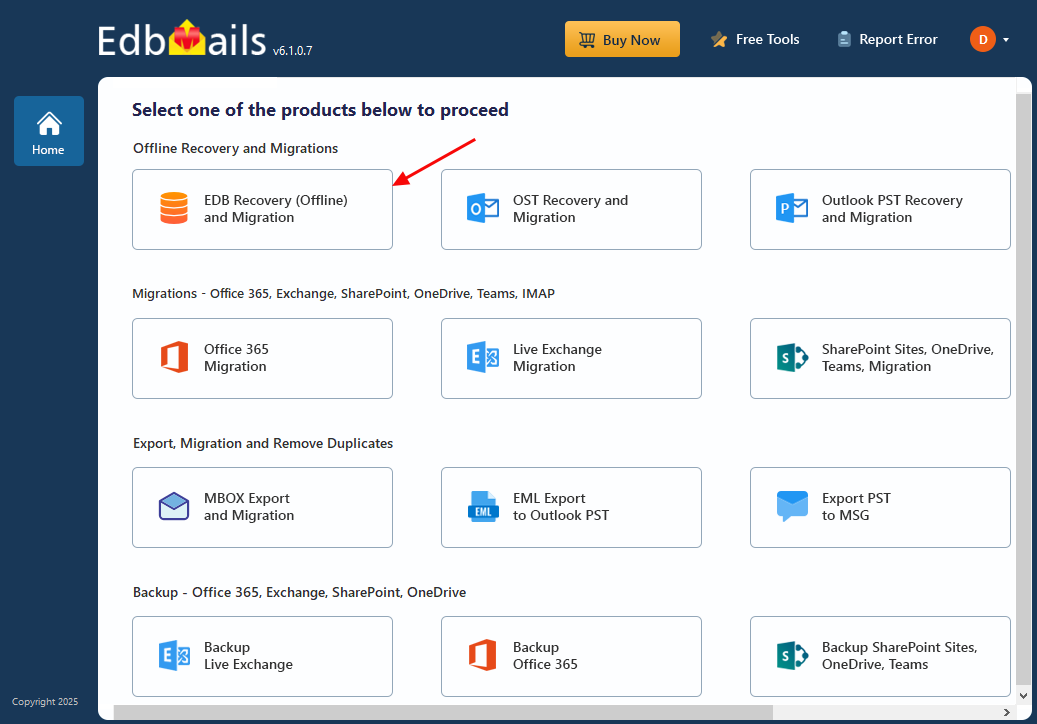
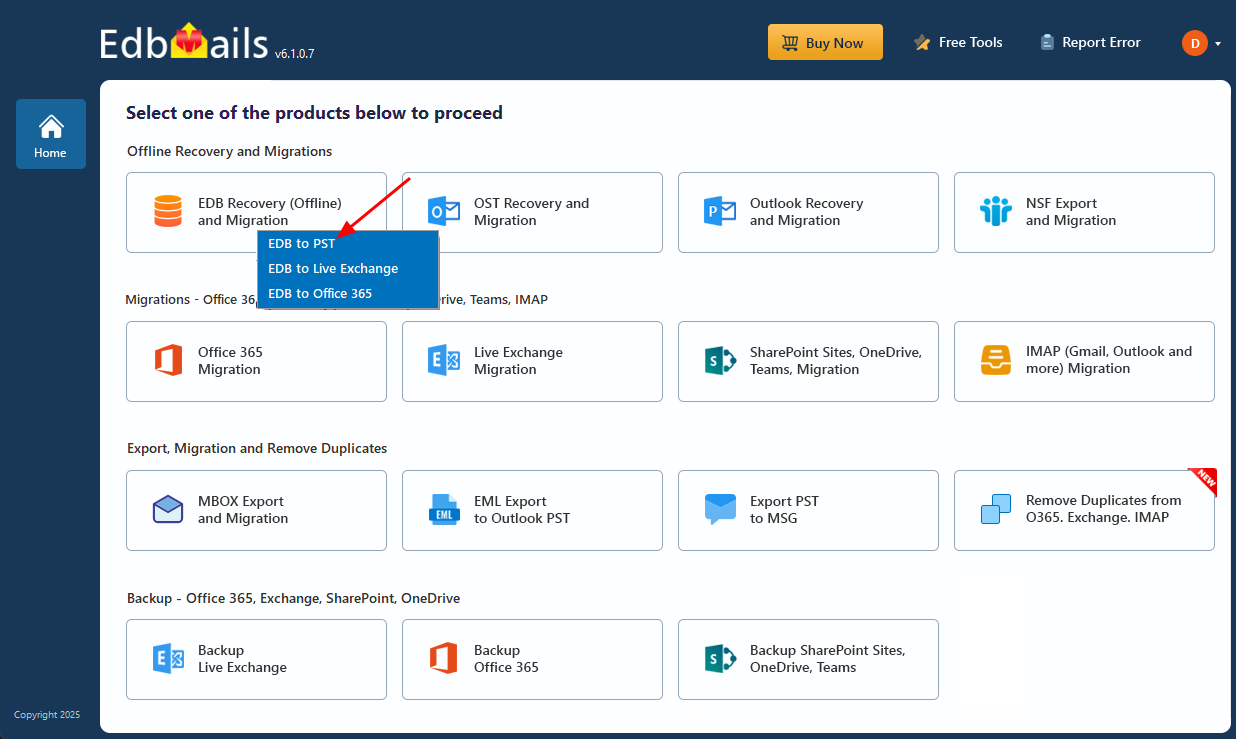
- Choose ‘EDB Recovery (Offline) and Migration’ from the available product options.
- Select the recovery technique as ‘EDB to PST’.
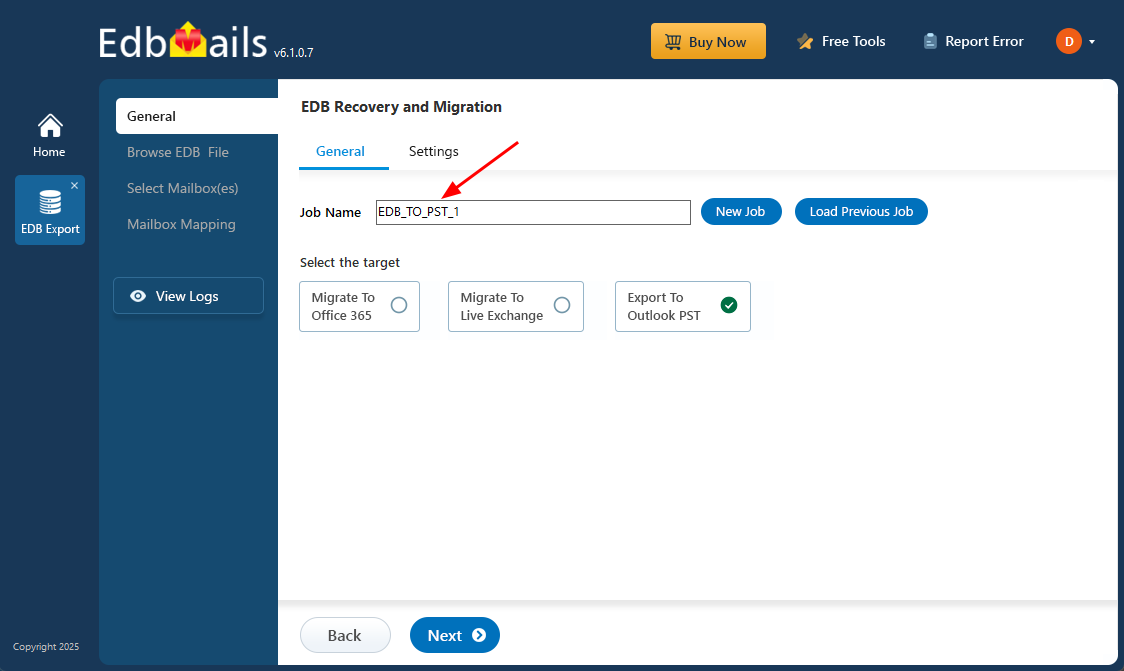
- You can either keep the default job name or click on ‘New Job’ to assign a custom job name that suits your preference.
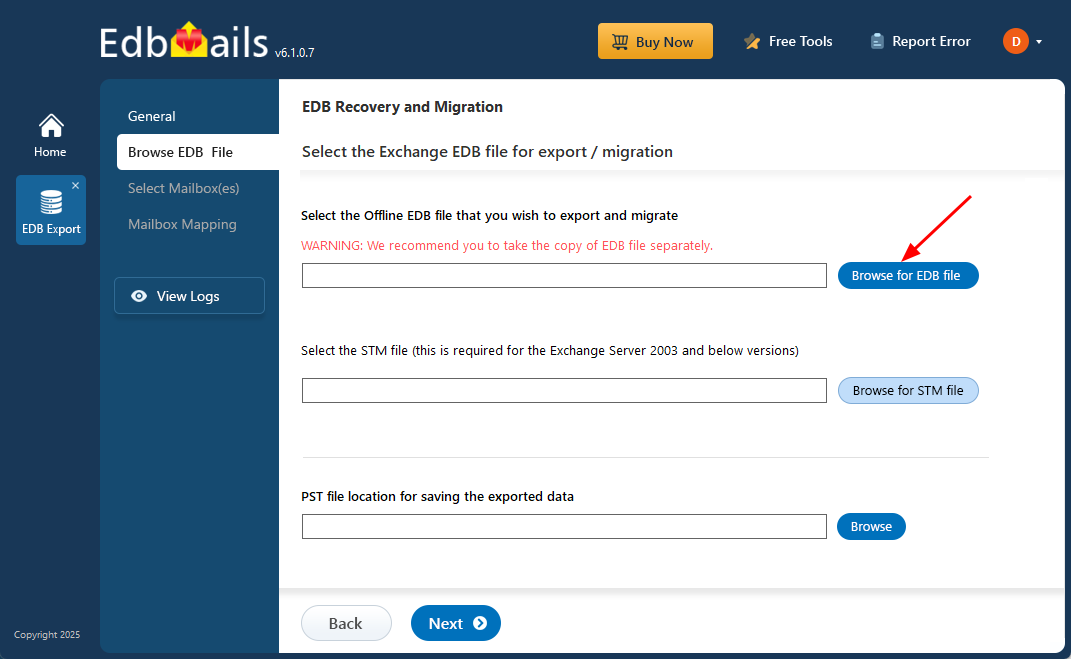
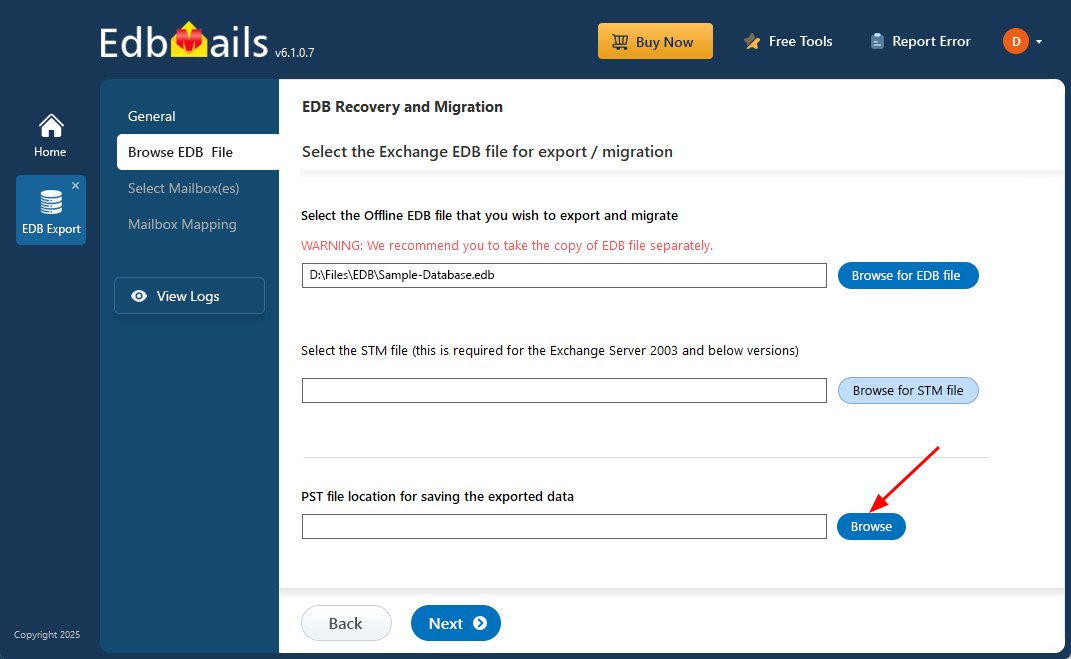
- Click ‘Browse for EDB file’ button
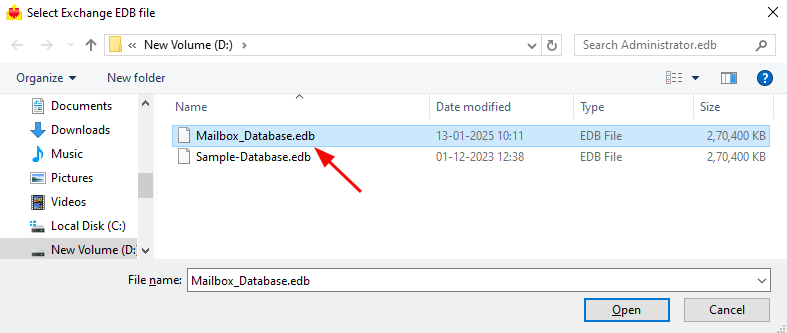
- Select the corrupted EDB file from your computer’s drive that you want to recover and convert to PST, then click the ‘Next’ button to continue. If the file is located on a shared network, ensure you have the necessary read and write permissions for a seamless process.
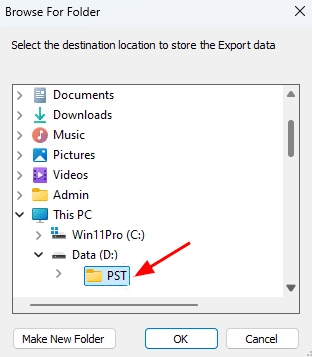
- Click ‘Browse’
- Select a location to store your exported PST files and make sure there is sufficient disk space available for the export process to finish successfully.
- EdbMails thoroughly scans and repairs corrupted EDB files from your Exchange server, ensuring full data recovery and seamless access.
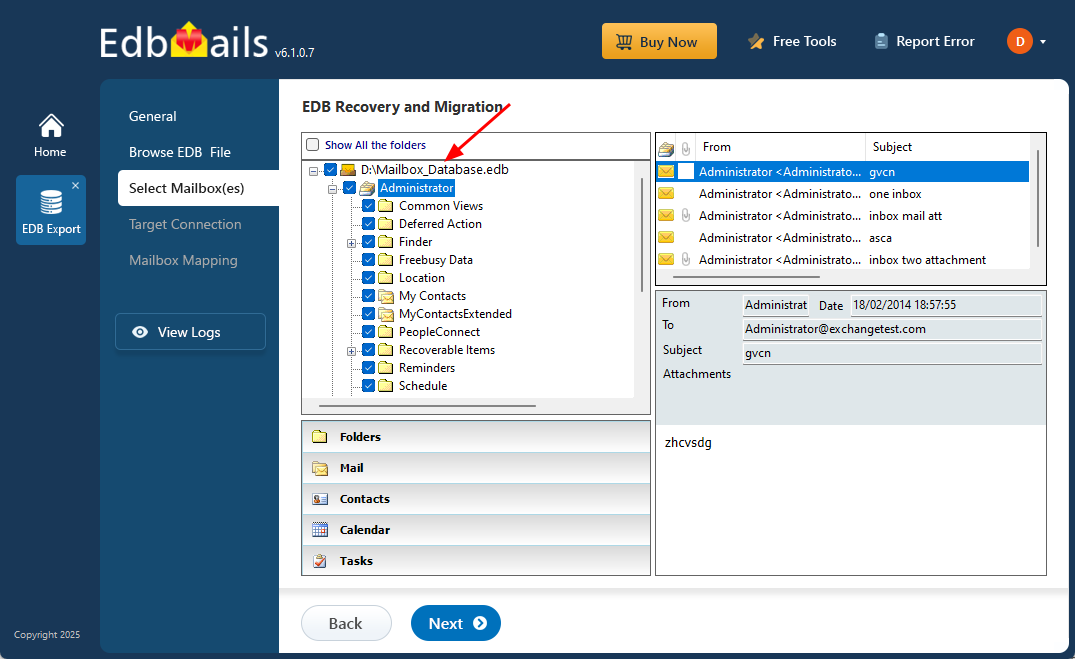
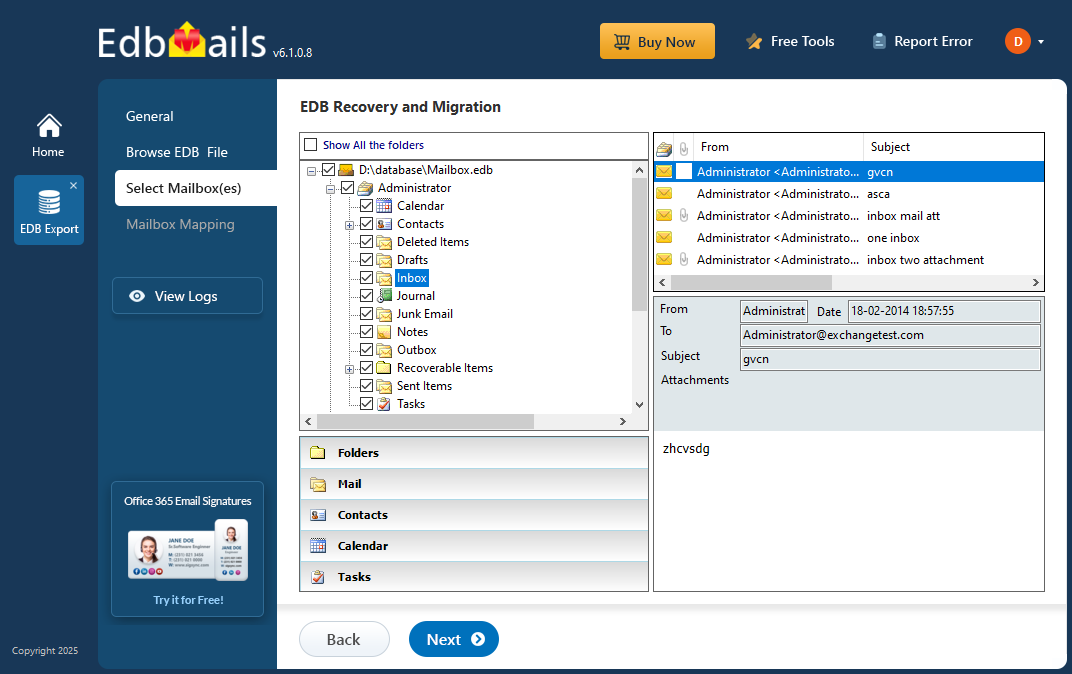
- After the recovery process is complete, expand the mailbox and choose any folder to preview its mail items, all displayed in the preview pane on the right.
- Select the mailboxes or folders you want to export, then click ‘Next’ to proceed.
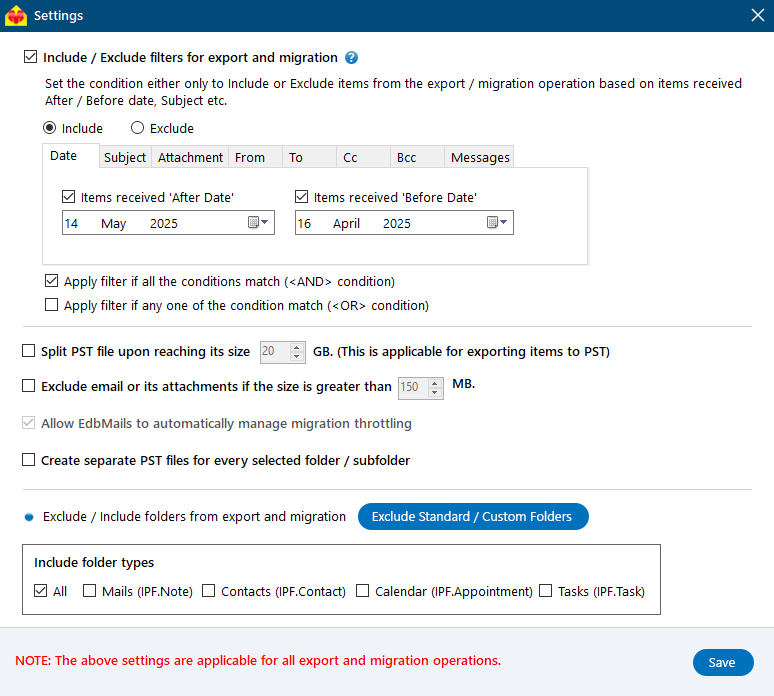
- You can apply the advanced filter settings to export the Exchange emails to PST based on Date, Subject, Attachment and so on.
- EdbMails comes with other additional settings for the export such as splitting a PST file and excluding emails whose size is greater than a specified limit.
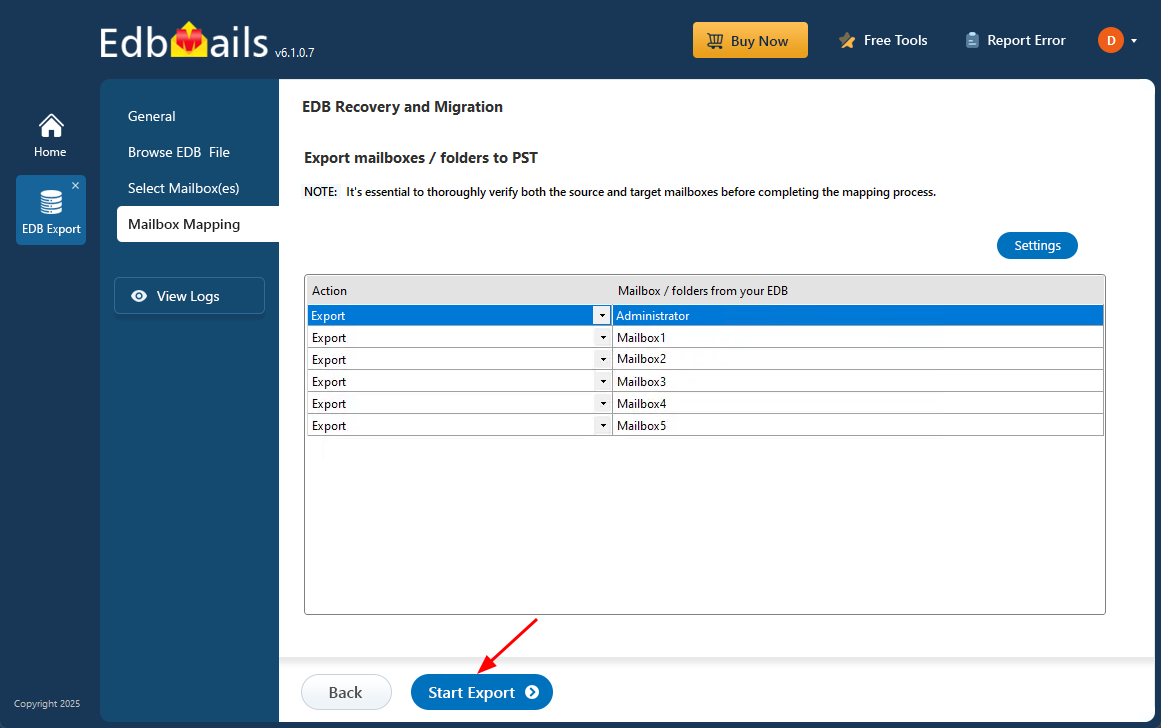
- Review the selected mailboxes and folders to ensure everything is in order. Make sure the 'Action' is set to 'Export', then click ‘Start Export’ to initiate the process.
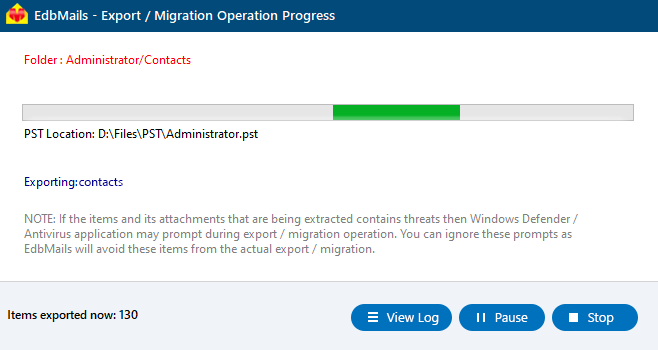
- During the export process, EdbMails shows a real-time progress window with options to pause or resume. Once the export is finished, click ‘View Log’ to see a detailed summary report.
- To restore and view all your mailboxes and mail items, add the exported PST file in Outlook.
Concluding Words
In this article, we've explored several methods to assess the health of an Exchange database. Maintaining a healthy database is essential for the smooth operation of the Exchange server. You can use tools like PowerShell scripts and Eseutil to check the database status. Additionally, repairing corrupted databases is crucial for resolving issues like Dirty Shutdown or Jet Engine errors. The EdbMails Exchange recovery tool offers an effective solution to repair, convert EDB files to PST, and back up Exchange server mailboxes. With EdbMails, you can free up database space and prevent it from growing excessively, helping keep your Exchange database in optimal health.